From a European Heart Journal study:
 When the five sleep factors were collapsed into binary categories of low risk vs. high risk (reference group), early chronotype, adequate sleep duration, free of insomnia, and no frequent daytime sleepiness were each independently associated with incident CVD, with a 7%, 12%, 8%, and 15% lower risk, respectively (Table 3). Early chronotype, adequate sleep duration, and free of insomnia were independently associated with a significantly reduced risk of CHD; while only adequate sleep duration was associated with stroke.
When the five sleep factors were collapsed into binary categories of low risk vs. high risk (reference group), early chronotype, adequate sleep duration, free of insomnia, and no frequent daytime sleepiness were each independently associated with incident CVD, with a 7%, 12%, 8%, and 15% lower risk, respectively (Table 3). Early chronotype, adequate sleep duration, and free of insomnia were independently associated with a significantly reduced risk of CHD; while only adequate sleep duration was associated with stroke.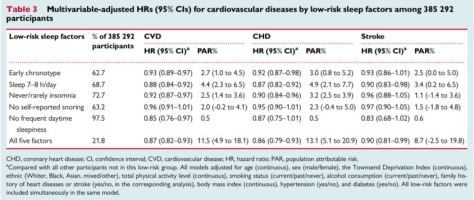 Cardiovascular disease (CVD), including coronary heart disease (CHD) and stroke, is among the leading causes of mortality globally.1 In addition to traditional lifestyle behaviours, emerging evidence has implicated several unhealthy sleep behaviours were important risk factors for CVD.2,3 For example, short or long sleep duration,4–9 late chronotype,10,11 insomnia,12–17 snoring,18,19 and excessive daytime sleepiness20,21 were associated with a 10–40% increased CVD risk.
Cardiovascular disease (CVD), including coronary heart disease (CHD) and stroke, is among the leading causes of mortality globally.1 In addition to traditional lifestyle behaviours, emerging evidence has implicated several unhealthy sleep behaviours were important risk factors for CVD.2,3 For example, short or long sleep duration,4–9 late chronotype,10,11 insomnia,12–17 snoring,18,19 and excessive daytime sleepiness20,21 were associated with a 10–40% increased CVD risk. 
To read more: https://academic.oup.com/eurheartj/advance-article/doi/10.1093/eurheartj/ehz849/5678714



 ‘Successful Aging’ uses research from developmental neuroscience and the psychology of individual differences to show that sixty-plus years is a unique developmental stage that, like infancy or adolescence, has its own demands and distinct advantages. Levitin looks at the science behind what we all can learn from those who age joyously, as well as how to adapt our culture to take full advantage of older people’s wisdom and experience. Throughout his exploration of what aging really means, Levitin reveals resilience strategies and practical, cognitive enhancing tricks everyone should do as they age.
‘Successful Aging’ uses research from developmental neuroscience and the psychology of individual differences to show that sixty-plus years is a unique developmental stage that, like infancy or adolescence, has its own demands and distinct advantages. Levitin looks at the science behind what we all can learn from those who age joyously, as well as how to adapt our culture to take full advantage of older people’s wisdom and experience. Throughout his exploration of what aging really means, Levitin reveals resilience strategies and practical, cognitive enhancing tricks everyone should do as they age.


 When the five sleep factors were collapsed into binary categories of low risk vs. high risk (reference group), early chronotype, adequate sleep duration, free of insomnia, and no frequent daytime sleepiness were each independently associated with incident CVD, with a 7%, 12%, 8%, and 15% lower risk, respectively (Table
When the five sleep factors were collapsed into binary categories of low risk vs. high risk (reference group), early chronotype, adequate sleep duration, free of insomnia, and no frequent daytime sleepiness were each independently associated with incident CVD, with a 7%, 12%, 8%, and 15% lower risk, respectively (Table  Cardiovascular disease (CVD), including coronary heart disease (CHD) and stroke, is among the leading causes of mortality globally.
Cardiovascular disease (CVD), including coronary heart disease (CHD) and stroke, is among the leading causes of mortality globally.

