From a BMJ Open Journal study release (February 20, 2020):
 Aspirin is an inhibitor of prostaglandin production and may influence the cellular basis of bone remodelling responsible for maintaining the material and structural strength of bone.
Aspirin is an inhibitor of prostaglandin production and may influence the cellular basis of bone remodelling responsible for maintaining the material and structural strength of bone.
The consistent findings of reduced risk of fracture across studies included in this review is encouraging. It is important to keep in mind that studies were quite diverse in design, populations included, data collection methods and follow-up periods and we did observe high heterogeneity especially for fracture risk. While we need to interpret this finding with some caution, there appeared to be a consistent indication that aspirin use is associated with positive bone outcomes.
The anti-inflammatory effects of aspirin via prostaglandin inhibition have recently gained attention. Chronic low-grade inflammation contributes to age-related cardiovascular, neurological, respiratory and musculoskeletal conditions. Low-grade inflammation is associated with increased bone loss and fracture risk. Prostaglandin, an important inflammatory mediator, is likely to have a key role in bone remodelling attributable to inflammation. Prostaglandin E2 stimulates bone resorption and formation and is produced largely from cyclooxygenase-2 induction. Prostaglandins acutely inhibit osteoclast function. However, their chronic effect is to stimulate bone resorption by increasing replication of osteoclast precursors, and differentiation to mature osteoclasts.



 We observed that increased adherence to the MedDiet modulates specific components of the gut microbiota that were associated with a reduction in risk of frailty, improved cognitive function and reduced inflammatory status.
We observed that increased adherence to the MedDiet modulates specific components of the gut microbiota that were associated with a reduction in risk of frailty, improved cognitive function and reduced inflammatory status.

 “Studies with financial links to the indoor tanning industry were much more likely to discuss perceived benefits of indoor tanning and to downplay the harms,” said
“Studies with financial links to the indoor tanning industry were much more likely to discuss perceived benefits of indoor tanning and to downplay the harms,” said  In 2012, Eleni Linos, professor of dermatology at Stanford university, published a systematic review and meta-analysis of the link between non-melanoma cancer and sun-beds. That bit of pretty standard research, and a particular rapid response to it, has kicked of years of work – and in this podcast I talk to Eleni and her colleagues Stanton…
In 2012, Eleni Linos, professor of dermatology at Stanford university, published a systematic review and meta-analysis of the link between non-melanoma cancer and sun-beds. That bit of pretty standard research, and a particular rapid response to it, has kicked of years of work – and in this podcast I talk to Eleni and her colleagues Stanton…
 Last year the Lancet published a paper on the impact of wearing gowns, surveying 928 adult patients and carrying out structured interviews with 10 patients. Over half (58%) reported wearing the gown despite feeling uncertain that it was a medical necessity. Gown design was considered inadequate, with 61% reporting that they struggled to put it on or required assistance and 67% reporting that it didn’t fit. Most worryingly, 72% felt exposed, 60% felt self-conscious, and 57% felt uncomfortable wearing the gown.
Last year the Lancet published a paper on the impact of wearing gowns, surveying 928 adult patients and carrying out structured interviews with 10 patients. Over half (58%) reported wearing the gown despite feeling uncertain that it was a medical necessity. Gown design was considered inadequate, with 61% reporting that they struggled to put it on or required assistance and 67% reporting that it didn’t fit. Most worryingly, 72% felt exposed, 60% felt self-conscious, and 57% felt uncomfortable wearing the gown.
 The intake of marine omega-3s has consistently been found to have antiarrhythmic effects. When marine omega-3s are consumed, there is an increase in cellular membrane fluidity, inhibition of L-type calcium channels and a reduction in the chance of arrhythmic events during susceptible times. Prospective data suggest that maintaining an omega-3 index of about 8%, which requires consuming seafood rich in omega-3 up to five times per week or consuming over 3 g of EPA and DHA per day, may provide the greatest protection against arrhythmic events.
The intake of marine omega-3s has consistently been found to have antiarrhythmic effects. When marine omega-3s are consumed, there is an increase in cellular membrane fluidity, inhibition of L-type calcium channels and a reduction in the chance of arrhythmic events during susceptible times. Prospective data suggest that maintaining an omega-3 index of about 8%, which requires consuming seafood rich in omega-3 up to five times per week or consuming over 3 g of EPA and DHA per day, may provide the greatest protection against arrhythmic events.
 The 10 year CVD (cardiovascular disease) incidence increased significantly across the baseline SMI (skeletal muscle mass index) tertiles (p<0.001). Baseline SMM (Skeletal muscle mass) showed a significant inverse association with the 10 year CVD incidence (HR 0.06, 95% CI 0.005 to 0.78), even after adjusting for various confounders. Additionally, participants in the highest SMM tertile had 81% (95% CI 0.04 to 0.85) lower risk for a CVD event as compared with those in the lowest SMM tertile.
The 10 year CVD (cardiovascular disease) incidence increased significantly across the baseline SMI (skeletal muscle mass index) tertiles (p<0.001). Baseline SMM (Skeletal muscle mass) showed a significant inverse association with the 10 year CVD incidence (HR 0.06, 95% CI 0.005 to 0.78), even after adjusting for various confounders. Additionally, participants in the highest SMM tertile had 81% (95% CI 0.04 to 0.85) lower risk for a CVD event as compared with those in the lowest SMM tertile.

