From a New York Times online article (Feb 27, 2020):

Mr. Hood, a former Marine and Drug Enforcement Administration agent, held the plank on Feb. 15 for more time than an average day’s work.
The plank is a feat of static, but strenuous, exercise. The torso is sustained in a horizontal position, anchored by the toes on one end and the forearms on the other. The abdominal and thigh, back and arm muscles are among those firing away, turning most of the human body into a gravity-defying platform.
George E. Hood, a 62-year-old retiree from Naperville, Ill., strapped a heart monitor band across his chest, attached a catheter to his body, climbed onto a custom-built table covered with a lambskin and dialed up a curated rock ’n’ roll playlist on his phone.
And then he raised himself into a plank — and held the position for eight hours, 15 minutes and 15 seconds to set a Guinness World Record.









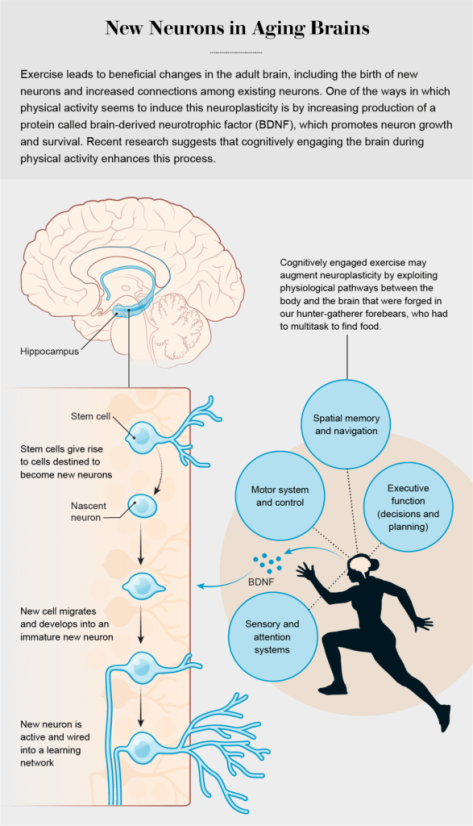
 In conclusion, increased CRF (cardiorespiratory fitness) following this six-month intervention was associated with enhanced brain glucose metabolism in the PCC (posterior cingulate cortex), a region linked to AD, and cognition among late-middle-aged individuals at risk for AD. If these findings are supported by a larger-scale study, this would provide strong evidence that adults at risk for AD may enhance brain function and cognition by engaging in aerobic exercise training.
In conclusion, increased CRF (cardiorespiratory fitness) following this six-month intervention was associated with enhanced brain glucose metabolism in the PCC (posterior cingulate cortex), a region linked to AD, and cognition among late-middle-aged individuals at risk for AD. If these findings are supported by a larger-scale study, this would provide strong evidence that adults at risk for AD may enhance brain function and cognition by engaging in aerobic exercise training.
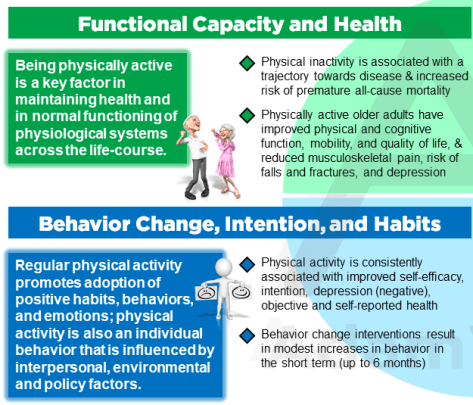
 The 10 year CVD (cardiovascular disease) incidence increased significantly across the baseline SMI (skeletal muscle mass index) tertiles (p<0.001). Baseline SMM (Skeletal muscle mass) showed a significant inverse association with the 10 year CVD incidence (HR 0.06, 95% CI 0.005 to 0.78), even after adjusting for various confounders. Additionally, participants in the highest SMM tertile had 81% (95% CI 0.04 to 0.85) lower risk for a CVD event as compared with those in the lowest SMM tertile.
The 10 year CVD (cardiovascular disease) incidence increased significantly across the baseline SMI (skeletal muscle mass index) tertiles (p<0.001). Baseline SMM (Skeletal muscle mass) showed a significant inverse association with the 10 year CVD incidence (HR 0.06, 95% CI 0.005 to 0.78), even after adjusting for various confounders. Additionally, participants in the highest SMM tertile had 81% (95% CI 0.04 to 0.85) lower risk for a CVD event as compared with those in the lowest SMM tertile.