From a New Scientist online review:
The prevailing narrative of “battling cancer” in Western society has its own issues, with its discourse of personal triumph that values individual responsibility and determination. But the alternative – to lie outright – might seem inconceivable, particularly to those accustomed to the norms of Western culture. It is, however, a common practice in China, rooted in the belief that telling a person about their diagnosis can make their condition deteriorate quicker.
 The plot line of The Farewell is familiar to me. Like Billi’s Nai Nai, my aunt was diagnosed with metatastic lung cancer. Nobody in the family told her – nor did the doctors when she later underwent surgery to remove a tumour. The last time I saw her was in north-eastern China a few years ago. Her once-plump figure had shrunk to a wiry frame. She was in her early 70s, in good spirits, but a far cry from the feisty matriarch who used to dominate conversations.
The plot line of The Farewell is familiar to me. Like Billi’s Nai Nai, my aunt was diagnosed with metatastic lung cancer. Nobody in the family told her – nor did the doctors when she later underwent surgery to remove a tumour. The last time I saw her was in north-eastern China a few years ago. Her once-plump figure had shrunk to a wiry frame. She was in her early 70s, in good spirits, but a far cry from the feisty matriarch who used to dominate conversations.
The Farewell is a heartfelt film, punctuated by moments of unexpected – and unexpectedly uplifting – humour. In a darkly comical scene in a printing shop, Nai Nai’s younger sister demands that the results of a medical report be doctored to edit out references to cancerous nodules and replaced with the nebulous term “benign shadows”.





 The tool is simply called Preventive Health, and is now available to Facebook users in the United States. It takes a user’s age and sex from their Facebook profile and provides them with a list of recommended screenings based on those two data points.
The tool is simply called Preventive Health, and is now available to Facebook users in the United States. It takes a user’s age and sex from their Facebook profile and provides them with a list of recommended screenings based on those two data points.
 First place prize awarded to MapHabit: This mobile software provides behavior prompts with customizable picture and keyword visual maps to assist memory-impaired people with accomplishing activities of daily living. The care management platform employs different interfaces depending on whether the user is a person with impaired memory, caregiver or long-term care community manager. Caregivers can monitor adherence to medication schedules or track other activities.
First place prize awarded to MapHabit: This mobile software provides behavior prompts with customizable picture and keyword visual maps to assist memory-impaired people with accomplishing activities of daily living. The care management platform employs different interfaces depending on whether the user is a person with impaired memory, caregiver or long-term care community manager. Caregivers can monitor adherence to medication schedules or track other activities.
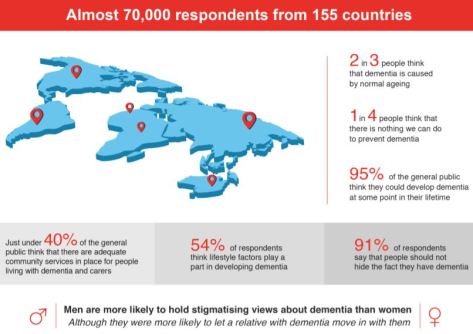
 LSE developed the survey to target four key groups:
LSE developed the survey to target four key groups: In the survey analysis we highlight the behavioural element first, giving prominence to the voices and experiences of people living with dementia as direct assessment of actual behaviour is central to discrimination and is the closest representation of the true impact of stigma on people living with dementia.
In the survey analysis we highlight the behavioural element first, giving prominence to the voices and experiences of people living with dementia as direct assessment of actual behaviour is central to discrimination and is the closest representation of the true impact of stigma on people living with dementia.
 The current study points to the role of norepinephrine, a neurotransmitter that signals arousal and stress in the central nervous system. This chemical is present in low levels in the brain while we sleep, but when production ramps up it arouses our nerve cells, causing us to wake up and become alert. The study showed that norepinephrine also acts on a specific receptor, the beta2 adrenergic receptor, which is expressed at high levels in microglia. When this chemical is present in the brain, the microglia slip into a sort of hibernation.
The current study points to the role of norepinephrine, a neurotransmitter that signals arousal and stress in the central nervous system. This chemical is present in low levels in the brain while we sleep, but when production ramps up it arouses our nerve cells, causing us to wake up and become alert. The study showed that norepinephrine also acts on a specific receptor, the beta2 adrenergic receptor, which is expressed at high levels in microglia. When this chemical is present in the brain, the microglia slip into a sort of hibernation.
 The prototype revealed that using artificial intelligence and machine learning to examine certain combinations of vital signs and other biomarkers could strongly
The prototype revealed that using artificial intelligence and machine learning to examine certain combinations of vital signs and other biomarkers could strongly 
 The top 10 most commonly administered antibiotics in the ER for nonadmitted patients were:
The top 10 most commonly administered antibiotics in the ER for nonadmitted patients were:
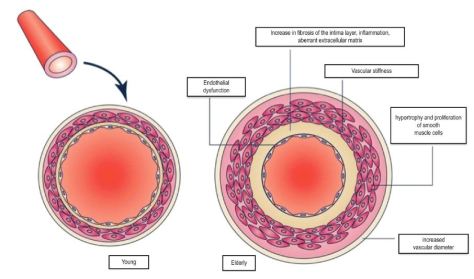

 “The risk for dementia is elevated about twofold in people who have diabetes or
“The risk for dementia is elevated about twofold in people who have diabetes or