In London, some 12,000 fireworks lit up the capital’s skyline, with 100,000 tickets being bought for the event. Big Ben’s chimes sounded the start of the display, despite them being silent this year while renovation work is completed.
In London, some 12,000 fireworks lit up the capital’s skyline, with 100,000 tickets being bought for the event. Big Ben’s chimes sounded the start of the display, despite them being silent this year while renovation work is completed.
British painter J.M.W. Turner was both prolific and peripatetic, producing more than 30,000 watercolors during a lifetime in which he traveled throughout Europe.
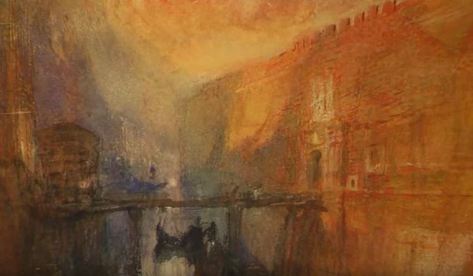
But these works are extremely susceptible to light damage and can be shown only once in a generation. Now, they’re on view at the Mystic Seaport Museum in Connecticut — their only North American stop. Jared Bowen of WGBH reports.
 The Surrealist eye informed everything Miller did, and her work presents the world in a way that encourages us to view it in a different manner. Written and collected by her son Antony, Surrealist Lee Miller amasses more than one hundred full-page images from throughout the artist’s life as an attestation to her wonderful way of seeing.
The Surrealist eye informed everything Miller did, and her work presents the world in a way that encourages us to view it in a different manner. Written and collected by her son Antony, Surrealist Lee Miller amasses more than one hundred full-page images from throughout the artist’s life as an attestation to her wonderful way of seeing.
A Surrealist before she even knew of the movement, Lee Miller was one of the most original photographic artists of the twentieth century. David E. Scherman, LIFE photographer and Miller’s close friend, described her as “caustically brilliant, yet totally loyal, unpretentious, human and intolerant of sham.
She was a consummate artist and a consummate clown; at once an upstate New York hick and cosmopolitan grande dame; a cold, soignée fashion model and a hoyden. . . . She was the nearest thing I knew to a mid-20th century renaissance woman.”
5. France – Johnny Hallyday (“Mon Plus Beau Noël”)

4. England – Pet Shop Boys (“Always On My Mind”)

3. Germany – Helene Fischer (“Stille Nacht”)

2. Japan – Yamashita Tatsuro (“Christmas Eve”)

1. United States – Mariah Carey (“All I Want For Christmas Is You”)

 “Nikas combines extensive research into a previously unavailable and highly detailed archive of Donald Healey’s personal records with the author’s masterful ability to weave together an amazing level of detail while making it an eminently readable story. The result is a book that both seasoned automotive historians and anyone with an interest in the story of a life well lived will enjoy. Until you’ve read this book, you don’t know the true story of Donald Healey and his cars”
“Nikas combines extensive research into a previously unavailable and highly detailed archive of Donald Healey’s personal records with the author’s masterful ability to weave together an amazing level of detail while making it an eminently readable story. The result is a book that both seasoned automotive historians and anyone with an interest in the story of a life well lived will enjoy. Until you’ve read this book, you don’t know the true story of Donald Healey and his cars”
(Reid Trummel, Editor in Chief, Healey Marque)
Written in collaboration with Gerry Coker, the designer responsible for the iconic Austin-Healey 100 and Sprite, this volume represents the most complete account ever of the sports cars built at Warwick, Longbridge, Abingdon and West Bromwich. With unprecedented access to Donald and Geoffrey Healey’s private papers, diaries, scrapbooks and photo albums, corporate and financial records from BMC, Donald Healey Motor Company and Healey Automobile Consultants, the files of Jensen Motors and Nash-Kelvinator, dozens of personal interviews and exhaustive research into previously unavailable primary source material, this book provides a thorough account of the true story behind these automobiles and the individuals who created them.
From a Spectator Life online article:
 With just four tables, a few counter seats and no reservations, getting a spot at Kiln can be a challenge. But it is one that is absolutely worth the wait.
With just four tables, a few counter seats and no reservations, getting a spot at Kiln can be a challenge. But it is one that is absolutely worth the wait.
Chosen as the UK’s Best Restaurant in the 2018 National Restaurant Awards, this Soho hotspot specialises in a roadside barbeque style of Thai cooking. The kiln it is named after is the hulking stove which dominates the restaurant. On it sits countless rustic claypots from which wafts a tempting mix of palm sugar, sweet basil and hot charcoal.The 22 seats along the steel counter are the best in the house, as you can watch the chefs scrupulously chopping, flipping and searing ingredients – most of which have been picked or caught just a few hours before.

