
‘Journal of Neurology, Neurosurgery & Psychiatry” (July 10, 2020):
 We tested the hypothesis that apathy, but not depression, is associated with dementia in patients with SVD. We found that higher baseline apathy, as well as increasing apathy over time, were associated with an increased dementia risk. In contrast, neither baseline depression or change in depression was associated with dementia. The relationship between apathy and dementia remained after controlling for other well-established risk factors including age, education and cognition. Finally, adding apathy to models predicting dementia improved model fit. These results suggest that apathy may be a prodromal symptom of dementia in patients with SVD.
We tested the hypothesis that apathy, but not depression, is associated with dementia in patients with SVD. We found that higher baseline apathy, as well as increasing apathy over time, were associated with an increased dementia risk. In contrast, neither baseline depression or change in depression was associated with dementia. The relationship between apathy and dementia remained after controlling for other well-established risk factors including age, education and cognition. Finally, adding apathy to models predicting dementia improved model fit. These results suggest that apathy may be a prodromal symptom of dementia in patients with SVD.
Cerebral small vessel disease (SVD) is the leading vascular cause of dementia and plays a major role in cognitive decline and mortality.1 2 SVD affects the small vessels of the brain, leading to damage in the subcortical grey and white matter.1 The resulting clinical presentation includes cognitive and neuropsychiatric symptoms.1
Apathy is a reduction in goal-directed behaviour, which is a common neuropsychiatric symptom in SVD.3 Importantly, apathy is dissociable from depression,3 4 another symptom in SVD for which low mood is a predominant manifestation.5 Although there is some symptomatic overlap between the two,6 research using diffusion imaging reported that apathy, but not depression, was associated with white matter network damage in SVD.3 Many of the white matter pathways underlying apathy overlap with those related to cognitive impairment, and accordingly apathy, rather than depression, has been associated with cognitive deficits in SVD.7 These results suggest that apathy and cognitive impairment are symptomatic of prodromal dementia in SVD.
We observed that increased adherence to the MedDiet modulates specific components of the gut microbiota that were associated with a reduction in risk of frailty, improved cognitive function and reduced inflammatory status.
Dr Philip Smith, Digital and Education Editor of Gut and Consultant Gastroenterologist at the Royal Liverpool Hospital interviews Professor Paul O’Toole; who is Professor of Microbial Genomics, Head of School of Microbiology and Principal Investigator in APC Microbiome Ireland, an SFI funded centre at University College Cork, Ireland, on “Mediterranean diet intervention alters the gut microbiome in older people reducing frailty and improving health status: the NU-AGE 1-year dietary intervention across 5 European countries” published in paper copy in Gut in July 2020.

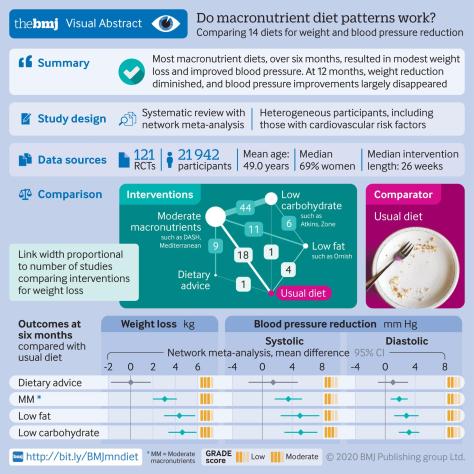
From a BMJ Study article (April, 2020):
Compared with usual diet, moderate certainty evidence supports modest weight loss and substantial reductions in systolic and diastolic blood pressure for low carbohydrate (eg, Atkins, Zone), low fat (eg, Ornish), and moderate macronutrient (eg, DASH, Mediterranean) diets at six but not 12 months. Differences between diets are, however, generally trivial to small, implying that people can choose the diet they prefer from among many of the available diets (fig 6) without concern about the magnitude of benefits.
The worldwide prevalence of obesity nearly tripled between 1975 and 2018.1 In response, authorities have made dietary recommendations for weight management and cardiovascular risk reduction.23 Diet programmes—some focusing on carbohydrate reduction and others on fat reduction—have been promoted widely by the media and have generated intense debates about their relative merit. Millions of people are trying to lose weight by changing their diet. Thus establishing the effect of dietary macronutrient patterns (carbohydrate reduction v fat reduction v moderate macronutrients) and popular named dietary programmes is important.
