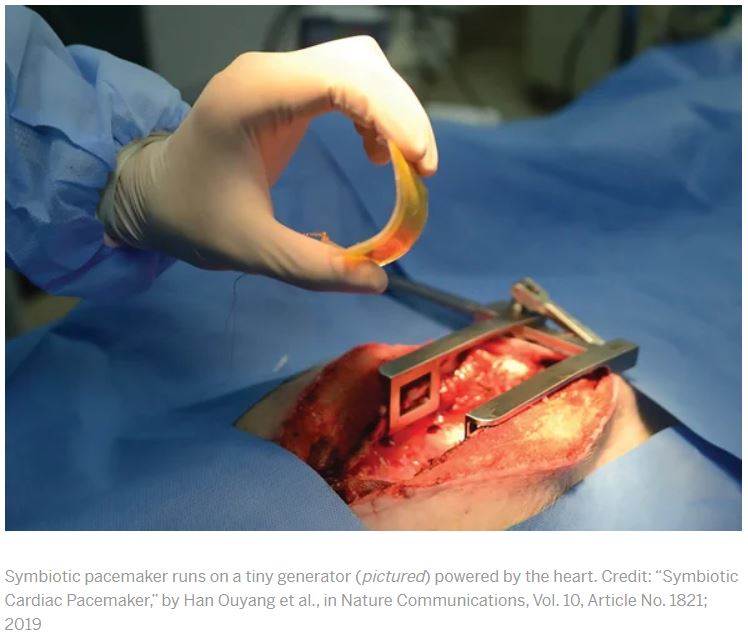
From Scientific American (March 1, 2021):
Enter the intranasal vaccine, which abandons the needle and syringe for a spray container that looks more like a nasal decongestant. With a quick spritz up the nose, intranasal vaccines are designed to bolster immune defenses in the mucosa, triggering production of an antibody known as immunoglobulin A, which can block infection. This overwhelming response, called sterilizing immunity, reduces the chance that people will pass on the virus.

The development of highly effective COVID vaccines in less than a year is an extraordinary triumph of science. But several coronavirus variants have emerged that could at least partly evade the immune response induced by the vaccines. These variants should serve as a warning against complacency—and encourage us to explore a different type of vaccination, delivered as a spray in the nose. Intranasal vaccines could provide an additional degree of protection, and help reduce the spread of the virus.



 In fact,
In fact, 
 Health journalist Judy Foreman talks about her new book Exercise Is Medicine: How Physical Activity Boosts Health and Slows Aging
Health journalist Judy Foreman talks about her new book Exercise Is Medicine: How Physical Activity Boosts Health and Slows Aging This is Scientific American’s Science Talk, posted on April 24th, 2020. I’m Steve Mirsky. And under our current, often locked-down situation, it’s still really important to try to get some exercise. Judy Foreman is the author of the new book Exercise is Medicine: How Physical Activity Boosts Health and Slows Aging. She’s a former nationally syndicated health columnist for the Boston Globe, LA times, Baltimore Sun and other places, and an author for the Oxford University Press.
This is Scientific American’s Science Talk, posted on April 24th, 2020. I’m Steve Mirsky. And under our current, often locked-down situation, it’s still really important to try to get some exercise. Judy Foreman is the author of the new book Exercise is Medicine: How Physical Activity Boosts Health and Slows Aging. She’s a former nationally syndicated health columnist for the Boston Globe, LA times, Baltimore Sun and other places, and an author for the Oxford University Press.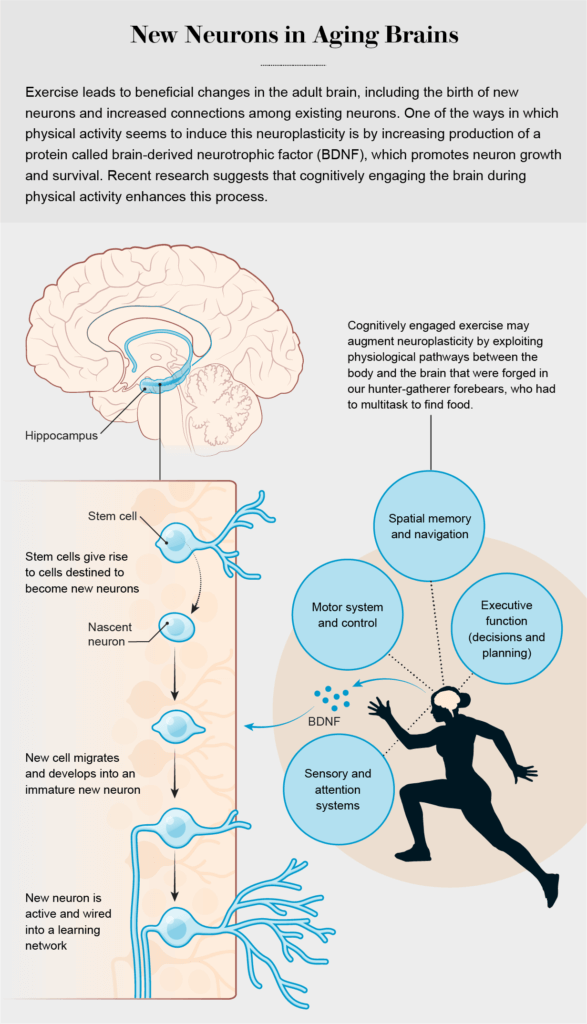


