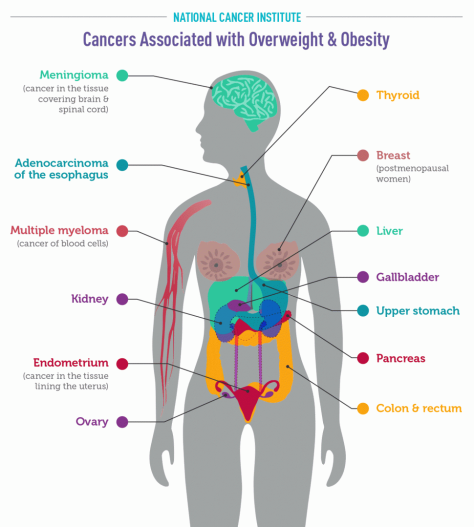
From Scientific American (June 23, 2020):
 In fact, research on actual cases, as well as models of the pandemic, indicate that between 10 and 20 percent of infected people are responsible for 80 percent of the coronavirus’s spread.
In fact, research on actual cases, as well as models of the pandemic, indicate that between 10 and 20 percent of infected people are responsible for 80 percent of the coronavirus’s spread.
Researchers have identified several factors that make it easier for superspreading to happen. Some of them are environmental.
- Poorly ventilated indoor areas seem especially conducive to the virus’s spread – A preliminary analysis of 110 COVID-19 cases in Japan found that the odds of transmitting the pathogen in a closed environment was more than 18 times greater than in an open-air space.
- Places where large numbers of people congregate – As a group’s size increases, so does the risk of transmitting the virus to a wider cluster. A large group size also increases the chance that someone present will be infectious.
- The longer a group stays in contact, the greater the likelihood that the virus will spread among them – The benchmark used for risk assessment in her contact-tracing work is 10 minutes of contact with an infectious person, though the CDC uses 15 minutes as a guideline.
- Some activities seem to make it easier to spread respiratory gunk – Speech emits more particles than normal breathing. And emissions also increase as people speak louder. Singing emits even more particles, which may partially explain the superspreader event at the Washington State choir practice. Breathing hard during exercise might also help the spread of COVID-19.







 The Wall Street Journal looks at how air travel will change and what it will be like to fly after the pandemic.
The Wall Street Journal looks at how air travel will change and what it will be like to fly after the pandemic.
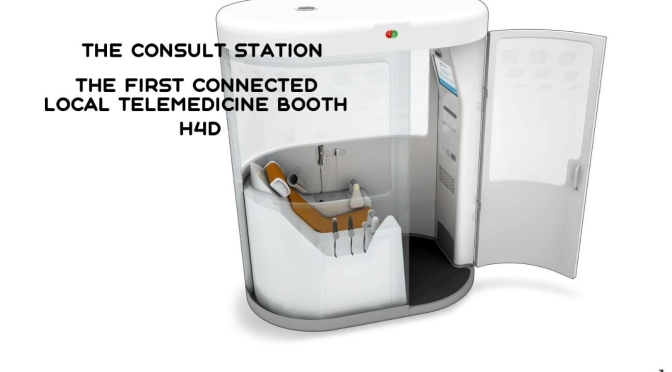
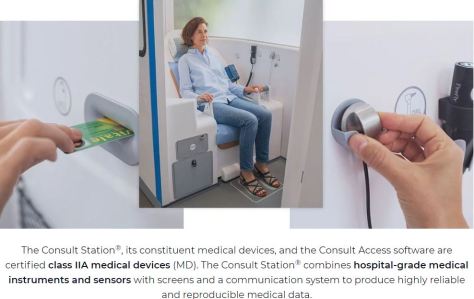
 For instance, more hospitals are remotely triaging and registering patients before they even arrive. Clinicians can consult with patients from their home via telemedicine to help determine how sick they are and if they need to come to the ER at all. From there, admissions are made with as little contact with staff or other patients as possible.
For instance, more hospitals are remotely triaging and registering patients before they even arrive. Clinicians can consult with patients from their home via telemedicine to help determine how sick they are and if they need to come to the ER at all. From there, admissions are made with as little contact with staff or other patients as possible.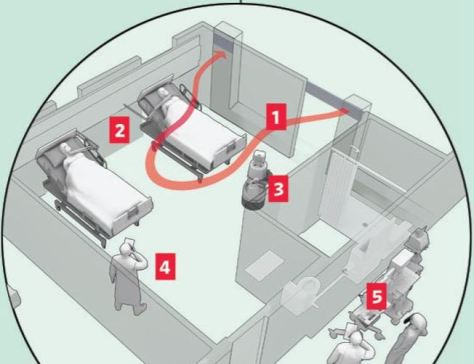
 With the potential for resurgences of the coronavirus, and some scientists warning about outbreaks of other infectious diseases, hospitals don’t want to be caught flat-footed again. So, more of them are turning to new protocols and new technology to overhaul standard operating procedure, from the time patients show up at an emergency room through admission, treatment and discharge.
With the potential for resurgences of the coronavirus, and some scientists warning about outbreaks of other infectious diseases, hospitals don’t want to be caught flat-footed again. So, more of them are turning to new protocols and new technology to overhaul standard operating procedure, from the time patients show up at an emergency room through admission, treatment and discharge.