From a BMJ Research study (March 4, 2020):
 Habitual fish oil supplementation is associated with a 13% lower risk of all cause mortality, a 16% lower risk of CVD mortality, and a 7% lower risk of CVD events among the general population
Habitual fish oil supplementation is associated with a 13% lower risk of all cause mortality, a 16% lower risk of CVD mortality, and a 7% lower risk of CVD events among the general population
Fish oil is a rich source of long chain omega 3 fatty acids, a group of polyunsaturated fats that primarily include eicosapentaenoic acid and docosahexaenoic acid. Initially, these compounds were recommended for daily omega 3 fatty acid supplementation for the prevention of cardiovascular disease (CVD). Consequently, the use of fish oil supplements is widespread in the United Kingdom and other developed countries.
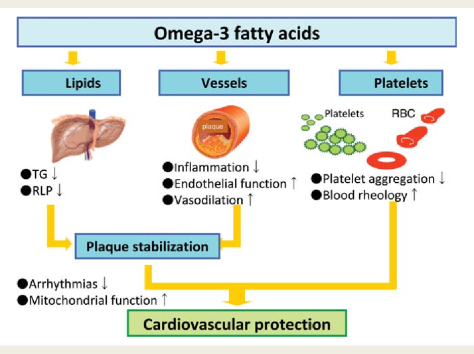
Several mechanisms could explain the benefits for clinical outcome derived from fish oil supplementation. Firstly, the results of several studies have indicated that supplementation with omega 3 fatty acids has beneficial effects on blood pressure, plasma triglycerides, and heart rate, all of which would exert a protective effect against the development of CVD. Secondly, several trials have shown that omega 3 fatty acids can improve flow mediated arterial dilatation, which is a measure of endothelial function and health. Thirdly, omega 3 fatty acids have been shown to possess antiarrhythmic properties that could be clinically beneficial. Finally, studies have reported that fish oil can reduce thrombosis. Additionally, studies have reported that the anti-inflammatory properties of fish oil could have a preventive role in the pathophysiology of CVD outcomes. Other mechanisms could also be involved to explain the effect of fish oil on CVD outcomes.



 Seasonal variation in blood pressure has been known for 40 years, but, to our knowledge, for the first time we show here that this occurs independently of temperature. The reduction in blood pressure is more marked with a rise in UVB than UVA, and in whites than black people. Dermatological concerns about the skin cancer inducing effects of UV radiation need to be balanced against the observed blood pressure lowering effects of sunlight, particularly given the greatly higher burden of disease caused by hypertension.
Seasonal variation in blood pressure has been known for 40 years, but, to our knowledge, for the first time we show here that this occurs independently of temperature. The reduction in blood pressure is more marked with a rise in UVB than UVA, and in whites than black people. Dermatological concerns about the skin cancer inducing effects of UV radiation need to be balanced against the observed blood pressure lowering effects of sunlight, particularly given the greatly higher burden of disease caused by hypertension. Sunlight exposure appears to lower blood pressure; insufficient exposure to natural ultraviolet radiation and/or active avoidance of sunlight may be new risk factors for hypertension.
Sunlight exposure appears to lower blood pressure; insufficient exposure to natural ultraviolet radiation and/or active avoidance of sunlight may be new risk factors for hypertension.
 We found no association between egg consumption and risk of cardiovascular disease in three large US cohorts. Results from the updated meta-analysis lend further support to the overall lack of an association between moderate egg consumption (up to one egg per day) and cardiovascular disease risk.
We found no association between egg consumption and risk of cardiovascular disease in three large US cohorts. Results from the updated meta-analysis lend further support to the overall lack of an association between moderate egg consumption (up to one egg per day) and cardiovascular disease risk. 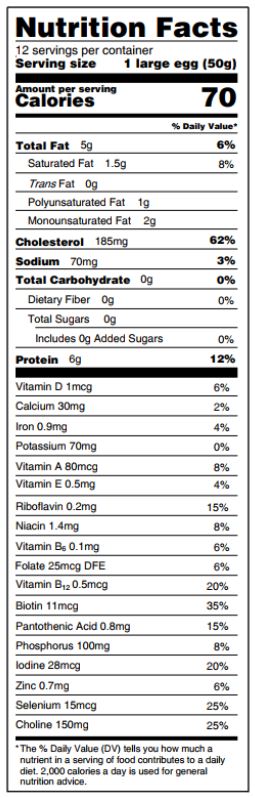 Eggs are a major source of dietary cholesterol, but they are also an affordable source of high quality protein, iron, unsaturated fatty acids, phospholipids, and carotenoids.
Eggs are a major source of dietary cholesterol, but they are also an affordable source of high quality protein, iron, unsaturated fatty acids, phospholipids, and carotenoids.
 “
“
 Eat less, live longer- If you want to reduce levels of inflammation throughout your body, delay the onset of age-related diseases and live longer—eat less food. That’s the conclusion of a new study by scientists from the US and China that provides the most detailed report to date of the cellular effects of a calorie-restricted diet in rats.
Eat less, live longer- If you want to reduce levels of inflammation throughout your body, delay the onset of age-related diseases and live longer—eat less food. That’s the conclusion of a new study by scientists from the US and China that provides the most detailed report to date of the cellular effects of a calorie-restricted diet in rats. 
 The study shows that wearable sensors coupled with machine learning analytics have predictive accuracy comparable to implanted devices.
The study shows that wearable sensors coupled with machine learning analytics have predictive accuracy comparable to implanted devices.

 The National Diabetes Statistics Report is a periodic publication of the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) that provides updated statistics about diabetes in the United States for a scientific audience. It includes information on prevalence and incidence of diabetes, prediabetes, risk factors for complications, acute and long-term complications, deaths, and costs. These data can help focus efforts to prevent and control diabetes across the United States.
The National Diabetes Statistics Report is a periodic publication of the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) that provides updated statistics about diabetes in the United States for a scientific audience. It includes information on prevalence and incidence of diabetes, prediabetes, risk factors for complications, acute and long-term complications, deaths, and costs. These data can help focus efforts to prevent and control diabetes across the United States.

 Aspirin is an inhibitor of prostaglandin production and may influence the cellular basis of bone remodelling responsible for maintaining the material and structural strength of bone.
Aspirin is an inhibitor of prostaglandin production and may influence the cellular basis of bone remodelling responsible for maintaining the material and structural strength of bone.
 We suggest this increase in mortality seen on DR in the 4-day switch treatment is due to either accrued physiological costs or more probable, a carryover of deaths directly resulting from the rich diet, but recorded on the DR diet.
We suggest this increase in mortality seen on DR in the 4-day switch treatment is due to either accrued physiological costs or more probable, a carryover of deaths directly resulting from the rich diet, but recorded on the DR diet.
 Across the 6 studies of 8699 participants, mean age ranged between 70 and 74 years and mean gait speed ranged between 1.05 and 1.26 m/s. Incident dementia ranged from 5 to 21 per 1000 person-years. Compared with usual agers, participants with only memory decline had 2.2 to 4.6 times higher risk for developing dementia…
Across the 6 studies of 8699 participants, mean age ranged between 70 and 74 years and mean gait speed ranged between 1.05 and 1.26 m/s. Incident dementia ranged from 5 to 21 per 1000 person-years. Compared with usual agers, participants with only memory decline had 2.2 to 4.6 times higher risk for developing dementia…