Vaccines are medicines that train the body to defend itself against future disease, and they have been saving human lives for hundreds of years. Vaccines are medicines that train the body to defend itself against future disease.
Tag Archives: Scientific American
Views: Scientific American – May 2021 Issue Features
Covid-19: ‘Intranasal Vaccines’ Might Be More Effective Than Needles

From Scientific American (March 1, 2021):
Enter the intranasal vaccine, which abandons the needle and syringe for a spray container that looks more like a nasal decongestant. With a quick spritz up the nose, intranasal vaccines are designed to bolster immune defenses in the mucosa, triggering production of an antibody known as immunoglobulin A, which can block infection. This overwhelming response, called sterilizing immunity, reduces the chance that people will pass on the virus.

The development of highly effective COVID vaccines in less than a year is an extraordinary triumph of science. But several coronavirus variants have emerged that could at least partly evade the immune response induced by the vaccines. These variants should serve as a warning against complacency—and encourage us to explore a different type of vaccination, delivered as a spray in the nose. Intranasal vaccines could provide an additional degree of protection, and help reduce the spread of the virus.
Covid-19: “Superspreading Events” Responsible For Up To 80% Of Infections
From Scientific American (June 23, 2020):
 In fact, research on actual cases, as well as models of the pandemic, indicate that between 10 and 20 percent of infected people are responsible for 80 percent of the coronavirus’s spread.
In fact, research on actual cases, as well as models of the pandemic, indicate that between 10 and 20 percent of infected people are responsible for 80 percent of the coronavirus’s spread.
Researchers have identified several factors that make it easier for superspreading to happen. Some of them are environmental.
- Poorly ventilated indoor areas seem especially conducive to the virus’s spread – A preliminary analysis of 110 COVID-19 cases in Japan found that the odds of transmitting the pathogen in a closed environment was more than 18 times greater than in an open-air space.
- Places where large numbers of people congregate – As a group’s size increases, so does the risk of transmitting the virus to a wider cluster. A large group size also increases the chance that someone present will be infectious.
- The longer a group stays in contact, the greater the likelihood that the virus will spread among them – The benchmark used for risk assessment in her contact-tracing work is 10 minutes of contact with an infectious person, though the CDC uses 15 minutes as a guideline.
- Some activities seem to make it easier to spread respiratory gunk – Speech emits more particles than normal breathing. And emissions also increase as people speak louder. Singing emits even more particles, which may partially explain the superspreader event at the Washington State choir practice. Breathing hard during exercise might also help the spread of COVID-19.
Podcast Interviews: “Exercise Is Medicine” Author Judy Foreman
 Health journalist Judy Foreman talks about her new book Exercise Is Medicine: How Physical Activity Boosts Health and Slows Aging
Health journalist Judy Foreman talks about her new book Exercise Is Medicine: How Physical Activity Boosts Health and Slows Aging
 This is Scientific American’s Science Talk, posted on April 24th, 2020. I’m Steve Mirsky. And under our current, often locked-down situation, it’s still really important to try to get some exercise. Judy Foreman is the author of the new book Exercise is Medicine: How Physical Activity Boosts Health and Slows Aging. She’s a former nationally syndicated health columnist for the Boston Globe, LA times, Baltimore Sun and other places, and an author for the Oxford University Press.
This is Scientific American’s Science Talk, posted on April 24th, 2020. I’m Steve Mirsky. And under our current, often locked-down situation, it’s still really important to try to get some exercise. Judy Foreman is the author of the new book Exercise is Medicine: How Physical Activity Boosts Health and Slows Aging. She’s a former nationally syndicated health columnist for the Boston Globe, LA times, Baltimore Sun and other places, and an author for the Oxford University Press.
Judy Foreman is the author of “A Nation in Pain” (2014), “The Global Pain Crisis” (2017), and “Exercise is Medicine,” (2020), all published by Oxford University Press, and was a staff writer at The Boston Globe for 22 years and the health columnist for many of these years. Her column was syndicated in national and international outlets including the Los Angeles Times, Dallas Morning News, Baltimore Sun and others.
