Does reducing salt improve our blood pressure?
There is consistent evidence that moderate reductions (i.e. a decrease of 3 to 5 g or ½ to 1 teaspoon a day) in salt intake can lead to a reduction in blood pressure.5,6 However, these effects may not be the same for everyone and will depend on an individual’s starting blood pressure (greater benefits are seen in those with higher blood pressure), their current level of salt intake, genetics, disease status and medication use.
It is important to note that salt is not the only lifestyle factor that can influence our blood pressure. Other factors such as eating enough potassium, maintaining a healthy body weight, not smoking, and being physically active are also important when it comes to reducing blood pressure. You can find 7 lifestyle tips to help reduce blood pressure here.
High salt foods:
- Processed meats such as bacon, salami, sausages and ham
- Cheeses
- Gravy granules, stock cubes, yeast extracts
- Olives, pickles and other pickled foods
- Salted and dry-roasted nuts and crisps
- Salted and smoked meat and fish
- Sauces: soy sauce, ketchup, mayonnaise, BBQ sauce

What is salt?
Salt is the common name for sodium chloride (or NaCl). It consists of 40% sodium and 60% chloride. In other words, 2.5 g of salt contains 1 g of sodium and 1.5 g of chloride.
Why do we need salt?
Both sodium and chloride are essential for many body functions. They help regulate blood pressure, control fluid balance, maintain the right conditions for muscle and nerve function and allow for the absorption and transport of nutrients across cell membranes. Chloride is also used to produce stomach acid (hydrochloric acid, HCl) which helps us digest foods.
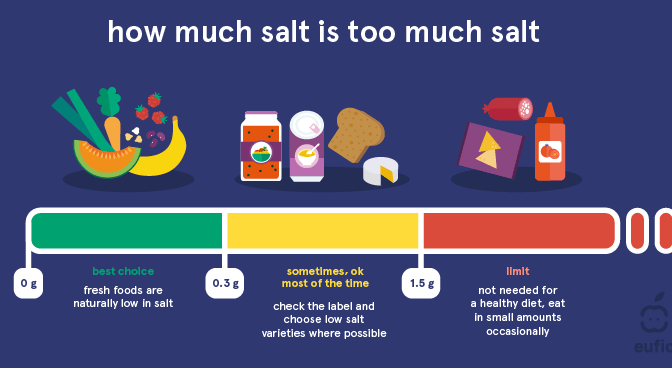
How much salt do we need per day?
The exact minimum daily requirement for salt is unknown, but it is thought to be around 1.25 g – 2.5 g (0.5 – 1 g sodium) per day.1 As salt is found in a large variety of foods the risk of deficiency is low.1,2 The European Food Safety Authority (EFSA) has stated that a salt intake of 5 g per day (equivalent to 2 g of sodium) is sufficient to meet both our sodium and chloride requirements as well as reduce our risk of high blood pressure and heart disease.1,2 This is equivalent to around 1 teaspoon of salt per day from all sources.
Both sodium and chloride are released from our body through our urine and when we sweat. This means bouts of heavy sweating such as during exercise can increase our salt requirements slightly. However, as most people consume well above required levels it is usually not necessary to increase salt intake during these conditions.1



 Atlantic Sea Farms is the largest commercial seaweed farm in the U.S. They line-grow their seaweed in clear, icy cold Maine waters. The seaweed — which is sold frozen in pureed cubes and in ready to eat cut strands and fermented products — is never dyed or dehydrated.
Atlantic Sea Farms is the largest commercial seaweed farm in the U.S. They line-grow their seaweed in clear, icy cold Maine waters. The seaweed — which is sold frozen in pureed cubes and in ready to eat cut strands and fermented products — is never dyed or dehydrated.


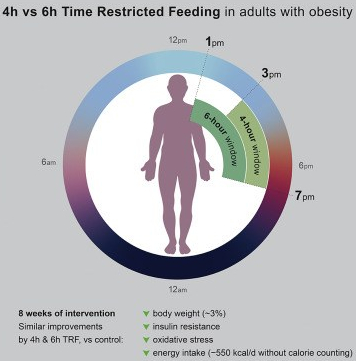 Two daily fasting diets, also known as time-restricted feeding diets, are effective for weight loss, according to a new study published by researchers from the University of Illinois at Chicago.
Two daily fasting diets, also known as time-restricted feeding diets, are effective for weight loss, according to a new study published by researchers from the University of Illinois at Chicago.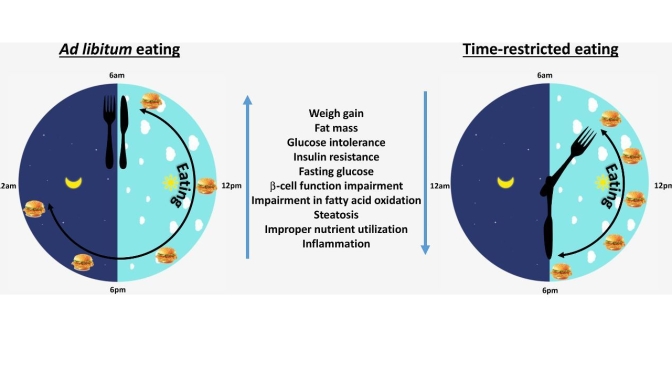
 …the beneficial effects of TRE are dose dependent, with greater reductions in body weight, fat mass, and improvement in glucose tolerance when a 9-h protocol was implemented versus 12 and 15 h. The optimal TRE time frame to recommend for people has not been tested. Clear improvements have been noted after 6-, 8-, 9-, and 10-h protocols. It is likely that the greater time restriction would result in greater weight losses, which may maximize the metabolic benefits.
…the beneficial effects of TRE are dose dependent, with greater reductions in body weight, fat mass, and improvement in glucose tolerance when a 9-h protocol was implemented versus 12 and 15 h. The optimal TRE time frame to recommend for people has not been tested. Clear improvements have been noted after 6-, 8-, 9-, and 10-h protocols. It is likely that the greater time restriction would result in greater weight losses, which may maximize the metabolic benefits.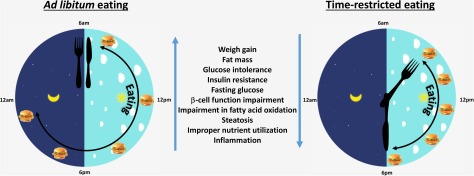

 “On a high-sugar diet, we find that the fruit flies’ dopaminergic neurons are less active, because the high sugar intake decreases the intensity of the sweetness signal that comes from the mouth,” Dus said. “Animals use this feedback from dopamine to make predictions about how rewarding or filling a food will be. In the high-sugar diet flies, this process is broken—they get less dopamine neuron activation and so end up eating more than they need, which over time makes them gain weight.”
“On a high-sugar diet, we find that the fruit flies’ dopaminergic neurons are less active, because the high sugar intake decreases the intensity of the sweetness signal that comes from the mouth,” Dus said. “Animals use this feedback from dopamine to make predictions about how rewarding or filling a food will be. In the high-sugar diet flies, this process is broken—they get less dopamine neuron activation and so end up eating more than they need, which over time makes them gain weight.”



 patrolling neighborhoods, or military soldiers during field-exercises. Thus, time-restricted eating removes the added stress of what to eat, and serves as a practical intervention conducive to the schedules of many people.
patrolling neighborhoods, or military soldiers during field-exercises. Thus, time-restricted eating removes the added stress of what to eat, and serves as a practical intervention conducive to the schedules of many people.