From a March 5, 2020 American Academy of Neurology release:
 “These results are exciting, as they suggest that people may potentially prevent brain shrinking and the effects of aging on the brain simply by becoming more active,” said study author Yian Gu, Ph.D., of Columbia University in New York and a member of the American Academy of Neurology.
“These results are exciting, as they suggest that people may potentially prevent brain shrinking and the effects of aging on the brain simply by becoming more active,” said study author Yian Gu, Ph.D., of Columbia University in New York and a member of the American Academy of Neurology.
“Recent studies have shown that as people age, physical activity may reduce the risk of cognitive decline and dementia. Our study used brain scans to measure the brain volumes of a diverse group of people and found that those who engaged in the top third highest level of physical activity had a brain volume the equivalent of four years younger in brain aging than people who were at the bottom third activity level.”
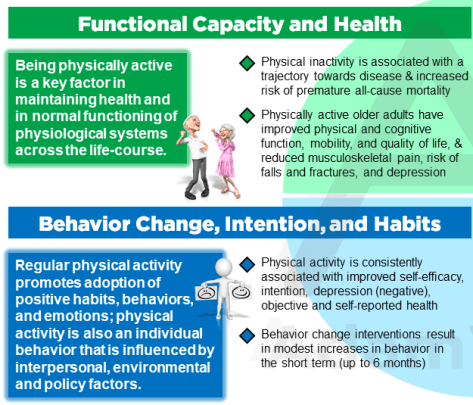
Older people who regularly walk, garden, swim or dance may have bigger brains than their inactive peers, according to a preliminary study to be presented at the American Academy of Neurology’s 72nd Annual Meeting in Toronto, Canada, April 25 to May 1, 2020. The effect of exercise was equal to four fewer years of brain aging. The study used magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) scans to measure the brains of people with a range of activity levels, including those who were inactive to those who were very active. The scans showed less active people had smaller brain volume.




 Across the 6 studies of 8699 participants, mean age ranged between 70 and 74 years and mean gait speed ranged between 1.05 and 1.26 m/s. Incident dementia ranged from 5 to 21 per 1000 person-years. Compared with usual agers, participants with only memory decline had 2.2 to 4.6 times higher risk for developing dementia…
Across the 6 studies of 8699 participants, mean age ranged between 70 and 74 years and mean gait speed ranged between 1.05 and 1.26 m/s. Incident dementia ranged from 5 to 21 per 1000 person-years. Compared with usual agers, participants with only memory decline had 2.2 to 4.6 times higher risk for developing dementia… 
 We observed that increased adherence to the MedDiet modulates specific components of the gut microbiota that were associated with a reduction in risk of frailty, improved cognitive function and reduced inflammatory status.
We observed that increased adherence to the MedDiet modulates specific components of the gut microbiota that were associated with a reduction in risk of frailty, improved cognitive function and reduced inflammatory status.



 o finds himself wondering if growing old in Paris might be the perfect antidote to the drama he left behind in New York. Unflinching, witty, and urbane as ever, Louis Begley delivers a spot-on satire of the world of New York’s aging elite, and uncovers the unexpected delights a late-in-life change can offer.
o finds himself wondering if growing old in Paris might be the perfect antidote to the drama he left behind in New York. Unflinching, witty, and urbane as ever, Louis Begley delivers a spot-on satire of the world of New York’s aging elite, and uncovers the unexpected delights a late-in-life change can offer.
 More schools are building or planning senior-living facilities on or near campus to cater to baby boomers who view college as a stimulating alternative to bingo at an archetypal retirement home. Some savor the pursuit of academic and cultural interests. Others are lured by the promise of interaction with younger students, for whom many hope to act as mentors.
More schools are building or planning senior-living facilities on or near campus to cater to baby boomers who view college as a stimulating alternative to bingo at an archetypal retirement home. Some savor the pursuit of academic and cultural interests. Others are lured by the promise of interaction with younger students, for whom many hope to act as mentors.
 The Social Security Administration (SSA) scam is the
The Social Security Administration (SSA) scam is the 
 “Our data indicate that there are no low-risk procedures among patients who are frail,” Dr. Hall and his co-authors concluded in their study.
“Our data indicate that there are no low-risk procedures among patients who are frail,” Dr. Hall and his co-authors concluded in their study.