Biological and physiological mechanisms have been proposed to explain why some dietary macronutrient patterns and popular dietary programmes should be better than others. A previous network meta-analysis, however, suggested that differences in weight loss between dietary patterns and individual popular named dietary programmes are small and unlikely to be important.4 No systematic review and network meta-analysis has examined the comparative effectiveness of popular dietary programmes for reducing risk factors for cardiovascular disease, an area of continuing controversy.

Conclusion: The study was inconclusive with respect to potential differences in progression of individual radiographic features after surgical and non-surgical treatment for degenerative meniscal tear. Further, we found no strong evidence in support of differences in development of incident radiographic knee osteoarthritis or patient-reported outcomes between exercise therapy and arthroscopic partial meniscectomy.
Objective: To evaluate progression of individual radiographic features 5 years following exercise therapy or arthroscopic partial meniscectomy as treatment for degenerative meniscal tear.
Design: Randomized controlled trial including 140 adults, aged 35-60 years, with a magnetic resonance image verified degenerative meniscal tear, and 96% without definite radiographic knee osteoarthritis. Participants were randomized to either 12-weeks of supervised exercise therapy or arthroscopic partial meniscectomy. The primary outcome was between-group difference in progression of tibiofemoral joint space narrowing and marginal osteophytes at 5 years, assessed semi-quantitatively by the OARSI atlas. Secondary outcomes included incidence of radiographic knee osteoarthritis and symptomatic knee osteoarthritis, medial tibiofemoral fixed joint space width (quantitatively assessed), and patient-reported outcome measures. Statistical analyses were performed using a full analysis set. Per protocol and as treated analysis were also performed.
Results: The risk ratios (95% CI) for progression of semi-quantitatively assessed joint space narrowing and medial and lateral osteophytes for the surgery group were 0.89 (0.55-1.44), 1.15 (0.79-1.68) and 0.77 (0.42-1.42), respectively, compared to the exercise therapy group. In secondary outcomes (full-set analysis) no statistically significant between-group differences were found.
From a BMJ online release (March 17, 2020):
 “The finding in two randomised trials that advice to use ibuprofen results in more severe illness or complications helps confirm that the association seen in observational studies is indeed likely to be causal. Advice to use paracetamol (acetaminophen) is also less likely to result in complications.”
“The finding in two randomised trials that advice to use ibuprofen results in more severe illness or complications helps confirm that the association seen in observational studies is indeed likely to be causal. Advice to use paracetamol (acetaminophen) is also less likely to result in complications.”
Scientists and senior doctors have backed claims by France’s health minister that people showing symptoms of covid-19 should use paracetamol (acetaminophen) rather than ibuprofen, a drug they said might exacerbate the condition.
 Ian Jones, a professor of virology at the University of Reading, said that ibuprofen’s anti-inflammatory properties could “dampen down” the immune system, which could slow the recovery process. He added that it was likely, based on similarities between the new virus (SARS-CoV-2) and SARS I, that covid-19 reduces a key enzyme that part regulates the water and salt concentration in the blood and could contribute to the pneumonia seen in extreme cases. “Ibuprofen aggravates this, while paracetamol does not,” he said.
Ian Jones, a professor of virology at the University of Reading, said that ibuprofen’s anti-inflammatory properties could “dampen down” the immune system, which could slow the recovery process. He added that it was likely, based on similarities between the new virus (SARS-CoV-2) and SARS I, that covid-19 reduces a key enzyme that part regulates the water and salt concentration in the blood and could contribute to the pneumonia seen in extreme cases. “Ibuprofen aggravates this, while paracetamol does not,” he said.
From a BMJ Open Heart online study (March 8, 2020):
 Overall, the evidence in the literature suggests that spirulina improves several well-established CVD risk factors including hyperlipidaemia and seems to provide benefits around weight loss.
Overall, the evidence in the literature suggests that spirulina improves several well-established CVD risk factors including hyperlipidaemia and seems to provide benefits around weight loss.
Although caloric restriction and exercise are the mainstay treatments for obesity, spirulina has shown significant benefits in aiding weight loss. The phycocyanin in spirulina contains a light-harvesting chromophore called phycocyanobilin, which is capable of inhibiting nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate hydrogen (NADPH) oxidase, a significant source of oxidative stress in adipocytes playing a key role in inducing insulin resistance and shifting adipokine and cytokine production in hypertrophied adipocytes. Thus, by suppressing adipocyte oxidative stress, spirulina may lead to systemic anti-inflammatory and insulin-sensitising effects.

