“Our findings show dining out is a recipe for unhealthy eating most of the time,” said Dariush Mozaffarian, senior author and dean of the Friedman School.
At fast-food restaurants, 70 percent of the meals Americans consumed were of poor dietary quality in 2015-16, down from 75 percent in 2003-04. At full-service restaurants, about 50 percent were of poor nutritional quality, an amount that remained stable over the study period. The remainder were of intermediate nutritional quality.
BOSTON (Jan. 29, 2020, 9:00 a.m. EST)—The typical American adult gets one of every five  calories from a restaurant, but eating out is a recipe for meals of poor nutritional quality in most cases, according to a new study by researchers at the Friedman School of Nutrition Science and Policy at Tufts University.
calories from a restaurant, but eating out is a recipe for meals of poor nutritional quality in most cases, according to a new study by researchers at the Friedman School of Nutrition Science and Policy at Tufts University.

Published today in The Journal of Nutrition, the study analyzed the dietary selections of more than 35,000 U.S. adults from 2003-2016 in the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES) who dined at full-service (those with wait staff) or fast-food restaurants, which included pizza shops and what has become known as fast-casual. The researchers assessed nutritional quality by evaluating specific foods and nutrients in the meals, based on the American Heart Association 2020 diet score.



 The 10 year CVD (cardiovascular disease) incidence increased significantly across the baseline SMI (skeletal muscle mass index) tertiles (p<0.001). Baseline SMM (Skeletal muscle mass) showed a significant inverse association with the 10 year CVD incidence (HR 0.06, 95% CI 0.005 to 0.78), even after adjusting for various confounders. Additionally, participants in the highest SMM tertile had 81% (95% CI 0.04 to 0.85) lower risk for a CVD event as compared with those in the lowest SMM tertile.
The 10 year CVD (cardiovascular disease) incidence increased significantly across the baseline SMI (skeletal muscle mass index) tertiles (p<0.001). Baseline SMM (Skeletal muscle mass) showed a significant inverse association with the 10 year CVD incidence (HR 0.06, 95% CI 0.005 to 0.78), even after adjusting for various confounders. Additionally, participants in the highest SMM tertile had 81% (95% CI 0.04 to 0.85) lower risk for a CVD event as compared with those in the lowest SMM tertile.

 There are many named diets that receive a great deal of attention. But what are they and do they work? David Heber, MD, PhD, from the UCLA Center for Human Nutrition explains these diets.
There are many named diets that receive a great deal of attention. But what are they and do they work? David Heber, MD, PhD, from the UCLA Center for Human Nutrition explains these diets.
 “Patients can go home after a shorter length of stay in the hospital without increased risk of complications and rehospitalizations,” said Dr. Malaisrie. “Because we found no detrimental effect of accelerated discharge, both patients and physicians should not be averse to discharging patients when medically ready.”
“Patients can go home after a shorter length of stay in the hospital without increased risk of complications and rehospitalizations,” said Dr. Malaisrie. “Because we found no detrimental effect of accelerated discharge, both patients and physicians should not be averse to discharging patients when medically ready.”
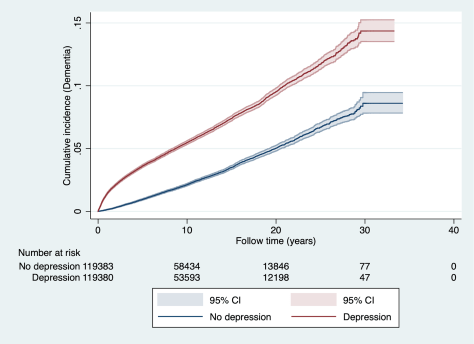

 Scientists have just discovered a new mechanism that can be key in regulating these immune attacks, raising new hopes of drugs that can protect against joint inflammation and the ailments it can bring.
Scientists have just discovered a new mechanism that can be key in regulating these immune attacks, raising new hopes of drugs that can protect against joint inflammation and the ailments it can bring.

 replicating a
replicating a 
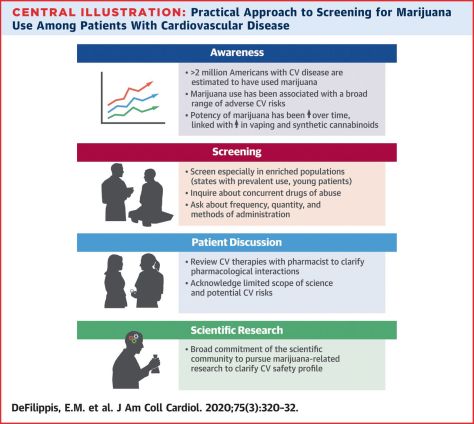
 “We were able to show that if you can stop the plasmid from replicating, then most of the bacteria lose the plasmid as the bacteria grow and divide. This means that infections that might otherwise be hard to control, even with the most powerful antibiotics available, are more likely to be treatable with standard antibiotics.”
“We were able to show that if you can stop the plasmid from replicating, then most of the bacteria lose the plasmid as the bacteria grow and divide. This means that infections that might otherwise be hard to control, even with the most powerful antibiotics available, are more likely to be treatable with standard antibiotics.”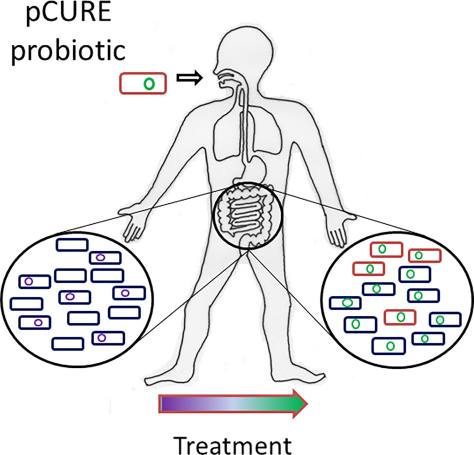

 “Our data showed that rates of accelerating blood pressure elevation were significantly higher in women than men, starting earlier in life,” said Cheng, the Erika J. Glazer Chair in Women’s Cardiovascular Health, who also serves as director of Cardiovascular Population Sciences at the Barbra Streisand Women’s Heart Center. “This means that if we define the hypertension threshold the exact same way, a 30-year old woman with high blood pressure is probably at higher risk for cardiovascular disease than a man with high blood pressure at the same age.”
“Our data showed that rates of accelerating blood pressure elevation were significantly higher in women than men, starting earlier in life,” said Cheng, the Erika J. Glazer Chair in Women’s Cardiovascular Health, who also serves as director of Cardiovascular Population Sciences at the Barbra Streisand Women’s Heart Center. “This means that if we define the hypertension threshold the exact same way, a 30-year old woman with high blood pressure is probably at higher risk for cardiovascular disease than a man with high blood pressure at the same age.”