By Michael Cummins, Editor, August 10, 2025
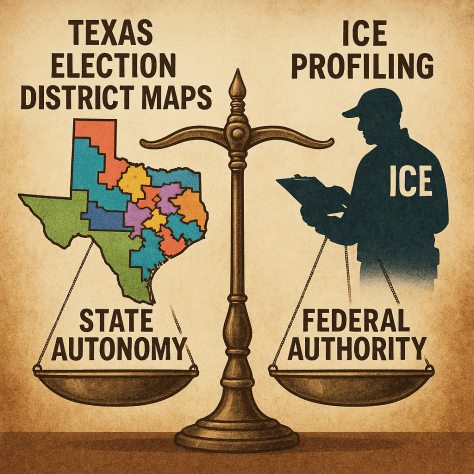
The American system of government, with its intricate web of checks and balances, is a continuous negotiation between competing sources of authority. At the heart of this negotiation lies the judiciary, tasked with the unenviable duty of acting as the final arbiter of power. The Bloomberg podcast “Weekend Law: Texas Maps, ICE Profiling & Agency Power” offers a compelling and timely exploration of this dynamic, focusing on two seemingly disparate legal battles that are, in essence, two sides of the same coin: the struggle to define the permissible boundaries of government action.
This essay will argue that the podcast’s true essence lies in its powerful synthesis of these cases, presenting them not as isolated political events but as critical manifestations of an ongoing judicial project: to determine the limits of legislative, executive, and administrative power in the face of constitutional challenges. This judicial project, as recent scholarly works have shown, is unfolding within a broader shift in American federalism, where a newly assertive judiciary and a highly politicized executive branch are rebalancing the relationship between federal and state power in unprecedented ways.
“The judiciary’s role is not merely to interpret the law, but to act as the ultimate check on a government’s temptation to consolidate power at the expense of its people.” — Emily Berman, law professor, Texas Law Review (2025)
The Supreme Court’s role as the final arbiter of these powers is not an original constitutional given, but rather a power it asserted for itself in the landmark 1803 case Marbury v. Madison. In that foundational ruling, Chief Justice John Marshall established the principle of judicial review, asserting that “it is emphatically the province and duty of the judicial department to say what the law is.” This declaration laid the groundwork for the judiciary to act as a check on both the legislative and executive branches, a power that would be tested and expanded throughout history. The two cases explored in the “Weekend Law” podcast are the latest iterations of this long-standing judicial project, demonstrating how the courts continue to shape the contours of governance in the face of contemporary challenges.
This is particularly relevant given the argument in the Harvard Law Review note “Federalism Rebalancing and the Roberts Court: A Departure from Historical Patterns” (March 2025), which contends that the Roberts Court has consciously moved away from historical trends and is now uniquely pro-state, often altering existing federal-state relationships. This broader jurisprudential shift provides a crucial backdrop for understanding Texas’s increasingly assertive actions, as it suggests the state is operating within a legal landscape more receptive to its claims of sovereignty.
Legislative Power and the Gerrymandering Divide
The first case study, the heated Texas redistricting battle, serves as a vivid illustration of the tension between legislative power and fundamental voting rights. The podcast effectively frames the drama: Texas Democrats, in a last-ditch effort, fled the state to deny the Republican-controlled legislature a quorum, thereby attempting to block the passage of a new congressional map. The stakes of this political chess match are immense, as the proposed map, crafted following the census, could solidify the Republican party’s narrow majority in the U.S. House. The legal conflict hinges on the subtle but consequential distinction between “racial” and “political” gerrymandering, a dichotomy that the Supreme Court has repeatedly struggled to define.
While the Court has held that drawing district lines to dilute the voting power of a racial minority is unconstitutional under the Fourteenth Amendment’s Equal Protection Clause and the Voting Rights Act of 1965, it has also ruled in cases like Rucho v. Common Cause (2019) that political gerrymandering is a “political question” beyond the purview of federal courts. The Bipartisan Policy Center’s explainer, “What to Know About Redistricting and Gerrymandering” (August 2025), is particularly relevant here, as it directly references a similar 2003 case where the Supreme Court allowed a Texas mid-decade map to stand. This history of judicial deference provides the specific legal precedent that empowers Texas to pursue its current redistricting efforts with confidence, and it helps contextualize the judiciary’s reluctance to intervene.
