From a University of Toronto Medicine article:
 “There are two important takeaways from this paper. One is that poor sleep is associated with brain immune dysregulation or dysfunction,” says Lim, the corresponding author for the paper.
“There are two important takeaways from this paper. One is that poor sleep is associated with brain immune dysregulation or dysfunction,” says Lim, the corresponding author for the paper.
“The second part is that dysfunction appears to be further associated with impaired cognition.”
The study shows that in adults with fragmented sleep – where people were waking up repeatedly instead of sleeping soundly – there was an effect on microglia, and the cells showed signs of accelerated aging and other abnormalities.
The researchers were then able to identify that these changes in the microglia could be associated with worse cognition in older adults, both with and without Alzheimer’s disease.
To read full study: https://advances.sciencemag.org/content/5/12/eaax7331
To read more: https://medicine.utoronto.ca/news/research-suggests-fragmented-sleep-may-affect-brain-s-immune-cells-impair-cognition



 Sleep problems may decrease the likelihood of recovery from chronic low
Sleep problems may decrease the likelihood of recovery from chronic low 
 This cohort study included 146 152 individuals from the Prostate, Lung, Colorectal, and Ovarian Cancer Screening Trial and found that aspirin use 3 or more times per week was associated with reduced risk of all-cause, cancer, gastrointestinal cancer, and colorectal cancer mortality.
This cohort study included 146 152 individuals from the Prostate, Lung, Colorectal, and Ovarian Cancer Screening Trial and found that aspirin use 3 or more times per week was associated with reduced risk of all-cause, cancer, gastrointestinal cancer, and colorectal cancer mortality.
 This systematic review and meta-analysis of 11 studies involving 21 517 physicians demonstrated an association between physician depressive symptoms and an increased risk for perceived medical errors (RR, 1.95; 95% CI, 1.63-2.33). We also found that the magnitude of the associations of physician depressive symptoms and perceived medical errors were relatively consistent across studies that assessed training and practicing physicians, providing additional evidence that physician depression has implications for the quality of care delivered by physicians at different career stages.
This systematic review and meta-analysis of 11 studies involving 21 517 physicians demonstrated an association between physician depressive symptoms and an increased risk for perceived medical errors (RR, 1.95; 95% CI, 1.63-2.33). We also found that the magnitude of the associations of physician depressive symptoms and perceived medical errors were relatively consistent across studies that assessed training and practicing physicians, providing additional evidence that physician depression has implications for the quality of care delivered by physicians at different career stages.
 The annual rate of death from cardiovascular disease was nearly four times higher in women with poor, compared to good, exercise capacity (2.2% versus 0.6%). Annual cancer deaths were doubled in patients with poor, compared to good, exercise capacity (0.9% versus 0.4%). The annual rate of death from other causes was more than four times higher in those with poor, compared to good, exercise capacity (1.4% vs. 0.3%).
The annual rate of death from cardiovascular disease was nearly four times higher in women with poor, compared to good, exercise capacity (2.2% versus 0.6%). Annual cancer deaths were doubled in patients with poor, compared to good, exercise capacity (0.9% versus 0.4%). The annual rate of death from other causes was more than four times higher in those with poor, compared to good, exercise capacity (1.4% vs. 0.3%).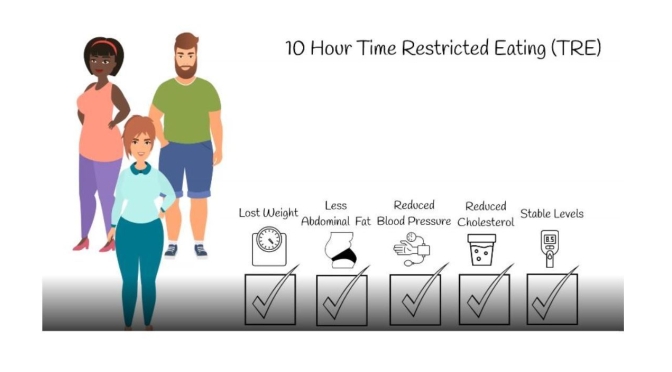
 Ten-hour time-restricted eating (TRE) limits daily dietary intake to a consistent 10-h window, creating a 14-h nightly fast. Researchers studied whether TRE for 12 weeks in people with metabolic syndrome receiving standard medical care (including medications to lower cholesterol and blood pressure) improves markers of health. TRE led to weight loss, healthier body composition (including decreased waist circumference), lower blood pressure and levels of cardiovascular disease-promoting lipids (i.e., “bad cholesterol” levels), and more restful sleep. TRE could be an effective dietary intervention to help those with metabolic syndrome.
