
From the Brain Plasticity Journal (Dec 26, 2019):
 In conclusion, increased CRF (cardiorespiratory fitness) following this six-month intervention was associated with enhanced brain glucose metabolism in the PCC (posterior cingulate cortex), a region linked to AD, and cognition among late-middle-aged individuals at risk for AD. If these findings are supported by a larger-scale study, this would provide strong evidence that adults at risk for AD may enhance brain function and cognition by engaging in aerobic exercise training.
In conclusion, increased CRF (cardiorespiratory fitness) following this six-month intervention was associated with enhanced brain glucose metabolism in the PCC (posterior cingulate cortex), a region linked to AD, and cognition among late-middle-aged individuals at risk for AD. If these findings are supported by a larger-scale study, this would provide strong evidence that adults at risk for AD may enhance brain function and cognition by engaging in aerobic exercise training.
PCC glucose metabolism correlated positively with change in VO2peak (the highest value of VO2 attained upon an incremental or other high-intensity exercise test, designed to bring the sub- ject to the limit of tolerance)…Improvement in executive function correlated with increased VO2peak. Favorable CRF adaptation after 26 weeks of aerobic exercise training was associated with improvements in PCC glucose metabolism and executive function, important markers of AD.
Aerobic exercise has been associated with reduced burden of brain and cognitive changes related to Alzheimer’s disease (AD). However, it is unknown whether exercise training in asymptomatic individuals harboring risk for AD improves outcomes associated with AD. We investigated the effect of 26 weeks of supervised aerobic treadmill exercise training on brain glucose metabolism and cognition among 23 late-middle-aged adults from a cohort enriched with familial and genetic risk of AD.
 Challenging widely held assumptions about the diminishing abilities of an ageing brain, leading neuroscientist Daniel Levitin argues that we should view getting older as a beneficial experience rather than a form of cognitive entropy. Persuasively argued and consistently surprising, The Changing Mind will alter your perception of the relationship between age and intellect.
Challenging widely held assumptions about the diminishing abilities of an ageing brain, leading neuroscientist Daniel Levitin argues that we should view getting older as a beneficial experience rather than a form of cognitive entropy. Persuasively argued and consistently surprising, The Changing Mind will alter your perception of the relationship between age and intellect.
We have long been encouraged to think of old age as synonymous with deterioration. Yet, recent studies show that our decision-making skills improve as we age and our happiness levels peak in our eighties. What really happens to our brains as we get older?
More of us are living into our eighties than ever before. In The Changing Mind, neuroscientist, psychologist and internationally-bestselling author Daniel Levitin invites us to dramatically shift our understanding of growing older, demonstrating its many cognitive benefits. He draws on cutting-edge research to challenge common and flawed beliefs, including assumptions around memory loss and the focus on lifespan instead of ‘healthspan’.
Levitin reveals the evolving power of the human brain from infancy to late adulthood. Distilling the findings from over 4000 papers, he explains the importance of personality traits, lifestyle, memory and community on ageing, offering actionable tips that we can all start now, at any age.
Featuring compelling insights from individuals who have thrived far beyond the conventional age of retirement, this book offers realistic guidelines and practical cognition-enhancing tricks for everyone to follow during every decade of their life. This is a radical exploration of what we all can learn from those who age joyously.
From a JAMA Network Open online release (Jan 31, 2020):
 Steep incidence increases between 49 and 50 years of age are consistent with previously undetected colorectal cancers diagnosed via screening uptake at 50 years. These cancers are not reflected in observed rates of colorectal cancer in the SEER registries among individuals younger than 50 years. Hence, using observed incidence rates from 45 to 49 years of age alone to assess potential outcomes of earlier screening may underestimate cancer prevention benefits.
Steep incidence increases between 49 and 50 years of age are consistent with previously undetected colorectal cancers diagnosed via screening uptake at 50 years. These cancers are not reflected in observed rates of colorectal cancer in the SEER registries among individuals younger than 50 years. Hence, using observed incidence rates from 45 to 49 years of age alone to assess potential outcomes of earlier screening may underestimate cancer prevention benefits.
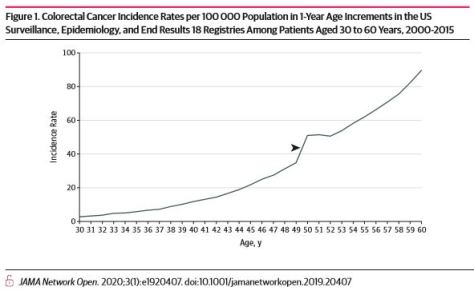
Early-onset colorectal cancer (EOCRC) incidence rates are increasing, and controversy exists regarding whether average-risk screening should begin at 45 or 50 years of age.1 In 2018, the American Cancer Society recommended that average-risk screening start at 45 years of age.2 Others recommend screening at 50 years of age, although the US Multi-Society Task Force on Colorectal Cancer recommends screening African American individuals at age 45 years of age owing to higher incidence, mortality, and earlier-onset disease.3–6 The American Cancer Society decision incorporated modeling studies that used updated incidence and mortality data encompassing time periods of increasing EOCRC incidence rates; modeling compared life-years gained by initiating screening at 45 vs 50 years.
From a Rush University Medical Center online article:
The study found that participants in the group with the highest flavonol consumption were 48% less likely to develop Alzheimer’s dementia later on in life than participants with the lowest level. Of the 186 people in the highest group, 28 people, or 15%, developed Alzheimer’s dementia, compared to 54 people, or 30%, of the 182 people in the lowest group.
