There is consistent evidence that higher amounts of body fat are associated with increased risks of a number of cancers (6), including:
- Endometrial cancer: Obese and overweight women are two to about four times as likely as normal-weight women to develop endometrial cancer (cancer of the lining of the uterus), and extremely obese women are about seven times as likely to develop the more common of the two main types of this cancer (7). The risk of endometrial cancer increases with increasing weight gain in adulthood, particularly among women who have never used menopausal hormone therapy (8).
- Esophageal adenocarcinoma: People who are overweight or obese are about twice as likely as normal-weight people to develop a type of esophageal cancer called esophageal adenocarcinoma, and people who are extremely obese are more than four times as likely (9).
- Gastric cardia cancer: People who are obese are nearly twice as likely as normal-weight people to develop cancer in the upper part of the stomach, that is, the part that is closest to the esophagus (10).
- Liver cancer: People who are overweight or obese are up to twice as likely as normal-weight people to develop liver cancer. The association between overweight/obesity and liver cancer is stronger in men than women (11, 12).
- Kidney cancer: People who are overweight or obese are nearly twice as likely as normal-weight people to develop renal cell cancer, the most common form of kidney cancer (13). The association of renal cell cancer with obesity is independent of its association with high blood pressure, a known risk factor for kidney cancer (14).
- Multiple myeloma: Compared with normal-weight individuals, overweight and obese individuals have a slight (10% to 20%) increase in the risk of developing multiple myeloma (15).
- Meningioma: The risk of this slow-growing brain tumor that arises in the membranes surrounding the brain and the spinal cord is increased by about 50% in people who are obese and about 20% in people who are overweight (16).
- Pancreatic cancer: People who are overweight or obese are about 1.5 times as likely to develop pancreatic cancer as normal-weight people (17).
- Colorectal cancer: People who are obese are slightly (about 30%) more likely to develop colorectal cancer than normal-weight people (18).A higher BMI is associated with increased risks of colon and rectal cancers in both men and in women, but the increases are higher in men than in women (18).
- Gallbladder cancer: Compared with normal-weight people, people who are overweight have a slight (about 20%) increase in risk of gallbladder cancer, and people who are obese have a 60% increase in risk of gallbladder cancer (19, 20). The risk increase is greater in women than men.
- Breast cancer: Many studies have shown that, in postmenopausal women, a higher BMI is associated with a modest increase in risk of breast cancer. For example, a 5-unit increase in BMI is associated with a 12% increase in risk (21). Among postmenopausal women, those who are obese have a 20% to 40% increase in risk of developing breast cancer compared with normal-weight women (22). The higher risks are seen mainly in women who have never used menopausal hormone therapy and for tumors that express hormone receptors. Obesity is also a risk factor for breast cancer in men (23).In premenopausal women, by contrast, overweight and obesity have been found to be associated with a 20% decreased risk of breast tumors that express hormone receptors (22).
- Ovarian cancer: Higher BMI is associated with a slight increase in the risk of ovarian cancer, particularly in women who have never used menopausal hormone therapy (24). For example, a 5-unit increase in BMI is associated with a 10% increase in risk among women who have never used menopausal hormone therapy (24).
- Thyroid cancer: Higher BMI (specifically, a 5-unit increase in BMI) is associated with a slight (10%) increase in the risk of thyroid cancer (25).



 Staff Writer Jocelyn Kaiser joins Sarah to talk about a recent Science paper describing the results of a large study on a blood test for multiple types of cancer. The trial’s results suggest such a blood test combined with follow-up scans may help detect cancers early, but there is a danger of too many false positives.
Staff Writer Jocelyn Kaiser joins Sarah to talk about a recent Science paper describing the results of a large study on a blood test for multiple types of cancer. The trial’s results suggest such a blood test combined with follow-up scans may help detect cancers early, but there is a danger of too many false positives. 
 The hope, Lee says, is that ultrasound will kill cancer cells in a specific way that will also engage the immune system and arouse it to attack any cancer cells remaining after the treatment.
The hope, Lee says, is that ultrasound will kill cancer cells in a specific way that will also engage the immune system and arouse it to attack any cancer cells remaining after the treatment. Ultrasound waves—sound waves with frequencies higher than humans can hear—have been used as a cancer treatment before, albeit in a broad-brush approach: high-intensity bursts of ultrasound can heat up tissue, killing cancer and normal cells in a target area. Now, scientists and engineers are exploring the use of low-intensity pulsed ultrasound (LIPUS) in an effort to create a more selective treatment.
Ultrasound waves—sound waves with frequencies higher than humans can hear—have been used as a cancer treatment before, albeit in a broad-brush approach: high-intensity bursts of ultrasound can heat up tissue, killing cancer and normal cells in a target area. Now, scientists and engineers are exploring the use of low-intensity pulsed ultrasound (LIPUS) in an effort to create a more selective treatment.
 Steep incidence increases between 49 and 50 years of age are consistent with previously undetected colorectal cancers diagnosed via screening uptake at 50 years. These cancers are not reflected in observed rates of colorectal cancer in the SEER registries among individuals younger than 50 years. Hence, using observed incidence rates from 45 to 49 years of age alone to assess potential outcomes of earlier screening may underestimate cancer prevention benefits.
Steep incidence increases between 49 and 50 years of age are consistent with previously undetected colorectal cancers diagnosed via screening uptake at 50 years. These cancers are not reflected in observed rates of colorectal cancer in the SEER registries among individuals younger than 50 years. Hence, using observed incidence rates from 45 to 49 years of age alone to assess potential outcomes of earlier screening may underestimate cancer prevention benefits.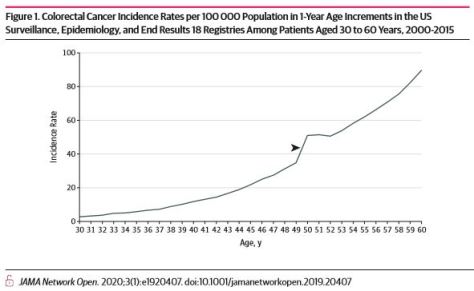





 This cohort study included 146 152 individuals from the Prostate, Lung, Colorectal, and Ovarian Cancer Screening Trial and found that aspirin use 3 or more times per week was associated with reduced risk of all-cause, cancer, gastrointestinal cancer, and colorectal cancer mortality.
This cohort study included 146 152 individuals from the Prostate, Lung, Colorectal, and Ovarian Cancer Screening Trial and found that aspirin use 3 or more times per week was associated with reduced risk of all-cause, cancer, gastrointestinal cancer, and colorectal cancer mortality.
 “But what’s really intriguing is that we can now see how vitamin D might help the immune system fight cancer. We know when the Wnt/beta-catenin pathway is active in melanoma, it can dampen down the immune response causing fewer immune cells to reach the inside of the tumor, where they could potentially fight the cancer better.
“But what’s really intriguing is that we can now see how vitamin D might help the immune system fight cancer. We know when the Wnt/beta-catenin pathway is active in melanoma, it can dampen down the immune response causing fewer immune cells to reach the inside of the tumor, where they could potentially fight the cancer better.