In this episode of the podcast, Nature reporter Davide Castelvecchi joins us to talk about the big science events to look out for in 2020. We’ll hear about multiple missions to Mars, a prototype electric car, efforts to prevent dengue, and more.
In this episode of the podcast, Nature reporter Davide Castelvecchi joins us to talk about the big science events to look out for in 2020. We’ll hear about multiple missions to Mars, a prototype electric car, efforts to prevent dengue, and more.
Category Archives: Science
Future Of Food: Scientist Mark Post Talks About Lab-Grown Meat (Podcast)
 Interview of Professor Mark Post by Monocle 24 “The Bulletin with UBS” podcast aired January 6, 2020.
Interview of Professor Mark Post by Monocle 24 “The Bulletin with UBS” podcast aired January 6, 2020.
Marcus Johannes “Mark” Post (born 20 July 1957) is a Dutch pharmacologist who is Professor of Vascular Physiology at Maastricht University and (until 2010) Professor of Angiogenesis in Tissue Engineering at the Eindhoven University of Technology. On 5 August 2013, he was the first in the world to present a proof of concept for cultured meat.
NASA: “James Webb Space Telescope” Mission (Video)
A look at the James Webb Space Telescope, it’s mission and the incredible technological challenge this mission presents.
Music credit: Universal Production
Music tracks: Future Generation Alternative Version by Dury; Moment of Anticipation Instrumental by Connolly; Dark Matter Instrumental by Beits
Credit: NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center
Michael McClare (KBRwyle): Lead Producer
Michael McClare (KBRwyle): Lead Writer
Adriana Manrique Gutierrez (USRA): Animator
Jonathan North (USRA): Animator
Walt Feimer (KBRwyle): Animator
Michael Lentz (USRA): Animator
Bailee DesRocher (USRA): Animator
Michael McClare (KBRwyle): Lead Editor
Michael McClare (KBRwyle): Lead Videographer
This video is public domain and along with other supporting visualizations can be downloaded from the Scientific Visualization Studio
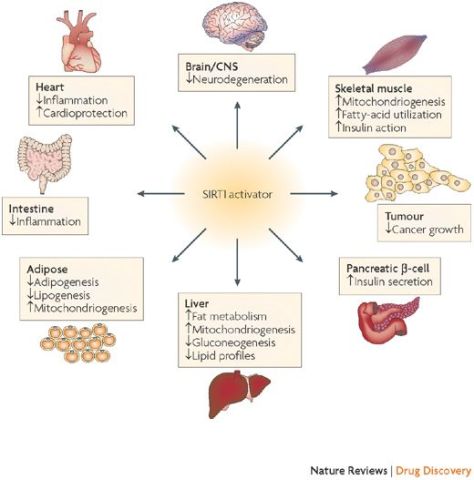
Fasting Activates Sirtuin Signaling Proteins (SIRT1), Accelerating Cell Repair
-
Sirtuins are a family of signaling proteins involved in metabolic regulation. SIRT1 (along with SIRT6 and SIRT7) are proteins are employed in DNA repair.
From Wikipedia:
Sirtuins are a class of proteins that possess either mono-ADP-ribosyltransferase, or deacylase activity, including deacetylase, desuccinylase, demalonylase, demyristoylase and depalmitoylase activity. The name Sir2 comes from the yeast gene ‘silent mating-type information regulation 2‘, the gene responsible for cellular regulation in yeast.
From in vitro studies, sirtuins are implicated in influencing cellular processes like aging, transcription, apoptosis, inflammation and stress resistance, as well as energy efficiency and alertness during low-calorie situations. As of 2018, there was no clinical evidence that sirtuins affect human aging.
Aging
Although preliminary studies with resveratrol, an activator of deacetylases such as SIRT1, led some scientists to speculate that resveratrol may extend lifespan, there was no clinical evidence for such an effect, as of 2018.
In vitro studies shown that calorie restriction regulates the plasma membrane redox system, involved in mitochondrial homeostasis, and the reduction of inflammation through cross-talks between SIRT1 and AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK), but the role of sirtuins in longevity is still unclear, as calorie restriction in yeast could extend lifespan in the absence of Sir2 or other sirtuins, while the in vivo activation of Sir2 by calorie restriction or resveratrol to extend lifespan has been challenged in multiple organisms.
Medicine: “Is It An Art Or Science?” (The Lancet)
From a The Lancet online article:
Effective physicians interrogate their patients’ choice of words as well as their body language; they attend to what they leave out of their stories as well as what they put in. More than 2000 years after Hippocrates, there remains as much poetry in medicine as there is science.
 WHO’s definition of health is famously “a state of complete physical, mental, and social well-being and not merely the absence of disease or infirmity”. One of the oldest medical texts we know of, The Science of Medicine attributed to Hippocrates, sets out the goal of medicine in comparable terms: “the complete removal of the distress of the sick”.