The Texas case exploits this judicial gray area. The state legislature, while acknowledging its aim to benefit the Republican Party—a seemingly permissible “political” objective—faces accusations from Democrats and civil rights groups that the new map disproportionately dilutes the power of Black and Hispanic voters, particularly in urban areas. The podcast highlights the argument that race and political preference are often so tightly intertwined that it becomes nearly impossible to separate them. This is precisely the kind of argument the Supreme Court has had to grapple with, as seen in recent cases like Alexander v. South Carolina State Conference of the NAACP (2024). In that case, the Court’s majority, led by Justice Alito, held that challengers must provide direct, not just circumstantial, evidence that race, rather than politics, was the “predominant” factor in drawing a district. This ruling, and others like it, effectively “stack the deck” against plaintiffs, creating novel and significant roadblocks to a successful racial gerrymandering claim.
“The Supreme Court has relied upon the incoherent racial gerrymandering claim because the Court lacks the right tools to police certain political conduct that might be impermissibly racist, partisan, or both.” — Rick Hasen, election law expert
Legal experts like Rick Hasen, whose work on election law is foundational, would likely view this trend with deep concern. Hasen has long argued for a more robust defense of voting rights, noting the Constitution’s surprising lack of an affirmative right to vote and the Supreme Court’s incremental, often restrictive, interpretations of voting protections. The Texas situation, in his view, is not a bug in the system but a feature of a constitutional framework that has been slowly eroded by a Court that has become increasingly deferential to state legislatures. The podcast’s narrative here is a cautionary tale of a legislative body wielding its power to entrench itself, and of a judiciary that, by its own precedents, may be unable or unwilling to intervene effectively.
The political theater of the Democrats’ walkout, therefore, is not merely a symbolic act; it is a desperate attempt to use the legislative process itself to challenge a power grab that the judiciary has made more difficult to contest. This is further complicated by the analysis in Publius – The Journal of Federalism article “State of American Federalism 2024–2025” (July 2025), which explores the concept of “transactional federalism,” where presidents reward loyal states and punish those that are not. This framework provides a vital lens for understanding how a state like Texas, with a strong political alignment to the executive branch, might feel empowered to take such aggressive redistricting actions.
Reining in Executive Overreach: The ICE Profiling Case
On the other side of the legal spectrum, the podcast turns to the Ninth Circuit’s ruling against U.S. Immigration and Customs Enforcement (ICE) in Southern California. This case shifts the focus from legislative overreach to executive overreach, particularly the conduct of an administrative agency. The court’s decision upheld a lower court’s temporary restraining order, barring ICE agents from making warrantless arrests based on a broad “profile” that included apparent race, ethnicity, language, and location. This is a critical challenge to the authority of a federal agency, forcing it to operate within the constraints of the Fourth Amendment. The court’s ruling, as highlighted in the podcast, was predicated on a “mountain of evidence” demonstrating that ICE’s practices amounted to unconstitutional racial profiling.
“The Ninth Circuit’s decision is a critical affirmation that the Fourth Amendment does not have a carve-out for immigration enforcement. A person’s skin color is not probable cause.” — David Carden, ACLU immigration attorney (July 2025)
The legal principles at play here are equally profound. The Fourth Amendment protects “the right of the people to be secure in their persons, houses, papers, and effects, against unreasonable searches and seizures.” The Ninth Circuit’s ruling essentially states that a person’s appearance, the language they speak, or where they work is not enough to establish the “reasonable suspicion” necessary for a warrantless stop. This decision is a powerful example of the judiciary acting as a check on the executive branch, affirming that even in the context of immigration enforcement, constitutional rights apply to all individuals within the nation’s borders. The podcast emphasizes the chilling effect of these raids, which created an atmosphere of fear and terror in communities of color. The court’s decision serves as a crucial bulwark against an “authoritarian” approach to law enforcement, as noted by ACLU attorneys.
Immigration attorney Leon Fresco, who is featured in the podcast, provides a nuanced perspective on the case, discussing the complexities of agency authority. While the government argued that its agents were making stops based on a totality of factors, not just race, the court’s rejection of this argument underscores a significant judicial shift. This is not a new conflict, as highlighted in the Georgetown Law article “Sovereign Resistance To Federal Immigration Enforcement In State Courthouses” (published after November 2020), which examines the historical and legal foundation for state and individual resistance to federal immigration enforcement. The article identifies the “normative underpinnings” of this resistance and explores the constitutional claims that states and individuals use to challenge federal authorities.