 In our own study of more than 7,000 middle-aged to older adults in the U.K., published in 2019 in Brain Imaging and Behavior, we demonstrated that people who spent more time engaged in moderate to vigorous physical activity had larger hippocampal volumes. Although it is not yet possible to say whether these effects in humans are related to neurogenesis or other forms of brain plasticity, such as increasing connections among existing neurons, together the results clearly indicate that exercise can benefit the brain’s hippocampus and its cognitive functions.
In our own study of more than 7,000 middle-aged to older adults in the U.K., published in 2019 in Brain Imaging and Behavior, we demonstrated that people who spent more time engaged in moderate to vigorous physical activity had larger hippocampal volumes. Although it is not yet possible to say whether these effects in humans are related to neurogenesis or other forms of brain plasticity, such as increasing connections among existing neurons, together the results clearly indicate that exercise can benefit the brain’s hippocampus and its cognitive functions.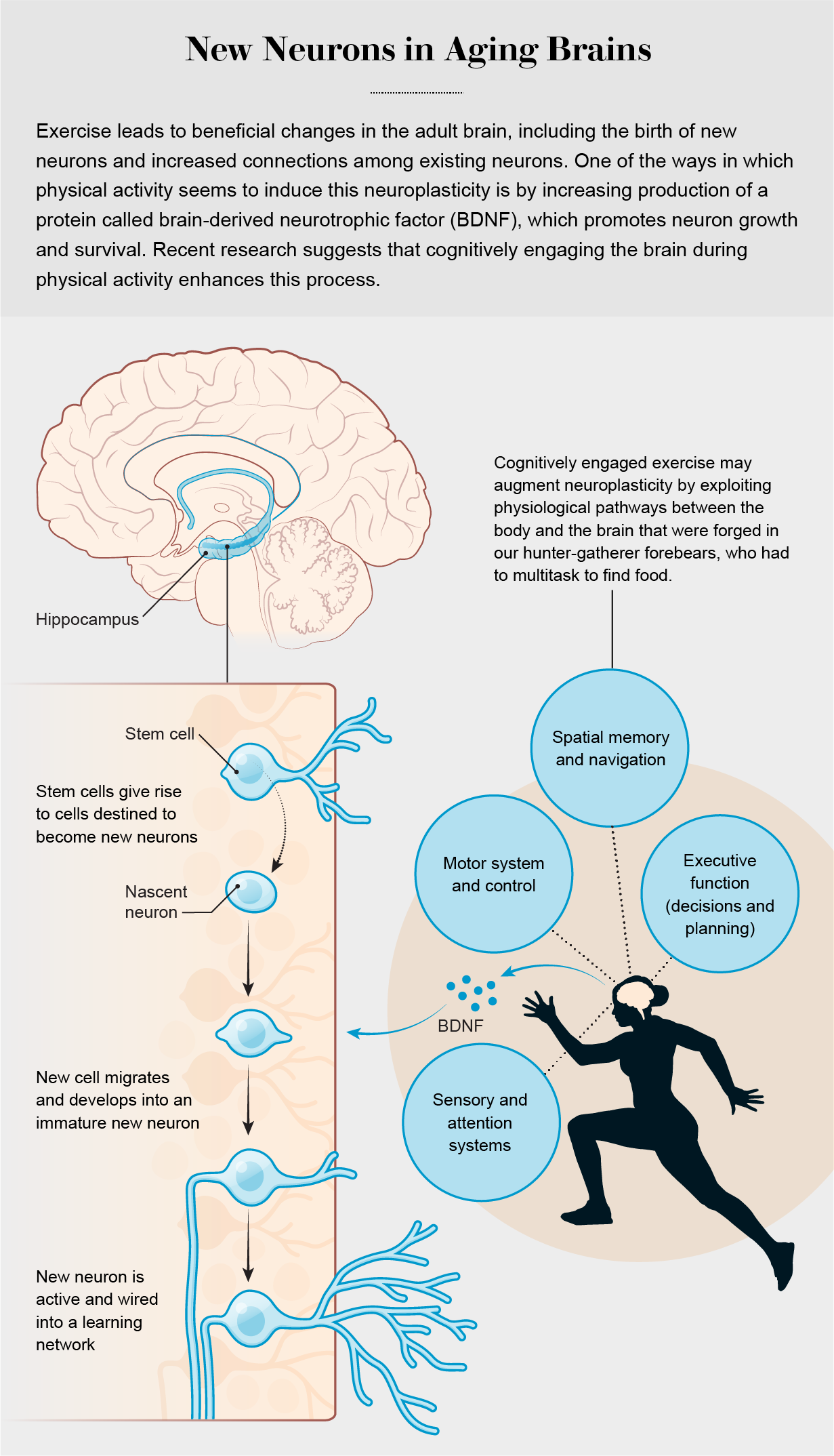

 One of the immune system’s jobs is to protect us from harmful bacterial. And the beneficial organisms that we refer to as probiotics contribute to this effort in a number of ways. In the gut, a robust population of beneficial bacteria can help crowd out harmful bacteria, making it harder for them to thrive. In addition, probiotic bacteria can influence the activity of our own immune cells, regulating inflammation, barrier function, and cell-to-cell signaling.