WHO’s definition of health is famously “a state of complete physical, mental, and social well-being and not merely the absence of disease or infirmity”. One of the oldest medical texts we know of, The Science of Medicine attributed to Hippocrates, sets out the goal of medicine in comparable terms: “the complete removal of the distress of the sick”.
In my working life as a physician, I’ve never found the distinction between arts and sciences a particularly useful one. In the earliest ancient Greek texts, medicine is described as a techne—a word better translated as “know-how”. It conveys elements of science, art, and skill, but also of artisanal craft. The precise functions of medicine may have subtly shifted over the ages, but our need as human beings for doctors remains the same; we go to them because we wish to invoke some change in our lives, either to cure or prevent an illness or influence some unwelcome mental or bodily process. The goal of medicine is, and always has been, the relief of human suffering—the word patient, from the Latin patientem, means sufferer. And the word physician is from the Greek phusis, or nature: to be engaged in clinical work is to engage oneself with the nature of illness, the nature of recovery, the nature of humanity.
Top New Science Podcasts: Latest Trends In Research, Carnivorous Plant Traps
 We start our first episode of the new year looking at future trends in policy and research with host Joel Goldberg and several Science News writers. Jeffrey Mervis discusses upcoming policy changes, Kelly Servick gives a rundown of areas to watch in the life sciences, and Ann Gibbons talks about potential advances in ancient proteins and DNA.
We start our first episode of the new year looking at future trends in policy and research with host Joel Goldberg and several Science News writers. Jeffrey Mervis discusses upcoming policy changes, Kelly Servick gives a rundown of areas to watch in the life sciences, and Ann Gibbons talks about potential advances in ancient proteins and DNA.
In research news, host Meagan Cantwell talks with Beatriz Pinto-Goncalves, a postdoctoral researcher at the John Innes Centre, about carnivorous plant traps. Through understanding the mechanisms that create these traps, Pinto-Goncalves and colleagues elucidate what this could mean for how they emerged in the evolutionary history of plants.
Healthy Diets: “The Science Behind Fasting – Ketosis” (Infographic)
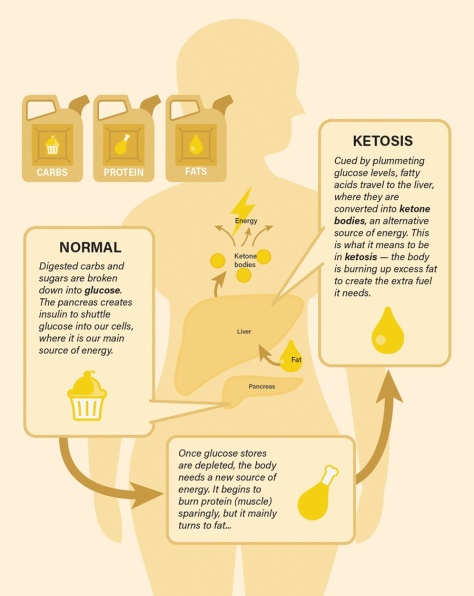
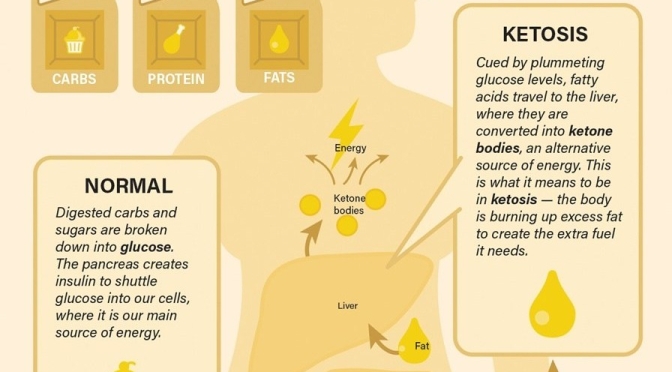
…It seems fasting triggers a dramatic switch in the body’s metabolism, according  to a paper Mattson and colleagues published in February in the experimental biology journal FASEB. In humans, fasting for 12 hours or more drops the levels of glycogen, a form of cellular glucose. Like changing to a backup gas tank, the body switches from glucose to fatty acids, a more efficient fuel. The switch generates the production of ketones, which are energy molecules that are made in the liver. “When the fats are mobilized and used to produce ketones, we think that is a key factor in accruing the health benefits,” says Mattson.
to a paper Mattson and colleagues published in February in the experimental biology journal FASEB. In humans, fasting for 12 hours or more drops the levels of glycogen, a form of cellular glucose. Like changing to a backup gas tank, the body switches from glucose to fatty acids, a more efficient fuel. The switch generates the production of ketones, which are energy molecules that are made in the liver. “When the fats are mobilized and used to produce ketones, we think that is a key factor in accruing the health benefits,” says Mattson.