 Our findings suggest that promotion of a healthy lifestyle would help to reduce the healthcare burdens through lowering the risk of developing multiple chronic diseases, including cancer, cardiovascular disease, and diabetes, and extending disease-free life expectancy. Public policies for improving food and the physical environment conducive to adopting a healthy diet and lifestyle, as well as relevant policies and regulations (for example, smoking ban in public places or trans-fat restrictions), are critical to improving life expectancy, especially life expectancy free of major chronic diseases.
Our findings suggest that promotion of a healthy lifestyle would help to reduce the healthcare burdens through lowering the risk of developing multiple chronic diseases, including cancer, cardiovascular disease, and diabetes, and extending disease-free life expectancy. Public policies for improving food and the physical environment conducive to adopting a healthy diet and lifestyle, as well as relevant policies and regulations (for example, smoking ban in public places or trans-fat restrictions), are critical to improving life expectancy, especially life expectancy free of major chronic diseases.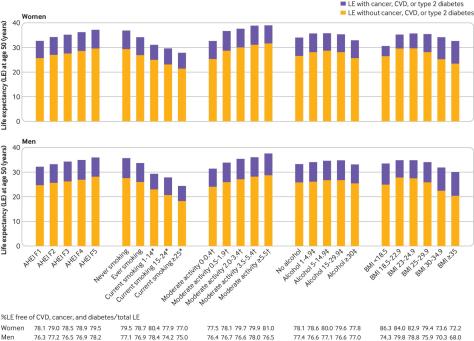

 The proportion of patients who have two or more medical conditions simultaneously is, however, rising steadily. This is currently termed multimorbidity, although patient groups prefer the more intuitive “multiple health conditions.” In high income countries, multimorbidity is mainly driven by age, and the proportion of the population living with two or more diseases is steadily increasing because of demographic change. This trend will continue.
The proportion of patients who have two or more medical conditions simultaneously is, however, rising steadily. This is currently termed multimorbidity, although patient groups prefer the more intuitive “multiple health conditions.” In high income countries, multimorbidity is mainly driven by age, and the proportion of the population living with two or more diseases is steadily increasing because of demographic change. This trend will continue.
 In studies of aerobic exercise in patients with knee OA, very few interventions met guideline-recommended dose; there were small to moderate changes in markers of cardiovascular health and no decrease in markers of systemic inflammation. These findings question whether aerobic exercise is being used to its full potential in patients with knee OA.
In studies of aerobic exercise in patients with knee OA, very few interventions met guideline-recommended dose; there were small to moderate changes in markers of cardiovascular health and no decrease in markers of systemic inflammation. These findings question whether aerobic exercise is being used to its full potential in patients with knee OA.