From a The Architectural Review online article (April 9, 2020):
 The sleep industry caters to a working consumer’s wish to sleep less, yet sleep more productively, and accommodates transnational industry which has joined the state as a custodian of biopolitics. Jonathan Crary’s 24/7 spells out in detail how the state and a capitalist economy are encroaching stupendously on the private sphere, in which sleep was one of the last vestiges of unfettered time.
The sleep industry caters to a working consumer’s wish to sleep less, yet sleep more productively, and accommodates transnational industry which has joined the state as a custodian of biopolitics. Jonathan Crary’s 24/7 spells out in detail how the state and a capitalist economy are encroaching stupendously on the private sphere, in which sleep was one of the last vestiges of unfettered time.
About 15 years ago, someone calculated the financial loss US companies incurred through workers’ illicit practice of sleeping on the job. Indeed, the trope of the lazy sleeper is an old one, resignified at present in our more than callous attitude towards the homeless, whose sleeping bodies punctuate many a journey to and from work.
Even in this most passive stance – someone simply disregarding normative codes and regulations by giving in to a physical need – sleep seems suspiciously subversive. Less an act than a way of being, the sleeper, by sleeping when and where it is not condoned, challenges everyone else, who is doing/working/functioning/functionalised. Contrary to the tree falling in the forest, the sleeper in the workplace or in public space affects and thus ever so slightly transforms those around them.




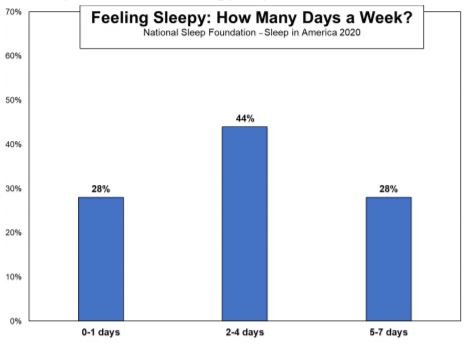


 “
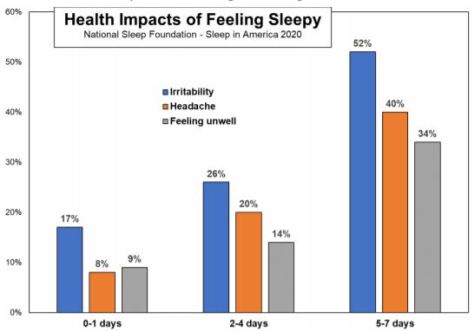
“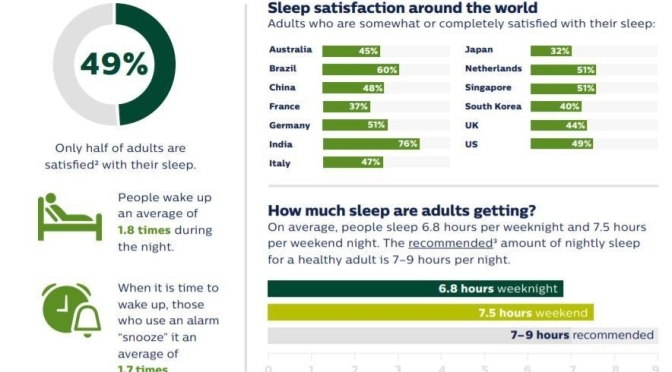
 “The decrease in people taking action to improve sleep is alarming, especially when it is clear people around the world deeply value sleep. Sleep deficit impacts people both mentally and physically, so we need to educate people on available sleep resources and empower them with the confidence that their efforts will pay off,” said Mark Aloia, PhD, Global Lead for Behavior Change, Sleep & Respiratory Care at Philips.
“The decrease in people taking action to improve sleep is alarming, especially when it is clear people around the world deeply value sleep. Sleep deficit impacts people both mentally and physically, so we need to educate people on available sleep resources and empower them with the confidence that their efforts will pay off,” said Mark Aloia, PhD, Global Lead for Behavior Change, Sleep & Respiratory Care at Philips.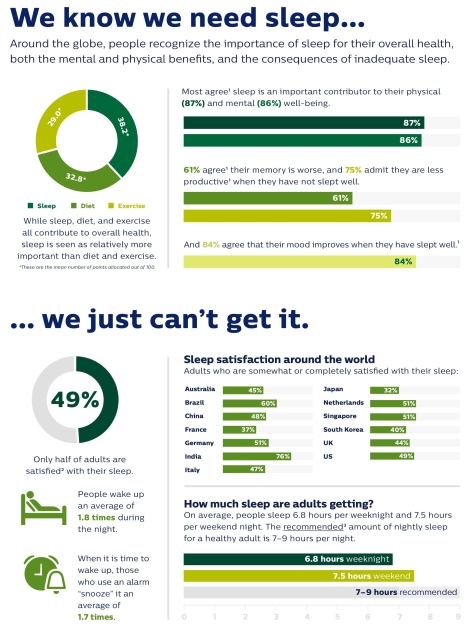

