 President Trump’s preferred coronavirus treatment is the focus of a new study suggesting it could cause more harm than good, but not everybody agrees. We discuss the fallout as trials around the world are paused and countries diverge over policy advice.
President Trump’s preferred coronavirus treatment is the focus of a new study suggesting it could cause more harm than good, but not everybody agrees. We discuss the fallout as trials around the world are paused and countries diverge over policy advice.
12:12 Are we rushing science?
Coronavirus papers are being published extremely quickly, while normally healthy scientific debate is being blown up in the world’s press. Is there a balancing act between timely research and accurate messaging?
18:49 One good thing
Our hosts pick out things that have made them smile in the last week, including hedgerow brews and a trip into the past using AI.
Recipe: Elderflower ‘Champagne’
Video: Denis Shiryaev restores historic footage with AI
22:30 The latest coronavirus research papers
Noah Baker takes a look through some of the key coronavirus papers of the last few weeks.
News: Coronavirus research updates
medRxiv: Full genome viral sequences inform patterns of SARS-CoV-2 spread into and within Israel
Harvard Library: Reductions in commuting mobility predict geographic differences in SARS-CoV-2 prevalence in New York City
Science: DNA vaccine protection against SARS-CoV-2 in rhesus macaques



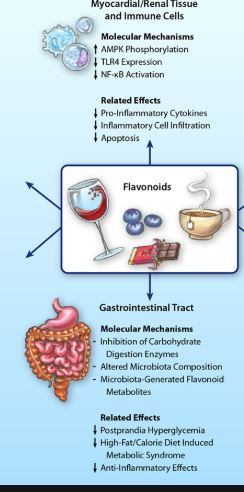 Our findings imply that higher long-term dietary intakes of flavonoids are associated with lower risks of ADRD and AD in US adults.
Our findings imply that higher long-term dietary intakes of flavonoids are associated with lower risks of ADRD and AD in US adults.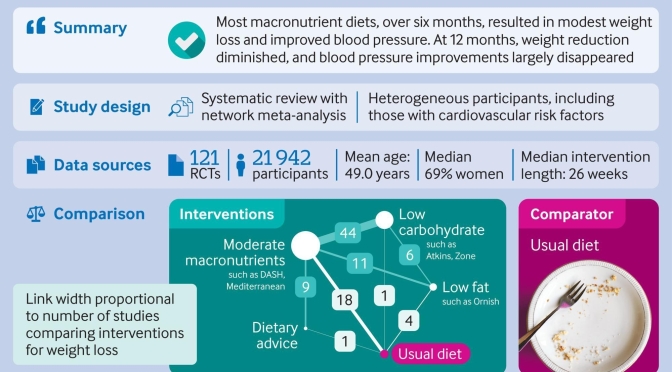
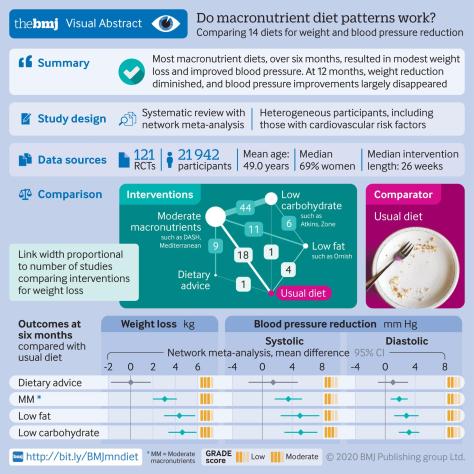

 “Having normal body weight is crucial in the prevention of type 2 diabetes, regardless of genetic predisposition.”
“Having normal body weight is crucial in the prevention of type 2 diabetes, regardless of genetic predisposition.”
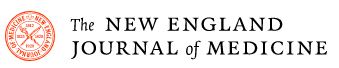
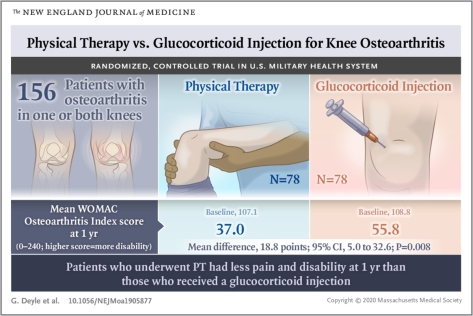
 This relationship between higher glucose levels and poorer cognitive functioning extended beyond just CASI z-score, as well, Cukierman-Yaffe noted. Higher HbA1c levels were also tied to significantly poorer performance in other psychological tests, including the clock making test of executive functioning, test of discriminative ability, and for the test of verbal fluency.
This relationship between higher glucose levels and poorer cognitive functioning extended beyond just CASI z-score, as well, Cukierman-Yaffe noted. Higher HbA1c levels were also tied to significantly poorer performance in other psychological tests, including the clock making test of executive functioning, test of discriminative ability, and for the test of verbal fluency.
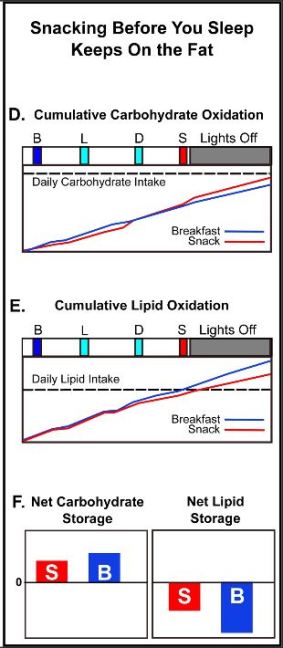
 These daily oscillations are controlled by the circadian clock, which is composed of an autoregulatory biochemical mechanism that is expressed in tissues throughout the body and is coordinated by a master pacemaker located in the suprachiasmatic nuclei of the brain (aka the SCN [
These daily oscillations are controlled by the circadian clock, which is composed of an autoregulatory biochemical mechanism that is expressed in tissues throughout the body and is coordinated by a master pacemaker located in the suprachiasmatic nuclei of the brain (aka the SCN [
 When your heart beats faster than usual, it can mean that you’re coming down with a cold, flu, coronavirus, or other viral infection. That’s the conclusion of recent medical
When your heart beats faster than usual, it can mean that you’re coming down with a cold, flu, coronavirus, or other viral infection. That’s the conclusion of recent medical 
 Overall, the evidence in the literature suggests that spirulina improves several well-established CVD risk factors including hyperlipidaemia and seems to provide benefits around weight loss.
Overall, the evidence in the literature suggests that spirulina improves several well-established CVD risk factors including hyperlipidaemia and seems to provide benefits around weight loss. 

 “These results are exciting, as they suggest that people may potentially prevent brain shrinking and the effects of aging on the brain simply by becoming more active,” said study author Yian Gu, Ph.D., of Columbia University in New York and a member of the American Academy of Neurology.
“These results are exciting, as they suggest that people may potentially prevent brain shrinking and the effects of aging on the brain simply by becoming more active,” said study author Yian Gu, Ph.D., of Columbia University in New York and a member of the American Academy of Neurology.