This historical context is essential for understanding the sustained nature of this conflict. This judicial skepticism toward expansive agency power is further illuminated by the Columbia Law School experts’ analysis of 2025 Supreme Court rulings (July 2025), which focuses on the federalism battle over immigration law and the potential for a ruling on the federal government’s ability to condition funding on state compliance with immigration laws. This expert commentary shows that the judicial challenges to federal immigration authority, as seen in the Ninth Circuit case, are part of a broader, ongoing legal battle at the highest levels of the judiciary.
The Judicial Project: Unifying Principles of Power
The true genius of the podcast is its ability to weave these two disparate threads into a single, cohesive tapestry of legal thought. The Texas redistricting fight and the ICE profiling case, while geographically and thematically distinct, are both fundamentally about the limits of power. In Texas, we see a state legislature exercising its power to draw district lines in a way that, critics argue, subverts democratic principles. In Southern California, we see a federal agency exercising its power to enforce immigration laws in a way that, the court has ruled, violates constitutional rights. In both scenarios, the judiciary is called upon to step in and draw a line.
“It is emphatically the province and duty of the judicial department to say what the law is.” — Chief Justice John Marshall, Marbury v. Madison (1803)
The podcast’s synthesis of these cases highlights the central role of the Supreme Court in this ongoing process. The Court, through its various rulings, has crafted the very legal tools and constraints that govern these conflicts. The precedents it sets—on gerrymandering, on the Voting Rights Act, and on judicial deference to agencies—become the battleground for these legal fights. The podcast suggests that the judiciary is not merely a passive umpire but an active player whose decisions over time have shaped the very rules of the game. For example, the Court’s decisions have made it harder to sue over gerrymandering and, simultaneously, have recently made it harder for agencies to act without judicial scrutiny. This creates a fascinating and potentially contradictory legal landscape where the judiciary appears to be simultaneously retreating from one area of political contention while advancing into another.
Conclusion: A New Era of Judicial Scrutiny
Ultimately, “Weekend Law” gets to the essence of a modern American dilemma. The legislative process is increasingly characterized by partisan gridlock, forcing a reliance on executive and administrative actions to govern. At the same time, a judiciary that is more ideological and assertive than ever before is stepping in to review these actions, often with a skepticism that questions the very foundations of the administrative state.
The cases in Texas and Southern California are not just about voting maps or immigration sweeps; they are about the fundamental structure of American governance. They illustrate how the judiciary, from district courts to the Supreme Court, has become the primary battleground for defining the scope of constitutional rights and the limits of state and federal power. This is occurring within a new legal environment where, according to the Harvard Law Review, the Roberts Court is uniquely pro-state, and where the executive branch, as discussed in the Publius article, is engaging in a form of “transactional federalism.”
The podcast masterfully captures this moment, presenting a world where the most profound political questions of our time are no longer settled in the halls of Congress, but in the solemn chambers of the American courthouse. As we look ahead, we are left to ponder a series of urgent questions. Will the judiciary’s new skepticism toward administrative power lead to a more accountable government or a paralyzed one? What will be the long-term impact on voting rights if the courts continue to make it more difficult to challenge gerrymandering?
“When the map is drawn to silence the voter, the very promise of democracy is fractured. The judiciary’s silence is not neutrality; it is complicity in the decay of a fundamental right.” — Professor Sarah Levinson, University of Texas School of Law (2025)
And, in an era of intense political polarization, can the judiciary—a branch of government itself increasingly viewed through a partisan lens—truly be trusted to fulfill its historic role as a neutral arbiter of the Constitution? The essence of the podcast, then, is a sober reflection on the state of American democracy, filtered through the lens of legal analysis. It portrays a system where power is constantly tested, and the judiciary, despite its own internal divisions and evolving doctrines, remains the indispensable mechanism for mediating these tests.
“A government that justifies racial profiling on the streets is no different from one that seeks to deny justice in its courthouses. The Ninth Circuit has held a line, declaring that our Constitution protects all people, not just citizens, from the long shadow of authoritarian overreach.” — Maria Elena Lopez, civil rights attorney, ACLU of Southern California (2025)
The podcast’s narrative arc—from the political brinkmanship in Texas to the constitutional defense of individual rights in California—serves as a powerful reminder that the rule of law is a dynamic, living concept, constantly being shaped and reshaped by the cases that come before the courts and the decisions that are rendered. It is a story of power, rights, and the enduring, if often contentious, role of the American judiciary in keeping the two in balance.
THIS ESSAY WAS WRITTEN AND EDITED UTILIZING AI