As one of the leading figures in the field of international relations, Joseph S. Nye, Jr., Harvard University Distinguished Service Professor Emeritus, has had a major influence on the way that policymakers think American foreign policy.
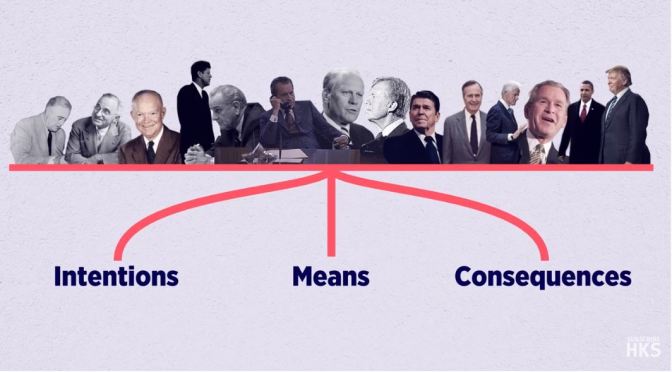
In his new book, “Do Morals Matter: Presidents and Foreign Policy from FDR to Trump,” Professor Nye explores the question of how heavily moral questions weigh on the decisions of U.S. presidents since the end of World War II. On this episode of Behind The Book, produced by Library and Knowledge Services at Harvard Kennedy School, we take a look at Professor Nye’s new book and how he assesses the legacy of past presidents based on the morality of their foreign policy.
“Do Morals Matter: Presidents and Foreign Policy from FDR to Trump” is published by Oxford University Press.
Joseph S. Nye Jr., is the University Distinguished Service Professor, Emeritus and former Dean of the Harvard’s Kennedy School of Government. He has served as Assistant Secretary of Defense for International Security Affairs, Chair of the National Intelligence Council, and Deputy Under Secretary of State for Security Assistance, Science and Technology.
His most recent books include The Power to Lead; The Future of Power; Presidential Leadership and the Creation of the American Era; and Is the American Century Over. He is a fellow of the American Academy of Arts and Sciences, the British Academy, and the American Academy of Diplomacy.
In a recent survey of international relations scholars, he was ranked as the most influential scholar on American foreign policy, and in 2011, Foreign Policy named him one of the top 100 Global Thinkers.




 Our findings suggest that promotion of a healthy lifestyle would help to reduce the healthcare burdens through lowering the risk of developing multiple chronic diseases, including cancer, cardiovascular disease, and diabetes, and extending disease-free life expectancy. Public policies for improving food and the physical environment conducive to adopting a healthy diet and lifestyle, as well as relevant policies and regulations (for example, smoking ban in public places or trans-fat restrictions), are critical to improving life expectancy, especially life expectancy free of major chronic diseases.
Our findings suggest that promotion of a healthy lifestyle would help to reduce the healthcare burdens through lowering the risk of developing multiple chronic diseases, including cancer, cardiovascular disease, and diabetes, and extending disease-free life expectancy. Public policies for improving food and the physical environment conducive to adopting a healthy diet and lifestyle, as well as relevant policies and regulations (for example, smoking ban in public places or trans-fat restrictions), are critical to improving life expectancy, especially life expectancy free of major chronic diseases.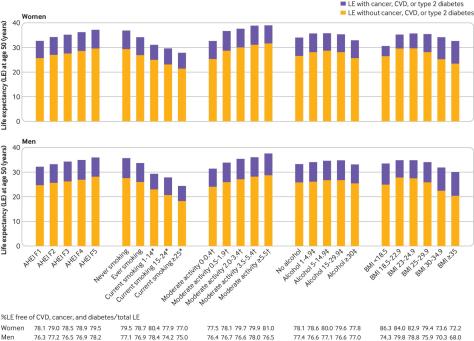



 Rock ’n’ roll, or even popular music, [was] often highly gendered and sexist. It certainly was paternalistic in the ’60s and prior, in terms of songs being directed at women as objects, women as needing to be “counseled” about love, [or] it was about coming on to them, even if it was just something innocent and romantic, “I Want to Hold Your Hand.” And the Beatles very consciously in 1965 began to change their tone. They created a very specific type of female character who would think for herself and did not need a man.
Rock ’n’ roll, or even popular music, [was] often highly gendered and sexist. It certainly was paternalistic in the ’60s and prior, in terms of songs being directed at women as objects, women as needing to be “counseled” about love, [or] it was about coming on to them, even if it was just something innocent and romantic, “I Want to Hold Your Hand.” And the Beatles very consciously in 1965 began to change their tone. They created a very specific type of female character who would think for herself and did not need a man.  Looking back at your favorite classic rock songs through the lens of today’s attitudes about women’s empowerment, male privilege, and even sexual violence can be cringeworthy at best. But just as they were trailblazers in music, film, fashion, and popular culture, the Beatles were ahead of their time in embracing feminism, argues Kenneth Womack, a well-known authority on the band and dean at Monmouth University, evolving from early patronizing “hey, girl” entreaties to songs filled with independent women who don’t need a man, not even a Beatle. Ideological Diversity, a Harvard Kennedy School student organization, hosts a free talk with Womack on Thursday about how the group explored issues of feminism, gender, and inclusion in ways few rock bands dared in the 1960s.
Looking back at your favorite classic rock songs through the lens of today’s attitudes about women’s empowerment, male privilege, and even sexual violence can be cringeworthy at best. But just as they were trailblazers in music, film, fashion, and popular culture, the Beatles were ahead of their time in embracing feminism, argues Kenneth Womack, a well-known authority on the band and dean at Monmouth University, evolving from early patronizing “hey, girl” entreaties to songs filled with independent women who don’t need a man, not even a Beatle. Ideological Diversity, a Harvard Kennedy School student organization, hosts a free talk with Womack on Thursday about how the group explored issues of feminism, gender, and inclusion in ways few rock bands dared in the 1960s.

 …a new study from the
…a new study from the  “A reduction in body weight of 12 percent is like getting a human from 200 pounds down to 176, which is a significant change,” said first author Md Nurunnabi, a former Postdoctoral Fellow at the Wyss Institute and SEAS who is now an Assistant Professor of Pharmaceutical Sciences at The University of Texas at El Paso. “Our goal is to translate this work into a product that can help people maintain a healthier weight, and this study marks the very beginning of that journey.”
“A reduction in body weight of 12 percent is like getting a human from 200 pounds down to 176, which is a significant change,” said first author Md Nurunnabi, a former Postdoctoral Fellow at the Wyss Institute and SEAS who is now an Assistant Professor of Pharmaceutical Sciences at The University of Texas at El Paso. “Our goal is to translate this work into a product that can help people maintain a healthier weight, and this study marks the very beginning of that journey.”