 During this decade, as in previous decades, Caltech scientists and engineers reinvented the landscape of scientific endeavor: from the first detection of gravitational waves and the discovery of evidence for a ninth planet in the solar system; to bold missions to explore and understand the solar system; to the development of new methods to see inside the body and the brain and understand the universe around us; to the invention of devices to improve human health, some taking inspiration from nature; to the initiation of a transformative new effort to support research into the most pressing challenges in environmental sustainability.
During this decade, as in previous decades, Caltech scientists and engineers reinvented the landscape of scientific endeavor: from the first detection of gravitational waves and the discovery of evidence for a ninth planet in the solar system; to bold missions to explore and understand the solar system; to the development of new methods to see inside the body and the brain and understand the universe around us; to the invention of devices to improve human health, some taking inspiration from nature; to the initiation of a transformative new effort to support research into the most pressing challenges in environmental sustainability. Though the brain orchestrates how we experience the world, many questions remain about its complex workings. During the past 10 years, Caltech scientists have discovered how the brain recognizes
Though the brain orchestrates how we experience the world, many questions remain about its complex workings. During the past 10 years, Caltech scientists have discovered how the brain recognizes  As modern technology advances, so do the possibilities for treating medical conditions that were previously considered untreatable. Caltech researchers used an electrode array to help a paralyzed patient
As modern technology advances, so do the possibilities for treating medical conditions that were previously considered untreatable. Caltech researchers used an electrode array to help a paralyzed patient 
 In our own study of more than 7,000 middle-aged to older adults in the U.K., published in 2019 in Brain Imaging and Behavior, we demonstrated that people who spent more time engaged in moderate to vigorous physical activity had larger hippocampal volumes. Although it is not yet possible to say whether these effects in humans are related to neurogenesis or other forms of brain plasticity, such as increasing connections among existing neurons, together the results clearly indicate that exercise can benefit the brain’s hippocampus and its cognitive functions.
In our own study of more than 7,000 middle-aged to older adults in the U.K., published in 2019 in Brain Imaging and Behavior, we demonstrated that people who spent more time engaged in moderate to vigorous physical activity had larger hippocampal volumes. Although it is not yet possible to say whether these effects in humans are related to neurogenesis or other forms of brain plasticity, such as increasing connections among existing neurons, together the results clearly indicate that exercise can benefit the brain’s hippocampus and its cognitive functions.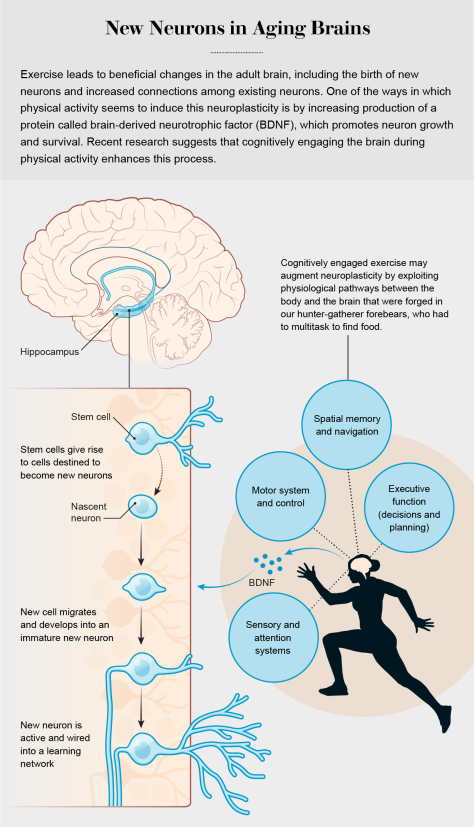


 Produced by WIRED Brand Lab with American Institute of Architects | How can design transform emergency rooms from one of the most stressful and chaotic places into a place of healing? Dr. Bon Ku and architect Billie Faircloth, AIA, break down the science behind designing a better work environment for hospitals.
Produced by WIRED Brand Lab with American Institute of Architects | How can design transform emergency rooms from one of the most stressful and chaotic places into a place of healing? Dr. Bon Ku and architect Billie Faircloth, AIA, break down the science behind designing a better work environment for hospitals.