From a Wall Street Journal Opinion article (Feb 10, 2020):
How to address the elder-care crisis? Ideally, doctors would screen older patients for dementia. An early diagnosis helps patients understand treatment options, plan for the future and receive appropriate care in the hospital.
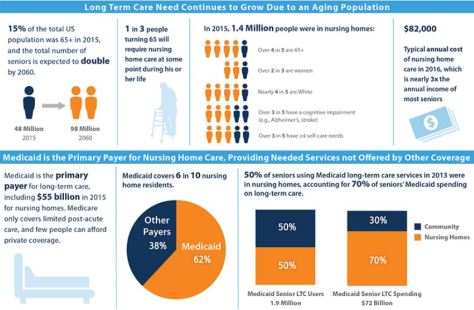
Other steps include: more preventive care, changes to Medicare’s rehabilitation policies, adopting new reimbursement methods, and developing new measures of success. Primary-care offices can prevent hospital visits, but Americans seeking primary care face an average wait time of 24 days. This might not be a problem for a patient in need of an annual physical, but conditions like chest pain or infections require prompt treatment. Primary-care offices that offer same-day sick visits, home visits for bed-bound older adults, or at-home monitoring of conditions could reduce emergency department volumes.



 “Studies with financial links to the indoor tanning industry were much more likely to discuss perceived benefits of indoor tanning and to downplay the harms,” said
“Studies with financial links to the indoor tanning industry were much more likely to discuss perceived benefits of indoor tanning and to downplay the harms,” said  In 2012, Eleni Linos, professor of dermatology at Stanford university, published a systematic review and meta-analysis of the link between non-melanoma cancer and sun-beds. That bit of pretty standard research, and a particular rapid response to it, has kicked of years of work – and in this podcast I talk to Eleni and her colleagues Stanton…
In 2012, Eleni Linos, professor of dermatology at Stanford university, published a systematic review and meta-analysis of the link between non-melanoma cancer and sun-beds. That bit of pretty standard research, and a particular rapid response to it, has kicked of years of work – and in this podcast I talk to Eleni and her colleagues Stanton…


 Intermittent fasting has salutary effects. Listen how Dr. Mark P. Mattson, co-author of a recent NEJM review on the topic, assesses the practice — and how he’s managed to skip breakfast for the past 30 years or so.
Intermittent fasting has salutary effects. Listen how Dr. Mark P. Mattson, co-author of a recent NEJM review on the topic, assesses the practice — and how he’s managed to skip breakfast for the past 30 years or so.

 Last year the Lancet published a paper on the impact of wearing gowns, surveying 928 adult patients and carrying out structured interviews with 10 patients. Over half (58%) reported wearing the gown despite feeling uncertain that it was a medical necessity. Gown design was considered inadequate, with 61% reporting that they struggled to put it on or required assistance and 67% reporting that it didn’t fit. Most worryingly, 72% felt exposed, 60% felt self-conscious, and 57% felt uncomfortable wearing the gown.
Last year the Lancet published a paper on the impact of wearing gowns, surveying 928 adult patients and carrying out structured interviews with 10 patients. Over half (58%) reported wearing the gown despite feeling uncertain that it was a medical necessity. Gown design was considered inadequate, with 61% reporting that they struggled to put it on or required assistance and 67% reporting that it didn’t fit. Most worryingly, 72% felt exposed, 60% felt self-conscious, and 57% felt uncomfortable wearing the gown.
 The hope, Lee says, is that ultrasound will kill cancer cells in a specific way that will also engage the immune system and arouse it to attack any cancer cells remaining after the treatment.
The hope, Lee says, is that ultrasound will kill cancer cells in a specific way that will also engage the immune system and arouse it to attack any cancer cells remaining after the treatment. Ultrasound waves—sound waves with frequencies higher than humans can hear—have been used as a cancer treatment before, albeit in a broad-brush approach: high-intensity bursts of ultrasound can heat up tissue, killing cancer and normal cells in a target area. Now, scientists and engineers are exploring the use of low-intensity pulsed ultrasound (LIPUS) in an effort to create a more selective treatment.
Ultrasound waves—sound waves with frequencies higher than humans can hear—have been used as a cancer treatment before, albeit in a broad-brush approach: high-intensity bursts of ultrasound can heat up tissue, killing cancer and normal cells in a target area. Now, scientists and engineers are exploring the use of low-intensity pulsed ultrasound (LIPUS) in an effort to create a more selective treatment.
 The intake of marine omega-3s has consistently been found to have antiarrhythmic effects. When marine omega-3s are consumed, there is an increase in cellular membrane fluidity, inhibition of L-type calcium channels and a reduction in the chance of arrhythmic events during susceptible times. Prospective data suggest that maintaining an omega-3 index of about 8%, which requires consuming seafood rich in omega-3 up to five times per week or consuming over 3 g of EPA and DHA per day, may provide the greatest protection against arrhythmic events.
The intake of marine omega-3s has consistently been found to have antiarrhythmic effects. When marine omega-3s are consumed, there is an increase in cellular membrane fluidity, inhibition of L-type calcium channels and a reduction in the chance of arrhythmic events during susceptible times. Prospective data suggest that maintaining an omega-3 index of about 8%, which requires consuming seafood rich in omega-3 up to five times per week or consuming over 3 g of EPA and DHA per day, may provide the greatest protection against arrhythmic events.