She graduated Phi Beta Kappa from Wellesley College and has a Master’s from the Harvard Graduate School of Education. She was a Lecturer on Medicine at Harvard Medical School, a Fellow in Medical Ethics at Harvard Medical School and a Knight Science Journalism Fellow at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology. She spent six months as a guest reporter for The Times of London. She was also a Senior Fellow at the Schuster Institute for Investigative Journalism at Brandeis University. She was also host of a live, weekly call-in radio show on Healthtalk.com.
Judy has won more than 50 journalism awards, including a 1998 George Foster Peabody award for co-writing a video documentary about a young woman dying of breast cancer and the 2015 Science in Society award from the National Association of Science Writers.
Health Infographics: How Exercise Creates “New Neurons In Aging Brains”
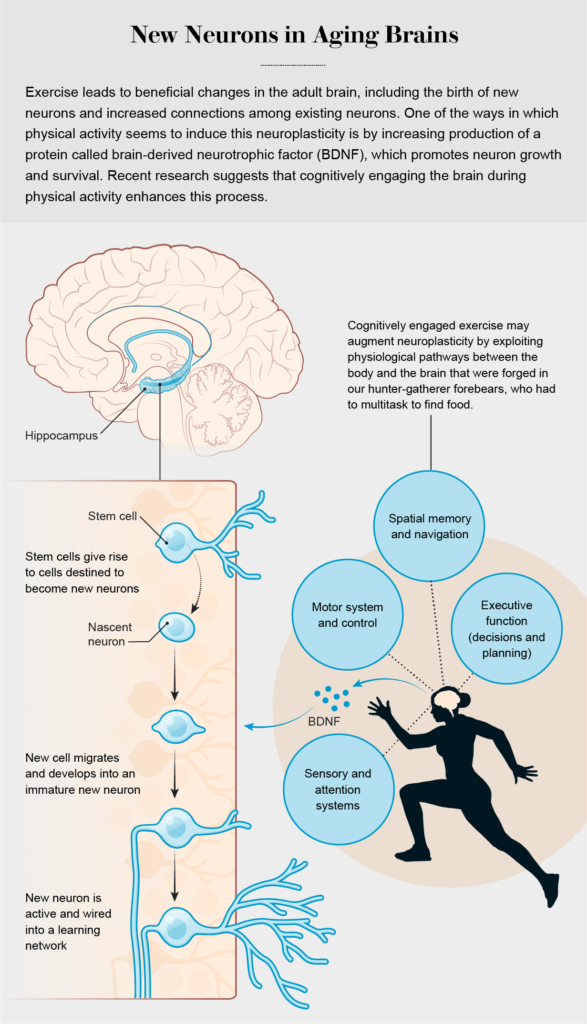

Researchers have also documented clear links between aerobic exercise and benefits to other parts of the brain, including expansion of the prefrontal cortex, which sits just behind the forehead. Such augmentation of this region has been tied to sharper executive cognitive functions, which involve aspects of planning, decision-making and multitasking—abilities that, like memory, tend to decline with healthy aging and are further degraded in the presence of Alzheimer’s. Scientists suspect that increased connections between existing neurons, rather than the birth of new neurons, are responsible for the beneficial effects of exercise on the prefrontal cortex and other brain regions outside the hippocampus.
Studies: “Why Your Brain Needs Exercise” (Scientific American)
From a Scientic American online article:
 In our own study of more than 7,000 middle-aged to older adults in the U.K., published in 2019 in Brain Imaging and Behavior, we demonstrated that people who spent more time engaged in moderate to vigorous physical activity had larger hippocampal volumes. Although it is not yet possible to say whether these effects in humans are related to neurogenesis or other forms of brain plasticity, such as increasing connections among existing neurons, together the results clearly indicate that exercise can benefit the brain’s hippocampus and its cognitive functions.
In our own study of more than 7,000 middle-aged to older adults in the U.K., published in 2019 in Brain Imaging and Behavior, we demonstrated that people who spent more time engaged in moderate to vigorous physical activity had larger hippocampal volumes. Although it is not yet possible to say whether these effects in humans are related to neurogenesis or other forms of brain plasticity, such as increasing connections among existing neurons, together the results clearly indicate that exercise can benefit the brain’s hippocampus and its cognitive functions.
