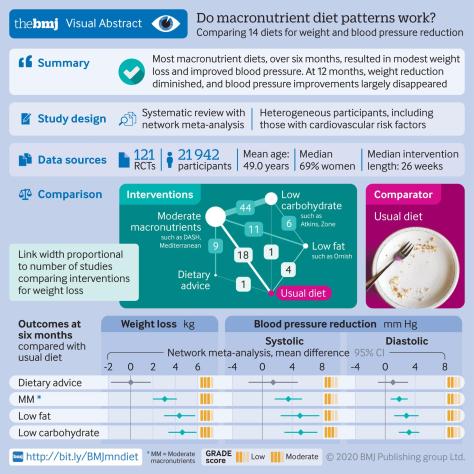
From a BMJ Study article (April, 2020):
Compared with usual diet, moderate certainty evidence supports modest weight loss and substantial reductions in systolic and diastolic blood pressure for low carbohydrate (eg, Atkins, Zone), low fat (eg, Ornish), and moderate macronutrient (eg, DASH, Mediterranean) diets at six but not 12 months. Differences between diets are, however, generally trivial to small, implying that people can choose the diet they prefer from among many of the available diets (fig 6) without concern about the magnitude of benefits.
Introduction
The worldwide prevalence of obesity nearly tripled between 1975 and 2018.1 In response, authorities have made dietary recommendations for weight management and cardiovascular risk reduction.23 Diet programmes—some focusing on carbohydrate reduction and others on fat reduction—have been promoted widely by the media and have generated intense debates about their relative merit. Millions of people are trying to lose weight by changing their diet. Thus establishing the effect of dietary macronutrient patterns (carbohydrate reduction v fat reduction v moderate macronutrients) and popular named dietary programmes is important.
Biological and physiological mechanisms have been proposed to explain why some dietary macronutrient patterns and popular dietary programmes should be better than others. A previous network meta-analysis, however, suggested that differences in weight loss between dietary patterns and individual popular named dietary programmes are small and unlikely to be important.4 No systematic review and network meta-analysis has examined the comparative effectiveness of popular dietary programmes for reducing risk factors for cardiovascular disease, an area of continuing controversy.


 “Having normal body weight is crucial in the prevention of type 2 diabetes, regardless of genetic predisposition.”
“Having normal body weight is crucial in the prevention of type 2 diabetes, regardless of genetic predisposition.”
 This relationship between higher glucose levels and poorer cognitive functioning extended beyond just CASI z-score, as well, Cukierman-Yaffe noted. Higher HbA1c levels were also tied to significantly poorer performance in other psychological tests, including the clock making test of executive functioning, test of discriminative ability, and for the test of verbal fluency.
This relationship between higher glucose levels and poorer cognitive functioning extended beyond just CASI z-score, as well, Cukierman-Yaffe noted. Higher HbA1c levels were also tied to significantly poorer performance in other psychological tests, including the clock making test of executive functioning, test of discriminative ability, and for the test of verbal fluency.
 These daily oscillations are controlled by the circadian clock, which is composed of an autoregulatory biochemical mechanism that is expressed in tissues throughout the body and is coordinated by a master pacemaker located in the suprachiasmatic nuclei of the brain (aka the SCN [
These daily oscillations are controlled by the circadian clock, which is composed of an autoregulatory biochemical mechanism that is expressed in tissues throughout the body and is coordinated by a master pacemaker located in the suprachiasmatic nuclei of the brain (aka the SCN [
 Nathan Pritikin was a college dropout who became an entrepreneur. While doing research for the government during World War II, he observed that populations that had extremely limited food availability because of the war had substantially reduced mortality from cardiovascular disease—something unexpected at a time when cardiovascular disease was thought to be due to stress.
Nathan Pritikin was a college dropout who became an entrepreneur. While doing research for the government during World War II, he observed that populations that had extremely limited food availability because of the war had substantially reduced mortality from cardiovascular disease—something unexpected at a time when cardiovascular disease was thought to be due to stress. 
 “Maintaining weight loss can get easier over time. Over time, less intentional effort, though not no effort, is needed to be successful. After about two years, healthy eating habits become part of the routine. Healthy choices become more automatic the longer people continue to make them. They feel weird when they don’t.”
“Maintaining weight loss can get easier over time. Over time, less intentional effort, though not no effort, is needed to be successful. After about two years, healthy eating habits become part of the routine. Healthy choices become more automatic the longer people continue to make them. They feel weird when they don’t.”
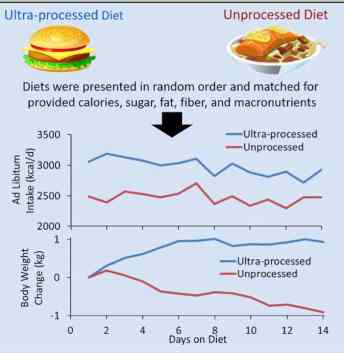 cookies and pies, salty snacks, frozen and shelf-stable dishes, pizza, and breakfast cereals.
cookies and pies, salty snacks, frozen and shelf-stable dishes, pizza, and breakfast cereals.
 Habitual fish oil supplementation is associated with a 13% lower risk of all cause mortality, a 16% lower risk of CVD mortality, and a 7% lower risk of CVD events among the general population
Habitual fish oil supplementation is associated with a 13% lower risk of all cause mortality, a 16% lower risk of CVD mortality, and a 7% lower risk of CVD events among the general population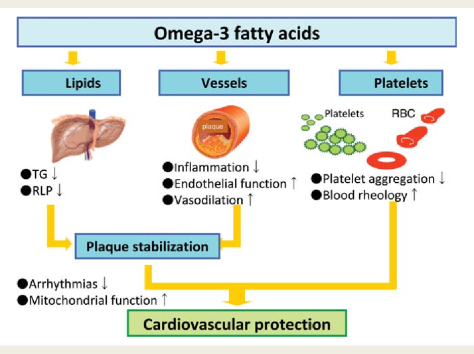

 Eat less, live longer- If you want to reduce levels of inflammation throughout your body, delay the onset of age-related diseases and live longer—eat less food. That’s the conclusion of a new study by scientists from the US and China that provides the most detailed report to date of the cellular effects of a calorie-restricted diet in rats.
Eat less, live longer- If you want to reduce levels of inflammation throughout your body, delay the onset of age-related diseases and live longer—eat less food. That’s the conclusion of a new study by scientists from the US and China that provides the most detailed report to date of the cellular effects of a calorie-restricted diet in rats. 
 We suggest this increase in mortality seen on DR in the 4-day switch treatment is due to either accrued physiological costs or more probable, a carryover of deaths directly resulting from the rich diet, but recorded on the DR diet.
We suggest this increase in mortality seen on DR in the 4-day switch treatment is due to either accrued physiological costs or more probable, a carryover of deaths directly resulting from the rich diet, but recorded on the DR diet.