MOTION:
“This House Believes AI Will Bring More Harm Than Good”
This debate was run in association with IBM Research.

Proposition:
Project Debater Project Debater is designed by IBM research. It will deliver a speech based on over 1,100 arguments collected from Union members and others over the past week. It will not be taking points of information.
Sharmila Parmanand
Sharmila Parmanand is a PhD Candidate in Gender Studies at the University of Cambridge and a Gates Scholar. She has served as a debate trainer or chief judge in debating events in 45 countries. She served as a chief judge for most major global debating competitions (World Universities, World Schools, European Universities, Asian Universities, Austral-Asian Universities, North American Universities, and PanAmerican Universities).
Professor Neil Lawrence
Neil Lawrence is the DeepMind Professor of Machine Learning at the University of Cambridge and the co-host of Talking Machines. Neil’s main research interest is machine learning through probabilistic models. He focuses on both the algorithmic side of these models and their application. His recent focus has been on the deployment of machine learning technology in practice, particularly under the banner of data science.
Opposition
Project Debater
Project Debater is designed by IBM research. It will deliver a speech based on over 1,100 arguments collected from Union members and others over the past week. It will not be taking points of information.
Harish Natarajan
Harish Natarajan is a graduate of the University of Oxford and the University of Cambridge. He was a grand fnalist and 2nd best speaker at the 2016 World Debating Championships and won the European Debating Championship in 2012. Harish holds the record for most competition victories. He currently works as the Head of Economic Risk Analysis at AKE International in London.
Professor Sylvie Delacroix
Sylvie Delacroix is professor in Law and Ethics at the University of Birmingham. Her work has notably been funded by the Wellcome Trust, the NHS and the Leverhulme Trust, from whom she received the Leverhulme Prize. She has recently been appointed to the Public Policy Commission on the use of algorithms in the justice system.
Website: https://www.cus.org/



 Who among us hasn’t wished we could read someone else’s mind, know exactly what they’re thinking? Well that’s impossible, of course, since our thoughts are, more than anything else, our own. Private, personal, unreachable. Or at least that’s what we’ve always, well, thought.
Who among us hasn’t wished we could read someone else’s mind, know exactly what they’re thinking? Well that’s impossible, of course, since our thoughts are, more than anything else, our own. Private, personal, unreachable. Or at least that’s what we’ve always, well, thought. 

 It is unclear why people in the 1950s thought this was a practical way to travel; not only it looks like it is impossible to breathe in there, who would want to stand upright while driving? It would definitely ease the traffic; however, probably no one would want to use it.
It is unclear why people in the 1950s thought this was a practical way to travel; not only it looks like it is impossible to breathe in there, who would want to stand upright while driving? It would definitely ease the traffic; however, probably no one would want to use it. Towering transmitters in the city and private-jet traffic in the sky… This is a prediction that was made probably too early and it is definitely not so far from reality. Today, we paint a similar future for smart-cities and sci-fi movies depict the future cities in the same manner. It seems that older generations and we have a similar vision of the future look of the world.
Towering transmitters in the city and private-jet traffic in the sky… This is a prediction that was made probably too early and it is definitely not so far from reality. Today, we paint a similar future for smart-cities and sci-fi movies depict the future cities in the same manner. It seems that older generations and we have a similar vision of the future look of the world.
 Every possible step is done online, and for most meals customers must reserve—and often pay—in advance, essentially buying tickets through a service called Tock that’s mostly used only by high-end restaurants. This means no host manning a podium, no reservation or PR teams, no extra staff on a slow night, almost no food waste, and better guest communications. It also allowed them to go from 20 employees to four full-time and three part-time workers.
Every possible step is done online, and for most meals customers must reserve—and often pay—in advance, essentially buying tickets through a service called Tock that’s mostly used only by high-end restaurants. This means no host manning a podium, no reservation or PR teams, no extra staff on a slow night, almost no food waste, and better guest communications. It also allowed them to go from 20 employees to four full-time and three part-time workers.



 You may have seen the aftermath of a landslide, driving along a twisty mountain road—a scattering of rocks and scree impinging on the pavement. And up until now, that’s pretty much how scientists have tracked landslides—roadside observations and spotty satellite images. Now, researchers are hoping to track landslides systematically by instrumenting an entire
You may have seen the aftermath of a landslide, driving along a twisty mountain road—a scattering of rocks and scree impinging on the pavement. And up until now, that’s pretty much how scientists have tracked landslides—roadside observations and spotty satellite images. Now, researchers are hoping to track landslides systematically by instrumenting an entire 
 “Originally designed as both a road and racing car, little compromise was made for comfort and practicality. With a light body and a peppy 2½ litre Riley engine, the Healey Silverstone performed well; even the headlights were brought inside behind the grille to make it more aerodynamic. It had a very limited run; just 105 produced making correct examples extremely desirable.
“Originally designed as both a road and racing car, little compromise was made for comfort and practicality. With a light body and a peppy 2½ litre Riley engine, the Healey Silverstone performed well; even the headlights were brought inside behind the grille to make it more aerodynamic. It had a very limited run; just 105 produced making correct examples extremely desirable. 

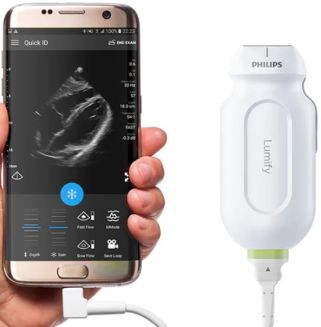 Philips Lumify ultrasound technology is an important component of the mobile ECMO unit. Members of the ECMO team use Lumify for real-time visual guidance when inserting tubes in veins and arteries in a process called ECMO cannulation.
Philips Lumify ultrasound technology is an important component of the mobile ECMO unit. Members of the ECMO team use Lumify for real-time visual guidance when inserting tubes in veins and arteries in a process called ECMO cannulation.
 Wi-Charge says it has a solution to the problem. Its technology allows users to power small devices, such as smartphones, smart fire alarms, and smart locks, from several feet away without any wires.
Wi-Charge says it has a solution to the problem. Its technology allows users to power small devices, such as smartphones, smart fire alarms, and smart locks, from several feet away without any wires.