
W

W

Hospitals across the U.S. are experiencing an influx of COVID-19 patients, but clinicians are reportedly seeing fewer patients going to the emergency room for heart attack or stroke.
Experts worry that patients who need critical care are delaying their treatment over COVID-19 concerns.
To encourage patients to pay close attention to their symptoms and call 9-1-1 immediately if they believe they are having a heart attack or stroke, ACC’s CardioSmart team developed the Coronavirus and Your Heart Infographic.
The infographic urges patients not to ignore symptoms, especially if they have a heart condition, and reassures them that hospitals have safety measures to protect patients from infection with the novel coronavirus.
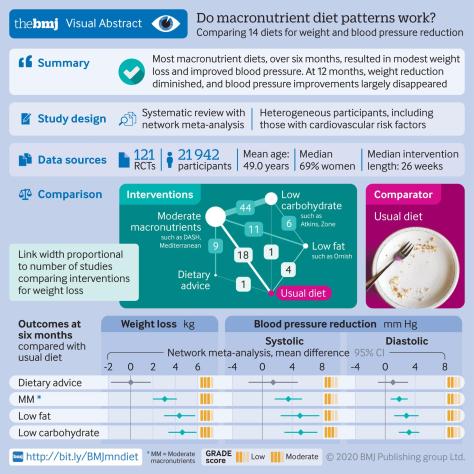
From a BMJ Study article (April, 2020):
Compared with usual diet, moderate certainty evidence supports modest weight loss and substantial reductions in systolic and diastolic blood pressure for low carbohydrate (eg, Atkins, Zone), low fat (eg, Ornish), and moderate macronutrient (eg, DASH, Mediterranean) diets at six but not 12 months. Differences between diets are, however, generally trivial to small, implying that people can choose the diet they prefer from among many of the available diets (fig 6) without concern about the magnitude of benefits.
The worldwide prevalence of obesity nearly tripled between 1975 and 2018.1 In response, authorities have made dietary recommendations for weight management and cardiovascular risk reduction.23 Diet programmes—some focusing on carbohydrate reduction and others on fat reduction—have been promoted widely by the media and have generated intense debates about their relative merit. Millions of people are trying to lose weight by changing their diet. Thus establishing the effect of dietary macronutrient patterns (carbohydrate reduction v fat reduction v moderate macronutrients) and popular named dietary programmes is important.
Biological and physiological mechanisms have been proposed to explain why some dietary macronutrient patterns and popular dietary programmes should be better than others. A previous network meta-analysis, however, suggested that differences in weight loss between dietary patterns and individual popular named dietary programmes are small and unlikely to be important.4 No systematic review and network meta-analysis has examined the comparative effectiveness of popular dietary programmes for reducing risk factors for cardiovascular disease, an area of continuing controversy.
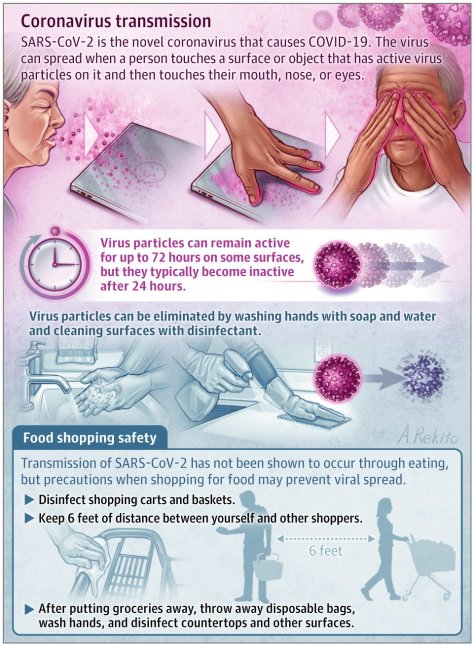
From The New York Times (April 14, 2020):
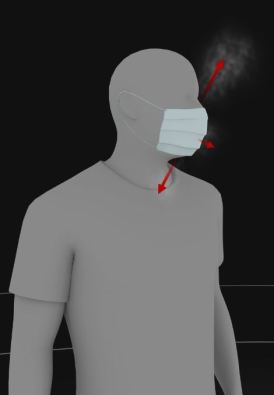
But as this simulation suggests, and scientists have argued, droplets can travel farther than six feet. And small droplets known as aerosols can remain suspended or travel through the air before they eventually settle on surfaces. This is how they could disperse over the next 20 minutes.
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention encourages people to stay home. If you must venture out, you should stay at least six feet away from others. The World Health Organization recommends a minimum of three feet of separation.
Scientists are learning about the novel coronavirus in real time, and those who study similar respiratory illnesses say that until it is better understood, no guideline is likely to offer perfect safety. Instead, understanding the possible transmission routes for the virus can help us see why keeping our distance is so important.

Conclusion: The study was inconclusive with respect to potential differences in progression of individual radiographic features after surgical and non-surgical treatment for degenerative meniscal tear. Further, we found no strong evidence in support of differences in development of incident radiographic knee osteoarthritis or patient-reported outcomes between exercise therapy and arthroscopic partial meniscectomy.
Objective: To evaluate progression of individual radiographic features 5 years following exercise therapy or arthroscopic partial meniscectomy as treatment for degenerative meniscal tear.
Design: Randomized controlled trial including 140 adults, aged 35-60 years, with a magnetic resonance image verified degenerative meniscal tear, and 96% without definite radiographic knee osteoarthritis. Participants were randomized to either 12-weeks of supervised exercise therapy or arthroscopic partial meniscectomy. The primary outcome was between-group difference in progression of tibiofemoral joint space narrowing and marginal osteophytes at 5 years, assessed semi-quantitatively by the OARSI atlas. Secondary outcomes included incidence of radiographic knee osteoarthritis and symptomatic knee osteoarthritis, medial tibiofemoral fixed joint space width (quantitatively assessed), and patient-reported outcome measures. Statistical analyses were performed using a full analysis set. Per protocol and as treated analysis were also performed.
Results: The risk ratios (95% CI) for progression of semi-quantitatively assessed joint space narrowing and medial and lateral osteophytes for the surgery group were 0.89 (0.55-1.44), 1.15 (0.79-1.68) and 0.77 (0.42-1.42), respectively, compared to the exercise therapy group. In secondary outcomes (full-set analysis) no statistically significant between-group differences were found.