Spirulina is both a salt and fresh water blue-green algae, which is being increasingly studied recently. Spirulina was initially classified under the plant kingdom due to its rich plant pigments and its ability to photosynthesize, but was later placed into bacterial kingdom (cyanobacteria) due to its genetic, physiological and biochemical makeup. Spirulina grows naturally in high salt alkaline water reservoirs in subtropical and tropical areas of America, Mexico, Asia and Central Africa.
From a BMJ Research study (March 4, 2020):
 Habitual fish oil supplementation is associated with a 13% lower risk of all cause mortality, a 16% lower risk of CVD mortality, and a 7% lower risk of CVD events among the general population
Habitual fish oil supplementation is associated with a 13% lower risk of all cause mortality, a 16% lower risk of CVD mortality, and a 7% lower risk of CVD events among the general population
Fish oil is a rich source of long chain omega 3 fatty acids, a group of polyunsaturated fats that primarily include eicosapentaenoic acid and docosahexaenoic acid. Initially, these compounds were recommended for daily omega 3 fatty acid supplementation for the prevention of cardiovascular disease (CVD). Consequently, the use of fish oil supplements is widespread in the United Kingdom and other developed countries.
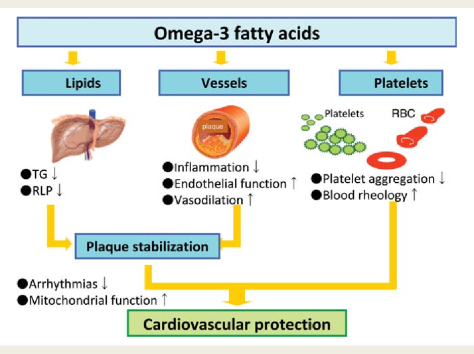
Several mechanisms could explain the benefits for clinical outcome derived from fish oil supplementation. Firstly, the results of several studies have indicated that supplementation with omega 3 fatty acids has beneficial effects on blood pressure, plasma triglycerides, and heart rate, all of which would exert a protective effect against the development of CVD. Secondly, several trials have shown that omega 3 fatty acids can improve flow mediated arterial dilatation, which is a measure of endothelial function and health. Thirdly, omega 3 fatty acids have been shown to possess antiarrhythmic properties that could be clinically beneficial. Finally, studies have reported that fish oil can reduce thrombosis. Additionally, studies have reported that the anti-inflammatory properties of fish oil could have a preventive role in the pathophysiology of CVD outcomes. Other mechanisms could also be involved to explain the effect of fish oil on CVD outcomes.
From a BMJ Research online study (March 4, 2020):
 We found no association between egg consumption and risk of cardiovascular disease in three large US cohorts. Results from the updated meta-analysis lend further support to the overall lack of an association between moderate egg consumption (up to one egg per day) and cardiovascular disease risk.
We found no association between egg consumption and risk of cardiovascular disease in three large US cohorts. Results from the updated meta-analysis lend further support to the overall lack of an association between moderate egg consumption (up to one egg per day) and cardiovascular disease risk.
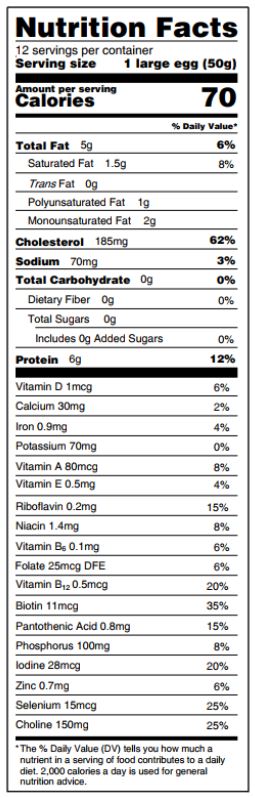 Eggs are a major source of dietary cholesterol, but they are also an affordable source of high quality protein, iron, unsaturated fatty acids, phospholipids, and carotenoids.
Eggs are a major source of dietary cholesterol, but they are also an affordable source of high quality protein, iron, unsaturated fatty acids, phospholipids, and carotenoids.
Introduction: In the United States, cardiovascular disease is the leading cause of death in men and women. Diet and lifestyle undisputedly play a major part in the development of cardiovascular disease. In the past, limiting dietary cholesterol intake to 300 mg per day was widely recommended to prevent cardiovascular disease. However, because of the weak association between dietary cholesterol and blood cholesterol, and considering that dietary cholesterol is no longer a nutrient of concern for overconsumption, the most recent 2015 dietary guidelines for Americans did not carry forward this recommendation.