From a European Heart Journal study:
 When the five sleep factors were collapsed into binary categories of low risk vs. high risk (reference group), early chronotype, adequate sleep duration, free of insomnia, and no frequent daytime sleepiness were each independently associated with incident CVD, with a 7%, 12%, 8%, and 15% lower risk, respectively (Table 3). Early chronotype, adequate sleep duration, and free of insomnia were independently associated with a significantly reduced risk of CHD; while only adequate sleep duration was associated with stroke.
When the five sleep factors were collapsed into binary categories of low risk vs. high risk (reference group), early chronotype, adequate sleep duration, free of insomnia, and no frequent daytime sleepiness were each independently associated with incident CVD, with a 7%, 12%, 8%, and 15% lower risk, respectively (Table 3). Early chronotype, adequate sleep duration, and free of insomnia were independently associated with a significantly reduced risk of CHD; while only adequate sleep duration was associated with stroke.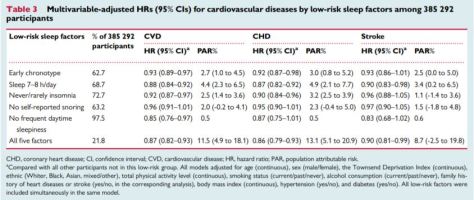 Cardiovascular disease (CVD), including coronary heart disease (CHD) and stroke, is among the leading causes of mortality globally.1 In addition to traditional lifestyle behaviours, emerging evidence has implicated several unhealthy sleep behaviours were important risk factors for CVD.2,3 For example, short or long sleep duration,4–9 late chronotype,10,11 insomnia,12–17 snoring,18,19 and excessive daytime sleepiness20,21 were associated with a 10–40% increased CVD risk.
Cardiovascular disease (CVD), including coronary heart disease (CHD) and stroke, is among the leading causes of mortality globally.1 In addition to traditional lifestyle behaviours, emerging evidence has implicated several unhealthy sleep behaviours were important risk factors for CVD.2,3 For example, short or long sleep duration,4–9 late chronotype,10,11 insomnia,12–17 snoring,18,19 and excessive daytime sleepiness20,21 were associated with a 10–40% increased CVD risk. 
To read more: https://academic.oup.com/eurheartj/advance-article/doi/10.1093/eurheartj/ehz849/5678714