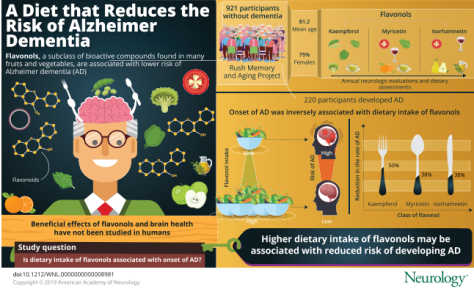
People who eat or drink more foods with flavonol, which is found in nearly all fruits and vegetables, plus tea and wine, may be less likely to develop Alzheimer’s dementia, according to the Rush researchers. They published the results of their study in the Jan. 29 online issue of Neurology.
Flavonols are a type of flavonoid, a group of phytochemicals found in plant pigments. They are known for their beneficial effects on health due to their antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties.
A total of 921 people with an average age of 81 participated in the Neurology study. These participants did not have Alzheimer’s dementia when starting the study.
Digital tools including mobile apps, wearable sensors, and social network platforms offer unprecedented opportunities in health research and healthcare. However, this rapidly emerging sector is outpacing existing regulatory structures and challenging norms for ethical practice.
Camille Nebeker, EdD, MS, Associate Professor of Behavioral Medicine in the Department of Family Medicine & Public Health at the UC San Diego School of Medicine describes how technologies, including wearable sensors and artificial intelligence, are leveraged to capture personal health data and infer health status. Nebeker presents the ethical considerations specific to informed consent, risks of harm and potential benefits while underscoring the role that funding agencies, policy makers, researchers, ethicists, and editors have in creating the infrastructure needed to advance safe digital health research and practice.
Excerpts from a NextAvenue.org online article interview:

“I don’t like the word ‘evolve,’” he says. “Art means the same thing today as it always has. Styles change, but art doesn’t.”
Hesitant to put too defining a label on his work, Wrayge claims his paintings have “a landscape feel.” He doesn’t consider them to be abstract. “That’s a word invented by the press, not by painters,” he says. “What I prefer to say [about my paintings] is that they are a visual manifestation of my values.”
 In James Wrayge’s quiet studio on an early winter afternoon, there is a tangible sense of purpose. Wrayge’s paintings line the walls along the portion of the space he shares with another artist at the Northrup King Building in Minneapolis. There are also some paintings on the floor propped up against the same walls. And there is one — in progress — set on an easel in the corner.
In James Wrayge’s quiet studio on an early winter afternoon, there is a tangible sense of purpose. Wrayge’s paintings line the walls along the portion of the space he shares with another artist at the Northrup King Building in Minneapolis. There are also some paintings on the floor propped up against the same walls. And there is one — in progress — set on an easel in the corner.

From a LitHub online article by Chip Walter, 69:
 And what if older neurons were replaced wholesale with new stem cells? They might scramble different sectors of the brain by destroying the new connections between the originals. Fiddle with those, and who knew what mayhem might follow? Memories, learning, and other cerebral functions that the brain had grown accustomed to might simply vanish. On the other hand, in the case of a disease like Alzheimer’s, maybe new memories would be better than no memories at all.
And what if older neurons were replaced wholesale with new stem cells? They might scramble different sectors of the brain by destroying the new connections between the originals. Fiddle with those, and who knew what mayhem might follow? Memories, learning, and other cerebral functions that the brain had grown accustomed to might simply vanish. On the other hand, in the case of a disease like Alzheimer’s, maybe new memories would be better than no memories at all.
Robert Hariri’s views on human health began to take an unusual turn a little more than 25 years ago, when he was working as a neurosurgeon and trauma doctor at the New York Hospital-Cornell Medical Center. Day after day, he watched patients come into the emergency room with severe brain injuries, and it was a painful thing to witness.
He never forgot the case of a woman who had arrived after a senseless automobile accident. She was young, and the injury was bad. Every time he spoke with the family, the big questions they asked were: “How will she be? Will she come back? Could she be a mother to her children again?” It broke his heart.
William J. (Chip) Walter Jr. (born May 23, 1951) is an author, journalist, National Geographic Fellow, educator, filmmaker and former CNN bureau chief. He has written five mainstream science books between 1991 and 2019. Walter was one of the original employees at Cable News Network when it went on the air June 1, 1980 and later became its youngest bureau chief when he created CNN’s first Southeast Bureau in 1981 before heading up the network’s San Francisco Bureau in 1982. He has written and produced several PBS science documentaries, served as an adjunct professor at Carnegie Mellon University in three different departments, worked with UNICEF on the issue of childhood trauma, spoken at Harvard, Xerox PARC, Carnegie Mellon University and the Chautauqua Institution. One of his three original screenplays was produced and released under the title Sunset Grill in 1993 starring Peter Weller, Lori Singer and Stacy Keach. In 2015 his feature story for National Geographic Magazine explored the origins of human art and symbolic thinking.
From Wikipedia
Did you know the food choices you make every day could help you feel younger? Try these 8 diet tips for feeling your best at any age.
Get more healthy living tips from the Mayo Clinic App: http://mayocl.in/2tbMb57
Huey Lewis and the News are in the mood to celebrate, joking about their age as they prepare for the release of what is almost certainly their last album, titled “Weather.” At 69, Lewis, who has performed in bands for most of his life, had no intention of slowing down, but his diagnosis of Meniere’s Disease – a hearing disorder which has affected his voice – has made the decision for him. John Blackstone reports.