At less than £7, the baked glass noodles with Tamworth pork belly and brown crab meat is probably the best value dish in London.
To read more: https://life.spectator.co.uk/articles/the-five-best-thai-restaurants-in-london/
From a The Modern House online article:
Fitzroy Park, London N6
 A stunning 6,200 sq ft space, this remarkable and sprawling house rises up through its surrounding landscaped gardens. Described by the Architects’ Journal as having a “beguilingly cave-like relationship to the outside world”, it is a bold vision of contemporary architecture in which the natural world has been thoroughly entwined with the design.
A stunning 6,200 sq ft space, this remarkable and sprawling house rises up through its surrounding landscaped gardens. Described by the Architects’ Journal as having a “beguilingly cave-like relationship to the outside world”, it is a bold vision of contemporary architecture in which the natural world has been thoroughly entwined with the design.
https://www.stantonwilliams.com/projects/fitzroy-park/
 Recline by the pool, listen to the artificial stream winding its way through the gardens, meander across the footbridge: this home was conceived for those long, dreamy summer days.
Recline by the pool, listen to the artificial stream winding its way through the gardens, meander across the footbridge: this home was conceived for those long, dreamy summer days.
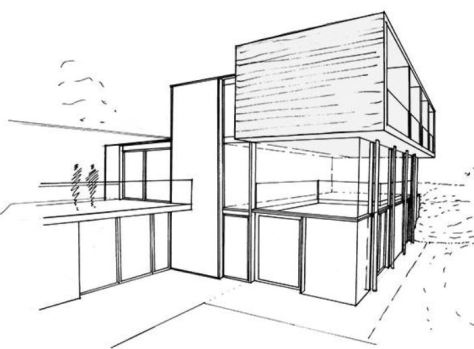

To read more: https://www.themodernhouse.com/sales-list/fitzroy-park/
 British architect Norman Foster reflects on his first high-tech building and how it shaped offices to come, in this exclusive video produced by Dezeen. Named after the electronics manufacturer that commissioned the building,
British architect Norman Foster reflects on his first high-tech building and how it shaped offices to come, in this exclusive video produced by Dezeen. Named after the electronics manufacturer that commissioned the building,
Reliance Controls was an industrial facility located in Swindon in Southwest England. Completed in 1967, the building was the last to be designed by Team 4, an architecture practice comprising Foster, Richard Rogers, Su Brumwell and Wendy Cheesman, before the group disbanded. The single-storey rectangular shed, which was designed to house the company’s factory and offices, was one of the first buildings labelled as high-tech – a style of architecture that Foster defines as a celebration of a building’s functional components.
Reliance Controls was the first building to dissolve the traditional boundaries between factory workers and office workers. “There was only a glass screen that would separate the assembly line for electronics from those who are managing the sales force,” said Foster. “They would all share the same kitchen and dining facilities, the same bathrooms. That we take for granted now but at that time it was it was really revolutionary – unheard of.”
Website: https://www.dezeen.com/2019/12/13/norman-foster-reliance-controls-video-interview/
 Melvyn Bragg and guests discuss the history and social impact of coffee. From its origins in Ethiopia, coffea arabica spread through the Ottoman Empire before reaching Western Europe where, in the 17th century, coffee houses were becoming established.
Melvyn Bragg and guests discuss the history and social impact of coffee. From its origins in Ethiopia, coffea arabica spread through the Ottoman Empire before reaching Western Europe where, in the 17th century, coffee houses were becoming established.There, caffeinated customers stayed awake for longer and were more animated, and this helped to spread ideas and influence culture. Coffee became a colonial product, grown by slaves or indentured labour, with coffea robusta replacing arabica where disease had struck, and was traded extensively by the Dutch and French empires; by the 19th century, Brazil had developed into a major coffee producer, meeting demand in the USA that had grown on the waggon trails.
With
Judith Hawley
Professor of 18th Century Literature at Royal Holloway, University of London
Markman Ellis
Professor of 18th Century Studies at Queen Mary University of London
And
Jonathan Morris
Professor in Modern History at the University of Hertfordshire
Producer: Simon Tillotson