
Globally, more people die from cardiovascular disease every year than from any other cause.

DOWNLOAD Report

Globally, more people die from cardiovascular disease every year than from any other cause.

DOWNLOAD Report

Frequent exercise is robustly associated with a decrease in cardiovascular mortality as well as the risk of developing cardiovascular disease. Physically active individuals have lower blood pressure, higher insulin sensitivity, and a more favorable plasma lipoprotein profile. Animal models of exercise show that repeated physical activity suppresses atherogenesis and increases the availability of vasodilatory mediators such as nitric oxide.
Exercise has also been found to have beneficial effects on the heart. Acutely, exercise increases cardiac output and blood pressure, but individuals adapted to exercise show lower resting heart rate and cardiac hypertrophy.


CARDIOLOGY MAGAZINE – MARCH 2023 ISSUE:

“It’s extremely important we as health care professionals address diabetes, poor sleep and poor sleep hygiene, and obesity as they are modifiable risk factors for cardiovascular disease,” says Nishant P. Shah, MD, FACC, a preventive cardiologist at Duke Heart Center, Duke University School of Medicine, in Durham, NC.
Obesity, diabetes and sleep-disordered breathing (SDB) are considered to be extant and growing public health crises. A wealth of information links these conditions to each other and to increased morbidity, reduced quality of life and death. While managing these conditions that often occur together may be challenging for patients and clinicians, successfully addressing them represents a real opportunity to reduce cardiovascular disease and prevent cardiovascular events.
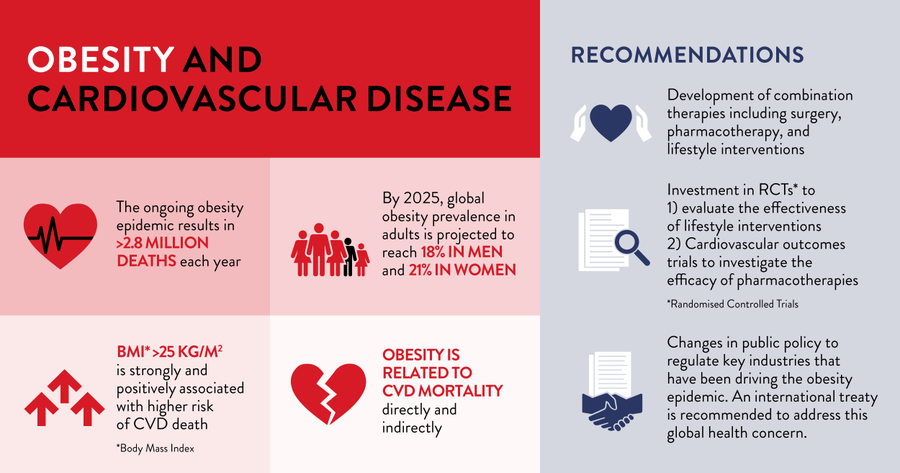
Our new position paper with @worldheartfed summarises the relationship between obesity and cardiovascular disease (#CVD) mortality.

World Obesity Federation (January 2023) – The ongoing obesity epidemic represents a global public health crisis that contributes to poor health outcomes, reduced quality of life, and >2.8 million deaths each year. Obesity is relapsing, progressive, and heterogeneous. It is considered a chronic disease by the World Obesity Federation (WOF) and a chronic condition by the World Heart Federation (WHF).
People living with overweight/obesity are at greater risk for cardiovascular (CV) morbidity and mortality. Increased adiposity (body fat), particularly visceral/abdominal fat, is linked to CV risk and CV disease (CVD) via multiple direct and indirect pathophysiological mechanisms. The development of CVD is driven, in part, by obesity-related metabolic, endocrinologic, immunologic, structural, humoral, haemodynamic, and functional alterations.
Learn more: http://bit.ly/3THvOZa
Less than 7% of the U.S. adult population has good cardiometabolic health, a devastating health crisis requiring urgent action, according to research led by a team from the Friedman School of Nutrition Science and Policy at Tufts University in a pioneering perspective on cardiometabolic health trends and disparities published in the July 12 issue of the Journal of the American College of Cardiology. Their team also included researchers from Tufts Medical Center.
Researchers evaluated Americans across five components of health: levels of blood pressure, blood sugar, blood cholesterol, adiposity (overweight and obesity), and presence or absence of cardiovascular disease (heart attack, stroke, etc.). They found that only 6.8 percent of U.S. adults had optimal levels of all five components as of 2017-2018.
The routine mammograms women receive to check for breast cancer may also offer clues to their risk for heart disease, new research suggests.
White spots or lines visible on mammograms indicate a buildup of calcium in breast arteries. This breast arterial calcification is different from coronary artery calcification, which is known to be a marker for higher cardiovascular risk. For the study, researchers followed 5,059 postmenopausal women (ages 60 to 79) for six and a half years. They found that those with breast arterial calcification were 51% more likely to develop heart disease or have a stroke than those without calcification. The study was published March 15, 2022, in Circulation: Cardiovascular Imaging.
Mayo Clinic Division of Preventive Cardiology will be preparing a series of recordings focusing on Cardiovascular Disease states. This is the Sleep Series and this particular one focuses on what is adequate sleep and does it benefit Cardiovascular Health.