
According to a recent study, obesity increases the risk of dying of Covid-19 by nearly 50%. Governments around the world are now hoping to encourage their citizens to lose weight. But with so much complex and often contradictory diet advice, as well as endless food fads, it can be hard to know what healthy eating actually looks like.
How many pieces of fruit and vegetables should you eat a day? Will cutting out carbs help you lose weight? Is breakfast really the most important meal of the day? Speaking to Tim Spector, professor of genetic epidemiology at King’s College London about his new book Spoon-Fed, Madeleine Finlay asks why we’re still getting food science wrong, and explores the current scientific evidence on snacking, supplements and calorie labels.
Tim Spector is a Professor of Genetic Epidemiology and Director of the TwinsUK Registry at Kings College, London and has recently been elected to the prestigious Fellowship of the Academy of Medical Sciences. He trained originally in rheumatology and epidemiology. In 1992 he moved into genetic epidemiology and founded the UK Twins Registry, of 13,000 twins, which is the richest collection of genotypic and phenotypic information worldwide. He is past President of the International Society of Twin Studies, directs the European Twin Registry Consortium (Discotwin) and collaborates with over 120 centres worldwide. He has demonstrated the genetic basis of a wide range of common complex traits, many previously thought to be mainly due to ageing and environment. Through genetic association studies (GWAS), his group have found over 500 novel gene loci in over 50 disease areas. He has published over 800 research articles and is ranked as being in the top 1% of the world’s most cited scientists by Thomson-Reuters. He held a prestigious European Research Council senior investigator award in epigenetics and is a NIHR Senior Investigator. His current work focuses on omics and the microbiome and directs the crowdfunded British Gut microbiome project. Together with an international team of leading scientists including researchers from King’s College London, Massachusetts General Hospital, Tufts University, Stanford University and nutritional science company ZOE he is conducting the largest scientific nutrition research project, showing that individual responses to the same foods are unique, even between identical twins. You can find more on https://joinzoe.com/ He is a prolific writer with several popular science books and a regular blog, focusing on genetics, epigenetics and most recently microbiome and diet (The Diet Myth). He is in demand as a public speaker and features regularly in the media.


