He went on to become a highly respected portraitist, counting Kaiser Wilhelm II of Germany, Benito Mussolini and opera star Lina Cavalieri among his subjects. In Coy’s view, however, his portraits were relatively conventional offerings — and Corcos’s ‘best work’ was his turn-of-the-century imagery of ‘dangerously independent women’.
Compare the biographies of Vittorio Corcos (1859-1933) and Amedeo Modigliani (1884-1920), and a remarkable number of similarities become apparent. Both were born into Jewish families in the Italian port city of Livorno in the second half of the 19th century; both would settle — and artistically come of age — in Paris. Both would even excel at the same type of paintings: their provocative depictions of women.
Their reputations, however, have suffered widely different fates. Modigliani, who struggled to sell much work before his death at the age of 35, is today regarded as a master of Modernism. Corcos, by contrast, who enjoyed a long and prosperous international career, posthumously became a rather forgotten figure.
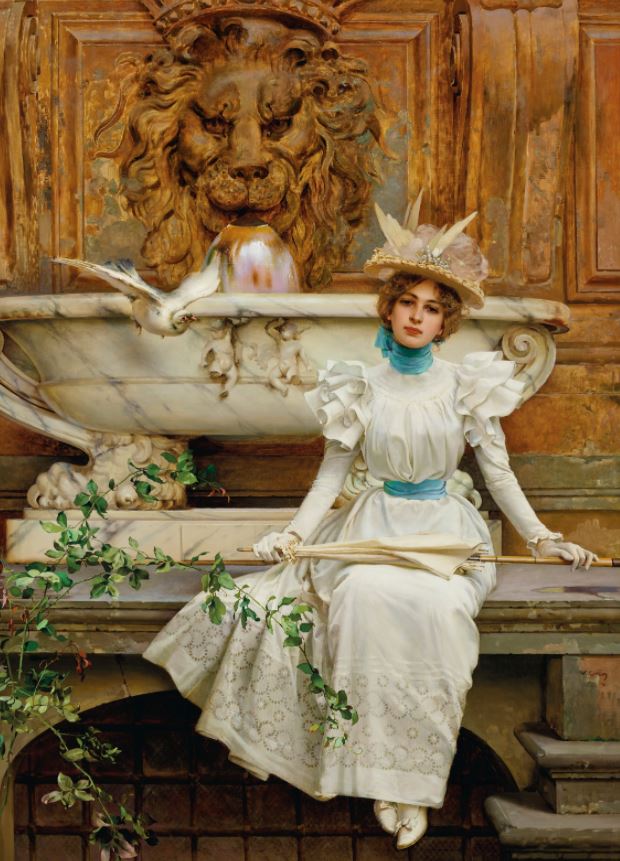








 These two magnificent paintings by Scottish artist David Roberts exquisitely capture the essence of life in Seville in the 1800s. Hear how Roberts, one of the most widely travelled artist explorers of the 19th century, executed these resplendent views of the Cathedral – one capturing the ceremony of the Corpus Christi festival, the other displaying the bustle of life outside. ‘Interior of the Cathedral of Seville’ and ‘The Moorish Tower at Seville’.
These two magnificent paintings by Scottish artist David Roberts exquisitely capture the essence of life in Seville in the 1800s. Hear how Roberts, one of the most widely travelled artist explorers of the 19th century, executed these resplendent views of the Cathedral – one capturing the ceremony of the Corpus Christi festival, the other displaying the bustle of life outside. ‘Interior of the Cathedral of Seville’ and ‘The Moorish Tower at Seville’.