In fact, a growing body of research suggests that exercise that is cognitively stimulating may indeed benefit the brain more than exercise that does not make such cognitive demands. For example, Gerd Kempermann and his colleagues at the Center for Regenerative Therapies Dresden in Germany explored this possibility by comparing the growth and survival of new neurons in the mouse hippocampus after exercise alone or after exercise combined with access to a cognitively enriched environment. They found an additive effect: exercise alone was good for the hippocampus, but combining physical activity with cognitive demands in a stimulating environment was even better, leading to even more new neurons. Using the brain during and after exercise seemed to trigger enhanced neuron survival.
To read more: https://www.scientificamerican.com/article/why-your-brain-needs-exercise/
Healthy Diet Podcasts: “Are Probiotics Safe for Your Immune System?” (Scientific American)
From a Scientific American online release:
 One of the immune system’s jobs is to protect us from harmful bacterial. And the beneficial organisms that we refer to as probiotics contribute to this effort in a number of ways. In the gut, a robust population of beneficial bacteria can help crowd out harmful bacteria, making it harder for them to thrive. In addition, probiotic bacteria can influence the activity of our own immune cells, regulating inflammation, barrier function, and cell-to-cell signaling.
One of the immune system’s jobs is to protect us from harmful bacterial. And the beneficial organisms that we refer to as probiotics contribute to this effort in a number of ways. In the gut, a robust population of beneficial bacteria can help crowd out harmful bacteria, making it harder for them to thrive. In addition, probiotic bacteria can influence the activity of our own immune cells, regulating inflammation, barrier function, and cell-to-cell signaling.
One way to foster healthy intestinal bacteria is to eat more of the foods these bugs like to eat—namely, fiber. Increasing your intake of plant fibers from vegetables, fruits, legumes, whole grains, nuts, and seeds is like filling a bird-feeder with the kind of seeds that the beautiful songbirds you want attract like best. If you feed them, they will come!
And if we want to attract a lot of different types of songbirds—er, bacteria—then we want to put out a variety of foods. That means you don’t just want to get all your fiber from a single source, such as a fiber supplement. You want to get it fiber from lots of different kinds of vegetables, fruits, legumes, grains, nuts and seeds.
Healthcare Update: Health-Professions Students And Workers Are “Exhausted And Sick”
From a Scientific American online article:
 Health care is a big business, and our system reimburses hospitals and health care workers for caring for the sickest people rather than healthiest ones. This process depletes healers’ energy and often causes them to become exhausted and sick. That means all of us who work in or study to work in health care are at risk. To break this vicious cycle, we need self-scrutiny and willingness to change.
Health care is a big business, and our system reimburses hospitals and health care workers for caring for the sickest people rather than healthiest ones. This process depletes healers’ energy and often causes them to become exhausted and sick. That means all of us who work in or study to work in health care are at risk. To break this vicious cycle, we need self-scrutiny and willingness to change.
Health-professions students and workers live in chronically stressful environments—responsible for an increasingly sick population, which they are expected to repeatedly rescue from failure. To heal others, our health care professionals need healing themselves.
American medical students, physicians and nurses: There’s good news and bad news.
The bad news is that our health care system and many of its workers are sick. The good news is that we can heal them. We should waste no time in starting.
To read more: https://blogs.scientificamerican.com/observations/american-health-care-is-sick-and-its-workers-are-too/
Boomers Health Care: “Population Health” Looks Beyond The Clinic For Better Outcomes
From a Scientific American online article by Adam Myers:
 I once witnessed the care of a patient who suffered from chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, which blocks airflow to lungs and makes it difficult to breathe. Over the course of a particularly hot Texas summer, he was admitted to the hospital time and time again—racking up more than $60,000 in medical expenses. Doctors were treating his breathing problems repeatedly, but they did not understand why the patient continued to have trouble.
I once witnessed the care of a patient who suffered from chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, which blocks airflow to lungs and makes it difficult to breathe. Over the course of a particularly hot Texas summer, he was admitted to the hospital time and time again—racking up more than $60,000 in medical expenses. Doctors were treating his breathing problems repeatedly, but they did not understand why the patient continued to have trouble.
One population health–oriented physician dug a bit deeper, holding in-depth conversations about the patient in the hospital—and later, having a team member visit his home. There, it was discovered that he lived without an air conditioner. A caring individual purchased and installed a $400 air conditioner for him, and his hospital visits stopped.
To read more click on following link: https://blogs.scientificamerican.com/observations/population-health-how-we-can-cure-whats-ailing-health-care/