Ten-hour time-restricted eating (TRE) limits daily dietary intake to a consistent 10-h window, creating a 14-h nightly fast. Researchers studied whether TRE for 12 weeks in people with metabolic syndrome receiving standard medical care (including medications to lower cholesterol and blood pressure) improves markers of health. TRE led to weight loss, healthier body composition (including decreased waist circumference), lower blood pressure and levels of cardiovascular disease-promoting lipids (i.e., “bad cholesterol” levels), and more restful sleep. TRE could be an effective dietary intervention to help those with metabolic syndrome.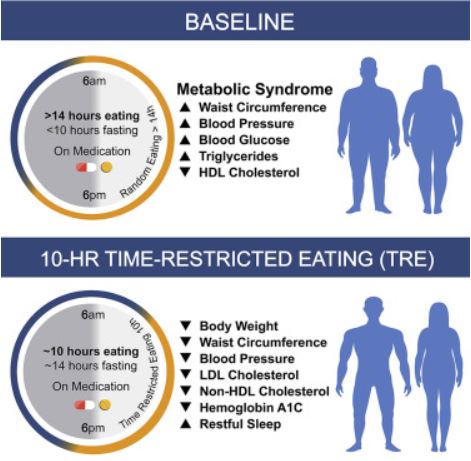

 Thus, while aging led to a pro-inflammatory profile within blood and muscle, lifelong exercise partially prevented this and generally preserved the acute inflammatory response to exercise seen in young exercising men. Lifelong exercise may positively impact muscle health throughout aging by promoting anti-inflammation in skeletal muscle.
Thus, while aging led to a pro-inflammatory profile within blood and muscle, lifelong exercise partially prevented this and generally preserved the acute inflammatory response to exercise seen in young exercising men. Lifelong exercise may positively impact muscle health throughout aging by promoting anti-inflammation in skeletal muscle.
 “This proof of concept study demonstrates a new paradigm that measurement of blood proteins can accurately deliver health information that spans across numerous medical specialties and that should be actionable for patients and their healthcare providers,” said Peter Ganz, MD, co-leader of this study and the Maurice Eliaser distinguished professor of medicine at UCSF and director of the Center of Excellence in Vascular Research at Zuckerberg San Francisco General Hospital and Trauma Center.
“This proof of concept study demonstrates a new paradigm that measurement of blood proteins can accurately deliver health information that spans across numerous medical specialties and that should be actionable for patients and their healthcare providers,” said Peter Ganz, MD, co-leader of this study and the Maurice Eliaser distinguished professor of medicine at UCSF and director of the Center of Excellence in Vascular Research at Zuckerberg San Francisco General Hospital and Trauma Center. 
 …a new study from the
…a new study from the  “A reduction in body weight of 12 percent is like getting a human from 200 pounds down to 176, which is a significant change,” said first author Md Nurunnabi, a former Postdoctoral Fellow at the Wyss Institute and SEAS who is now an Assistant Professor of Pharmaceutical Sciences at The University of Texas at El Paso. “Our goal is to translate this work into a product that can help people maintain a healthier weight, and this study marks the very beginning of that journey.”
“A reduction in body weight of 12 percent is like getting a human from 200 pounds down to 176, which is a significant change,” said first author Md Nurunnabi, a former Postdoctoral Fellow at the Wyss Institute and SEAS who is now an Assistant Professor of Pharmaceutical Sciences at The University of Texas at El Paso. “Our goal is to translate this work into a product that can help people maintain a healthier weight, and this study marks the very beginning of that journey.” They found that these physically active mice had fewer inflammatory cells (leukocytes) than sedentary mice, an effect they traced to diminished activity of hematopoietic stem and progenitor cells (HSPCs). The lower activity of HSPCs was due at least in part to exercise-induced reduction in the levels of leptin, a hormone produced by fat tissue that regulates cells within the hematopoietic bone marrow niche.
They found that these physically active mice had fewer inflammatory cells (leukocytes) than sedentary mice, an effect they traced to diminished activity of hematopoietic stem and progenitor cells (HSPCs). The lower activity of HSPCs was due at least in part to exercise-induced reduction in the levels of leptin, a hormone produced by fat tissue that regulates cells within the hematopoietic bone marrow niche.