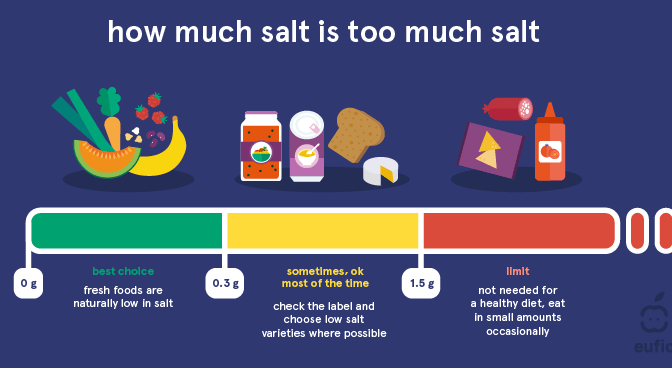



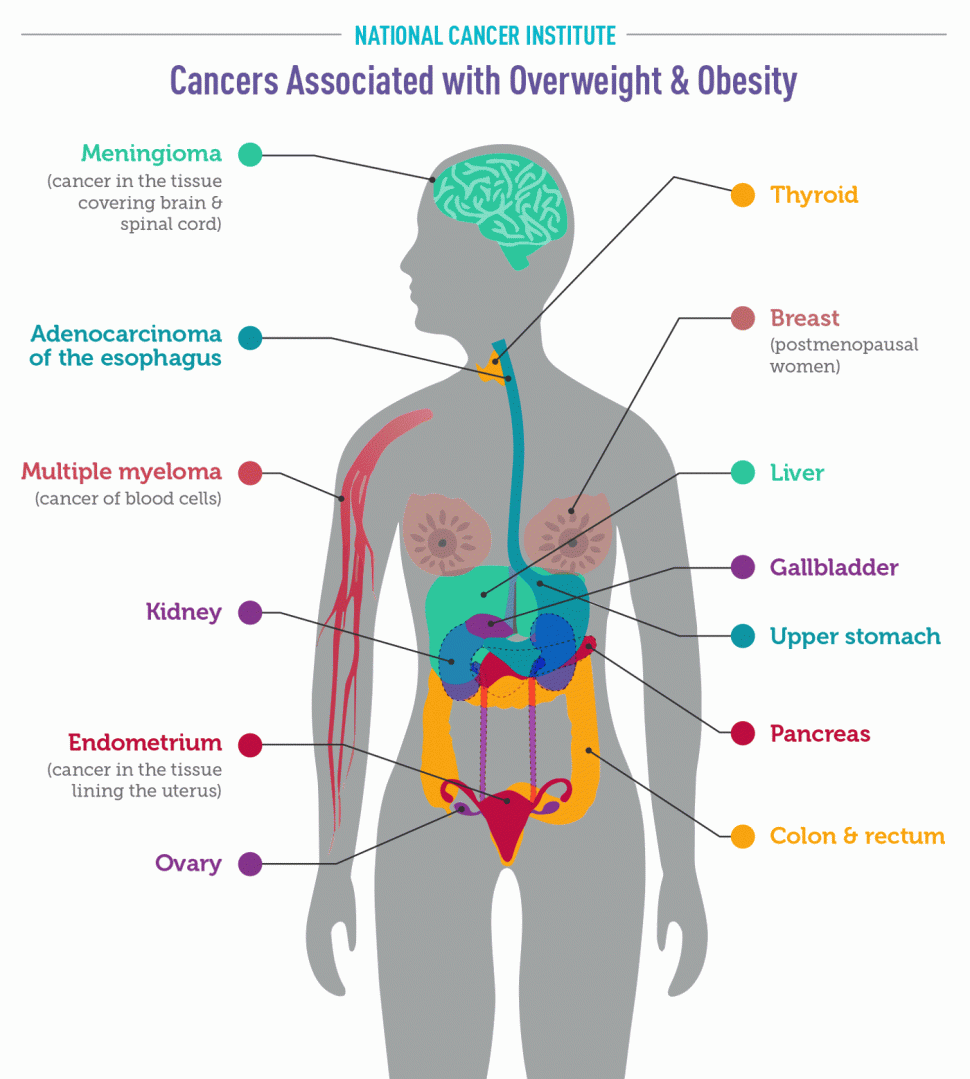


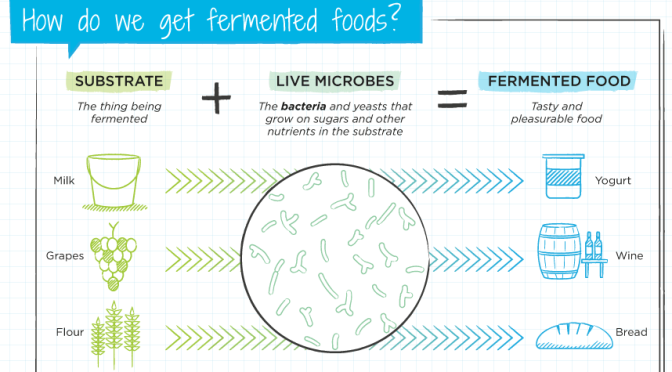




 Spices have been a part of our diets for thousands of years – it’s second nature to sprinkle our chips with pepper, sip on ginger tea and add chillies to our meals. But recently, some spices have been unofficially promoted from everyday culinary staples to all-healing superfoods.
Spices have been a part of our diets for thousands of years – it’s second nature to sprinkle our chips with pepper, sip on ginger tea and add chillies to our meals. But recently, some spices have been unofficially promoted from everyday culinary staples to all-healing superfoods.
 Nathan Pritikin was a college dropout who became an entrepreneur. While doing research for the government during World War II, he observed that populations that had extremely limited food availability because of the war had substantially reduced mortality from cardiovascular disease—something unexpected at a time when cardiovascular disease was thought to be due to stress.
Nathan Pritikin was a college dropout who became an entrepreneur. While doing research for the government during World War II, he observed that populations that had extremely limited food availability because of the war had substantially reduced mortality from cardiovascular disease—something unexpected at a time when cardiovascular disease was thought to be due to stress.