Top Science Podcasts: Soles And Calluses, Far Side Of The Moon & Nobel Prize Winner Q&A (Nature)
 The podcast team share some of their highlights from the past 12 months: A sole sensation, The make up of the far side of the Moon, Growth Mindset, ‘Manferences’ and Q&A with Nobel Prize winner John Goodenough.
The podcast team share some of their highlights from the past 12 months: A sole sensation, The make up of the far side of the Moon, Growth Mindset, ‘Manferences’ and Q&A with Nobel Prize winner John Goodenough.
In this episode:
00:33 A sole sensation
A study of people who do and don’t wear shoes looks into whether calluses make feet less sensitive. Nature Podcast: 26 June 2019; Research article: Holowka et al.; News and Views: Your sensitive sole
08:56 The make up of the far side of the Moon
Initial observations from the first lander to touch down on the far side of the Moon. Nature Podcast: 15 May 2019; Research article: Li et al.
15:43 Growth Mindset
How a one hour course could improve academic achievement. Nature Podcast: 07 August 2019; Research article: Yeager et al.
27:44 ‘Manferences’
Nature investigates the prevalence of conferences where most of the speakers are male. Nature Podcast: 11 September 2019; News Feature: How to banish manels and manferences from scientific meetings
34:02 Q&A with Nobel Prize winner John Goodenough
We talk to John Goodenough, who was jointly awarded the 2019 Nobel Prize in Chemistry for his role in the development of the lithium-ion battery. Podcast Extra: 09 October 2019
Podcasts: Poet Jane Hirshfield & Other Writers Discuss “Memory And Forgetting” (UCSF)
Memory sits at the core of both literature and lives. Yet forgetting is also a part of our brains’ daily working, bringing its own human truths and a necessary path for moving forward. Lewis Hyde’s new _A Primer for Forgetting: Getting Past the Past_, provides inspiration for a deep-dive discussion of memory’s other side, with this august panel of writers and neuroscientists: poets Jane Hirshfield and Margaret Gibson, author Lewis Hyde, and UCSF neuroscientists Aimee Kao, Bruce Miller, and Virginia Sturm.
Co-hosted by Litquake, San Francisco’s Literary Festival
Jane Hirshfield’s ninth poetry collection, Ledger (Knopf), appears in 2020. Chancellor emerita of the Academy of American Poets and recently elected into the American Academy of Arts & Sciences, she works frequently at the intersection of poetry and science. Her work appears in The New Yorker, Atlantic, Poetry, et al.
Listen to Poet and Professor Margaret Gibson below:
Margaret Gibson, current Connecticut Poet Laureate, is the author of 12 books of poetry, including Not Hearing the Wood Thrush (2018) and Broken Cup (2014), centered on memory loss from Alzheimer’s disease and the gifts of sustaining presence through lament, acceptance, and love. She is Professor Emerita at the University of Connecticut.
Listen to author Lewis Hyde below:
Lewis Hyde’s recent book, A Primer for Forgetting (FSG, 2019), explores the many situations in which forgetfulness is more useful than memory—in myth, personal psychology, politics, art and spiritual life. A MacArthur Fellow, Hyde taught for many years at Kenyon College.
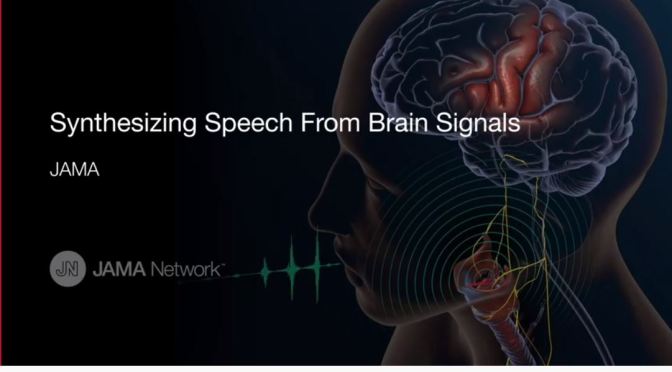
Medical Research Video: “Synthesizing Speech From Brain Signals” (JAMA)
Imagine you’re paralyzed and can’t move or speak. How would you communicate with the world? This video describes the principles of early brain-computer interfaces (BCIs) designed to read electrical brain signals, analyze how brain activity patterns contribute to vocal tract movements, and reproduce the sound patterns as speech. The model is a first step toward one day restoring paralyzed individuals’ natural rate of communication and quality of life.
For more information see https://ja.ma/37dfVSx and https://www.nature.com/articles/s4158….