From a New England Journal of Medicine online release:
In humans, intermittent-fasting interventions ameliorate obesity, insulin resistance, dyslipidemia, hypertension, and inflammation. Intermittent fasting seems to confer health benefits to a greater extent than can be attributed just to a reduction in caloric intake.
Evidence is accumulating that eating in a 6-hour period and fasting for 18 hours can trigger a metabolic switch from glucose-based to ketone-based energy, with increased stress resistance, increased longevity, and a decreased incidence of diseases, including cancer and obesity.
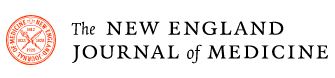
Preclinical studies and clinical trials have shown that intermittent fasting has broad-spectrum benefits for many health conditions, such as obesity, diabetes mellitus, cardiovascular disease, cancers, and neurologic disorders. Animal models show that intermittent fasting improves health throughout the life span, whereas clinical studies have mainly involved relatively short-term interventions, over a period of months.
BOOMERS-DAILY.COM “18-HOUR INTERMITTENT FASTING DIET” STUDY
How much of the benefit of intermittent fasting is due to metabolic switching and how much is due to weight loss? Many studies have indicated that several of the benefits of intermittent fasting are dissociated from its effects on weight loss. These benefits include improvements in glucose regulation, blood pressure, and heart rate; the efficacy of endurance training; and abdominal fat loss.



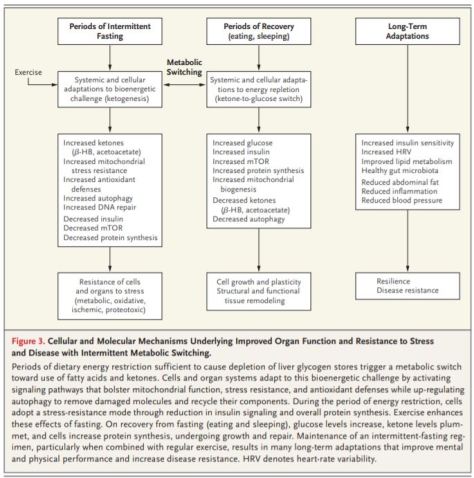
 When the five sleep factors were collapsed into binary categories of low risk vs. high risk (reference group), early chronotype, adequate sleep duration, free of insomnia, and no frequent daytime sleepiness were each independently associated with incident CVD, with a 7%, 12%, 8%, and 15% lower risk, respectively (Table
When the five sleep factors were collapsed into binary categories of low risk vs. high risk (reference group), early chronotype, adequate sleep duration, free of insomnia, and no frequent daytime sleepiness were each independently associated with incident CVD, with a 7%, 12%, 8%, and 15% lower risk, respectively (Table 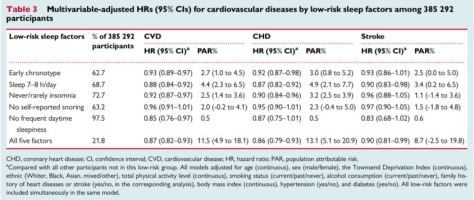 Cardiovascular disease (CVD), including coronary heart disease (CHD) and stroke, is among the leading causes of mortality globally.
Cardiovascular disease (CVD), including coronary heart disease (CHD) and stroke, is among the leading causes of mortality globally.

 In our own study of more than 7,000 middle-aged to older adults in the U.K., published in 2019 in Brain Imaging and Behavior, we demonstrated that people who spent more time engaged in moderate to vigorous physical activity had larger hippocampal volumes. Although it is not yet possible to say whether these effects in humans are related to neurogenesis or other forms of brain plasticity, such as increasing connections among existing neurons, together the results clearly indicate that exercise can benefit the brain’s hippocampus and its cognitive functions.
In our own study of more than 7,000 middle-aged to older adults in the U.K., published in 2019 in Brain Imaging and Behavior, we demonstrated that people who spent more time engaged in moderate to vigorous physical activity had larger hippocampal volumes. Although it is not yet possible to say whether these effects in humans are related to neurogenesis or other forms of brain plasticity, such as increasing connections among existing neurons, together the results clearly indicate that exercise can benefit the brain’s hippocampus and its cognitive functions.

 Technologists, particularly those who make consumer products, will have a strong influence over how we’ll live tomorrow. By treating older adults not as an ancillary market but as a core constituency, the tech sector can do much of the work required to redefine old age. But tech workplaces also skew infamously young. Asking young designers to merely step into the shoes of older consumers (and we at the MIT AgeLab have literally developed a physiological aging simulation suit for that purpose) is a good start, but it is not enough to give them true insight into the desires of older consumers. Luckily there’s a simpler route: hire older workers.
Technologists, particularly those who make consumer products, will have a strong influence over how we’ll live tomorrow. By treating older adults not as an ancillary market but as a core constituency, the tech sector can do much of the work required to redefine old age. But tech workplaces also skew infamously young. Asking young designers to merely step into the shoes of older consumers (and we at the MIT AgeLab have literally developed a physiological aging simulation suit for that purpose) is a good start, but it is not enough to give them true insight into the desires of older consumers. Luckily there’s a simpler route: hire older workers.
 Although the boomers may not have contributed much to the social and cultural changes of the nineteen-sixties, many certainly consumed them, embraced them, and identified with them. Still, the peak year of the boom was 1957, when 4.3 million people were born, and those folks did not go to Woodstock. They were twelve years old. Neither did the rest of the 33.5 million people born between 1957 and 1964. They didn’t start even going to high school until 1971. When the youngest boomer graduated from high school, Ronald Reagan was President and the Vietnam War had been over for seven years.
Although the boomers may not have contributed much to the social and cultural changes of the nineteen-sixties, many certainly consumed them, embraced them, and identified with them. Still, the peak year of the boom was 1957, when 4.3 million people were born, and those folks did not go to Woodstock. They were twelve years old. Neither did the rest of the 33.5 million people born between 1957 and 1964. They didn’t start even going to high school until 1971. When the youngest boomer graduated from high school, Ronald Reagan was President and the Vietnam War had been over for seven years.
 Away from Lake Placid, Lake George and other more crowded regional hubs, are several smaller hamlets that provide access to a handful of exceptionally remote lakeside campgrounds reachable only by pontooned floatplanes. With round-trip charters typically priced at $150 or less per person, some of the most secluded frontiers of
Away from Lake Placid, Lake George and other more crowded regional hubs, are several smaller hamlets that provide access to a handful of exceptionally remote lakeside campgrounds reachable only by pontooned floatplanes. With round-trip charters typically priced at $150 or less per person, some of the most secluded frontiers of 

 What does it mean for someone to flourish? Flourishing is more than just being happy—although that’s a part of it. But the idea of flourishing expands beyond happiness to look at a person’s overall well-being, taking into account things like life satisfaction or someone’s sense of purpose. That’s why studying flourishing is an interdisciplinary science drawing on public health, philosophy, psychology, and more.
What does it mean for someone to flourish? Flourishing is more than just being happy—although that’s a part of it. But the idea of flourishing expands beyond happiness to look at a person’s overall well-being, taking into account things like life satisfaction or someone’s sense of purpose. That’s why studying flourishing is an interdisciplinary science drawing on public health, philosophy, psychology, and more.
 After a dramatic intro set to “The Star-Spangled Banner,” the band kicked off with “Street Fighting Man,” a song Keith Richards recently told Rolling Stone “
After a dramatic intro set to “The Star-Spangled Banner,” the band kicked off with “Street Fighting Man,” a song Keith Richards recently told Rolling Stone “