One of the immune system’s jobs is to protect us from harmful bacterial. And the beneficial organisms that we refer to as probiotics contribute to this effort in a number of ways. In the gut, a robust population of beneficial bacteria can help crowd out harmful bacteria, making it harder for them to thrive. In addition, probiotic bacteria can influence the activity of our own immune cells, regulating inflammation, barrier function, and cell-to-cell signaling. 
 Health care is a big business, and our system reimburses hospitals and health care workers for caring for the sickest people rather than healthiest ones. This process depletes healers’ energy and often causes them to become exhausted and sick. That means all of us who work in or study to work in health care are at risk. To break this vicious cycle, we need self-scrutiny and willingness to change.
Health care is a big business, and our system reimburses hospitals and health care workers for caring for the sickest people rather than healthiest ones. This process depletes healers’ energy and often causes them to become exhausted and sick. That means all of us who work in or study to work in health care are at risk. To break this vicious cycle, we need self-scrutiny and willingness to change.
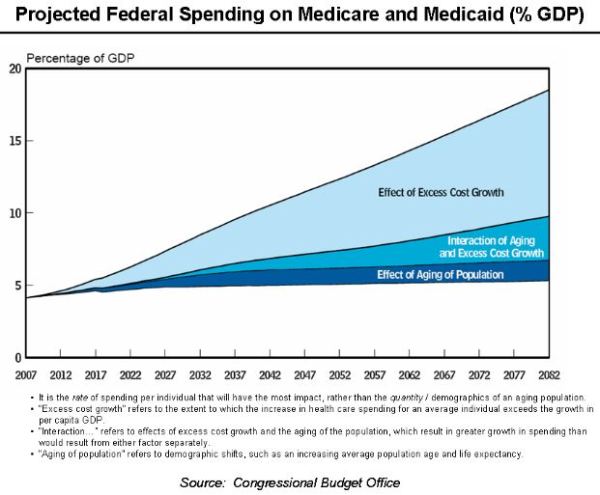 I once witnessed the care of a patient who suffered from chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, which blocks airflow to lungs and makes it difficult to breathe. Over the course of a particularly hot Texas summer, he was admitted to the hospital time and time again—racking up more than $60,000 in medical expenses. Doctors were treating his breathing problems repeatedly, but they did not understand why the patient continued to have trouble.
I once witnessed the care of a patient who suffered from chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, which blocks airflow to lungs and makes it difficult to breathe. Over the course of a particularly hot Texas summer, he was admitted to the hospital time and time again—racking up more than $60,000 in medical expenses. Doctors were treating his breathing problems repeatedly, but they did not understand why the patient continued to have trouble.