From a Stanford University online article (March 2, 2020):
 “The opioid epidemic has added fuel to the HCV fire, substantially increasing transmission,” said Owens. “HCV is now an enormous public health problem, affecting a much broader age range of people than before. Fortunately, we have the tools to identify people and treatment is now successful in the vast majority of patients, so screening can prevent the mortality and morbidity from HCV.”
“The opioid epidemic has added fuel to the HCV fire, substantially increasing transmission,” said Owens. “HCV is now an enormous public health problem, affecting a much broader age range of people than before. Fortunately, we have the tools to identify people and treatment is now successful in the vast majority of patients, so screening can prevent the mortality and morbidity from HCV.”
A task force of national health experts recommends clinicians screen all adults 18 to 79 for the hepatitis C virus (HCV), noting that the viral infection is now associated with more deaths in the United States than the top 60 reportable infectious diseases combined. Many people are unaware they are carrying the viral infection.

“People with hepatitis C do not always feel sick and may not know they have it,” says chair of the U.S. Preventive Services Task Force Douglas K. Owens, M.D, M.S. “Screening is key to finding this infection early, when it’s easier to treat and cure, helping reduce illnesses and deaths.”
Owens, who is the director of Stanford Health Policy and the Henry J. Kaiser, Jr., Professor of Medicine, said the opioid epidemic now plays an important role in the prevalence of HCV. There are more than three times the number of acute HCV cases than a decade ago, particularly among young, white, injection drug users who live in rural areas. Women aged 15 to 44 have also been hit hard by the virus that is spread through contaminated blood.
Read full Article






 Rocket scientist-turned-immunology expert Mark Kendall talks about his Nanopatch, which could revolutionise vaccinations and eradicate some diseases.
Rocket scientist-turned-immunology expert Mark Kendall talks about his Nanopatch, which could revolutionise vaccinations and eradicate some diseases.
 Seasonal variation in blood pressure has been known for 40 years, but, to our knowledge, for the first time we show here that this occurs independently of temperature. The reduction in blood pressure is more marked with a rise in UVB than UVA, and in whites than black people. Dermatological concerns about the skin cancer inducing effects of UV radiation need to be balanced against the observed blood pressure lowering effects of sunlight, particularly given the greatly higher burden of disease caused by hypertension.
Seasonal variation in blood pressure has been known for 40 years, but, to our knowledge, for the first time we show here that this occurs independently of temperature. The reduction in blood pressure is more marked with a rise in UVB than UVA, and in whites than black people. Dermatological concerns about the skin cancer inducing effects of UV radiation need to be balanced against the observed blood pressure lowering effects of sunlight, particularly given the greatly higher burden of disease caused by hypertension. Sunlight exposure appears to lower blood pressure; insufficient exposure to natural ultraviolet radiation and/or active avoidance of sunlight may be new risk factors for hypertension.
Sunlight exposure appears to lower blood pressure; insufficient exposure to natural ultraviolet radiation and/or active avoidance of sunlight may be new risk factors for hypertension.
 We found no association between egg consumption and risk of cardiovascular disease in three large US cohorts. Results from the updated meta-analysis lend further support to the overall lack of an association between moderate egg consumption (up to one egg per day) and cardiovascular disease risk.
We found no association between egg consumption and risk of cardiovascular disease in three large US cohorts. Results from the updated meta-analysis lend further support to the overall lack of an association between moderate egg consumption (up to one egg per day) and cardiovascular disease risk. 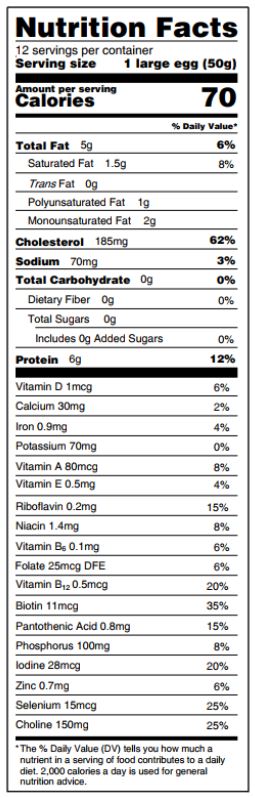 Eggs are a major source of dietary cholesterol, but they are also an affordable source of high quality protein, iron, unsaturated fatty acids, phospholipids, and carotenoids.
Eggs are a major source of dietary cholesterol, but they are also an affordable source of high quality protein, iron, unsaturated fatty acids, phospholipids, and carotenoids.

 What happens when you catch coronavirus? The Telegraph’s Global Health Security Editor Paul Nuki explains all the ways in which you could become infected with COVID-19 and how your body reacts to this virus.
What happens when you catch coronavirus? The Telegraph’s Global Health Security Editor Paul Nuki explains all the ways in which you could become infected with COVID-19 and how your body reacts to this virus.
 Listen to the latest from the world of science, with Benjamin Thompson and Nick Howe. This week, improving computers’ image identification, and a new method for growing crystals.
Listen to the latest from the world of science, with Benjamin Thompson and Nick Howe. This week, improving computers’ image identification, and a new method for growing crystals.
 “The opioid epidemic has added fuel to the HCV fire, substantially increasing transmission,” said Owens. “HCV is now an enormous public health problem, affecting a much broader age range of people than before. Fortunately, we have the tools to identify people and treatment is now successful in the vast majority of patients, so screening can prevent the mortality and morbidity from HCV.”
“The opioid epidemic has added fuel to the HCV fire, substantially increasing transmission,” said Owens. “HCV is now an enormous public health problem, affecting a much broader age range of people than before. Fortunately, we have the tools to identify people and treatment is now successful in the vast majority of patients, so screening can prevent the mortality and morbidity from HCV.”