From a BMJ Research online study (March 4, 2020):
 We found no association between egg consumption and risk of cardiovascular disease in three large US cohorts. Results from the updated meta-analysis lend further support to the overall lack of an association between moderate egg consumption (up to one egg per day) and cardiovascular disease risk.
We found no association between egg consumption and risk of cardiovascular disease in three large US cohorts. Results from the updated meta-analysis lend further support to the overall lack of an association between moderate egg consumption (up to one egg per day) and cardiovascular disease risk.
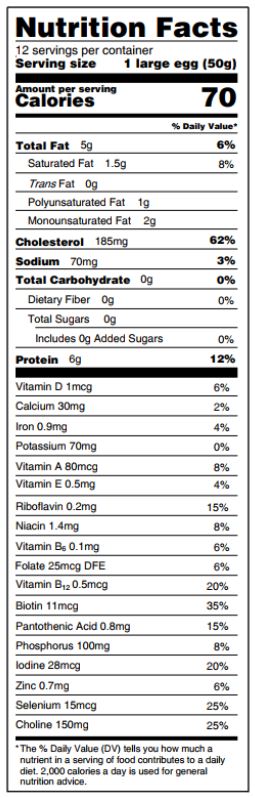 Eggs are a major source of dietary cholesterol, but they are also an affordable source of high quality protein, iron, unsaturated fatty acids, phospholipids, and carotenoids.
Eggs are a major source of dietary cholesterol, but they are also an affordable source of high quality protein, iron, unsaturated fatty acids, phospholipids, and carotenoids.
Introduction: In the United States, cardiovascular disease is the leading cause of death in men and women. Diet and lifestyle undisputedly play a major part in the development of cardiovascular disease. In the past, limiting dietary cholesterol intake to 300 mg per day was widely recommended to prevent cardiovascular disease. However, because of the weak association between dietary cholesterol and blood cholesterol, and considering that dietary cholesterol is no longer a nutrient of concern for overconsumption, the most recent 2015 dietary guidelines for Americans did not carry forward this recommendation.



 “
“
 Eat less, live longer- If you want to reduce levels of inflammation throughout your body, delay the onset of age-related diseases and live longer—eat less food. That’s the conclusion of a new study by scientists from the US and China that provides the most detailed report to date of the cellular effects of a calorie-restricted diet in rats.
Eat less, live longer- If you want to reduce levels of inflammation throughout your body, delay the onset of age-related diseases and live longer—eat less food. That’s the conclusion of a new study by scientists from the US and China that provides the most detailed report to date of the cellular effects of a calorie-restricted diet in rats. 
 The study shows that wearable sensors coupled with machine learning analytics have predictive accuracy comparable to implanted devices.
The study shows that wearable sensors coupled with machine learning analytics have predictive accuracy comparable to implanted devices.

 The National Diabetes Statistics Report is a periodic publication of the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) that provides updated statistics about diabetes in the United States for a scientific audience. It includes information on prevalence and incidence of diabetes, prediabetes, risk factors for complications, acute and long-term complications, deaths, and costs. These data can help focus efforts to prevent and control diabetes across the United States.
The National Diabetes Statistics Report is a periodic publication of the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) that provides updated statistics about diabetes in the United States for a scientific audience. It includes information on prevalence and incidence of diabetes, prediabetes, risk factors for complications, acute and long-term complications, deaths, and costs. These data can help focus efforts to prevent and control diabetes across the United States.

 Aspirin is an inhibitor of prostaglandin production and may influence the cellular basis of bone remodelling responsible for maintaining the material and structural strength of bone.
Aspirin is an inhibitor of prostaglandin production and may influence the cellular basis of bone remodelling responsible for maintaining the material and structural strength of bone.
 We suggest this increase in mortality seen on DR in the 4-day switch treatment is due to either accrued physiological costs or more probable, a carryover of deaths directly resulting from the rich diet, but recorded on the DR diet.
We suggest this increase in mortality seen on DR in the 4-day switch treatment is due to either accrued physiological costs or more probable, a carryover of deaths directly resulting from the rich diet, but recorded on the DR diet.
 Across the 6 studies of 8699 participants, mean age ranged between 70 and 74 years and mean gait speed ranged between 1.05 and 1.26 m/s. Incident dementia ranged from 5 to 21 per 1000 person-years. Compared with usual agers, participants with only memory decline had 2.2 to 4.6 times higher risk for developing dementia…
Across the 6 studies of 8699 participants, mean age ranged between 70 and 74 years and mean gait speed ranged between 1.05 and 1.26 m/s. Incident dementia ranged from 5 to 21 per 1000 person-years. Compared with usual agers, participants with only memory decline had 2.2 to 4.6 times higher risk for developing dementia… 
 Many Americans are willing to make significant personal tradeoffs to lower their health insurance rates or medical costs, such as agreeing to 24/7 personal monitoring or working with artificial intelligence instead of a human doctor, the Center for the Digital Future at the USC Annenberg School for Communication and Journalism finds.
Many Americans are willing to make significant personal tradeoffs to lower their health insurance rates or medical costs, such as agreeing to 24/7 personal monitoring or working with artificial intelligence instead of a human doctor, the Center for the Digital Future at the USC Annenberg School for Communication and Journalism finds.
 We observed that increased adherence to the MedDiet modulates specific components of the gut microbiota that were associated with a reduction in risk of frailty, improved cognitive function and reduced inflammatory status.
We observed that increased adherence to the MedDiet modulates specific components of the gut microbiota that were associated with a reduction in risk of frailty, improved cognitive function and reduced inflammatory status.