 The association between poor overall sleep quality and greater consumption of added sugars observed in the current study aligns with previous findings that intakes of confectionary and sugar‐sweetened beverages were higher in middle‐aged Japanese women reporting poor, compared with good, sleep quality.
The association between poor overall sleep quality and greater consumption of added sugars observed in the current study aligns with previous findings that intakes of confectionary and sugar‐sweetened beverages were higher in middle‐aged Japanese women reporting poor, compared with good, sleep quality.
 Our findings suggest that LAN (low-level light at night) exposure increases the incidence of diabetes in a general elderly population. Further research involving a large cohort with new-onset diabetes is warranted to elucidate these findings.
Our findings suggest that LAN (low-level light at night) exposure increases the incidence of diabetes in a general elderly population. Further research involving a large cohort with new-onset diabetes is warranted to elucidate these findings.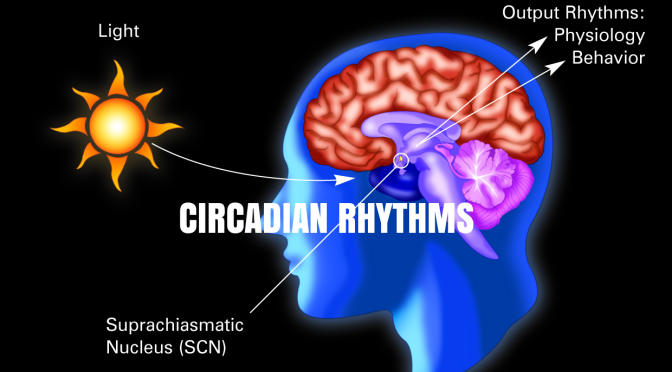
 By comparing the pancreatic cells of type 2 diabetic human donors with those of healthy people, researchers at the University of Geneva (UNIGE) and at the University Hospitals of Geneva (HUG), Switzerland, were able to demonstrate, for the first time, that the pancreatic islet cells derived from the Type 2 Diabetic human donors bear compromised circadian oscillators.
By comparing the pancreatic cells of type 2 diabetic human donors with those of healthy people, researchers at the University of Geneva (UNIGE) and at the University Hospitals of Geneva (HUG), Switzerland, were able to demonstrate, for the first time, that the pancreatic islet cells derived from the Type 2 Diabetic human donors bear compromised circadian oscillators. 

 can develop a conditioned fear of not being able to sleep, which puts them in a state of hyperarousal when they attempt to fall asleep. This makes their inability to sleep a self-fulfilling prophecy.
can develop a conditioned fear of not being able to sleep, which puts them in a state of hyperarousal when they attempt to fall asleep. This makes their inability to sleep a self-fulfilling prophecy.
 “Amyloid is important in initiating disease, but the actual damage in the brain is probably due to the accumulation of tau,” Holtzman told MedPage Today. “Normally, tau protein is inside cells, but there is more and more evidence suggesting that its spread to different parts of the brain is responsible for the progression of Alzheimer’s disease.”
“Amyloid is important in initiating disease, but the actual damage in the brain is probably due to the accumulation of tau,” Holtzman told MedPage Today. “Normally, tau protein is inside cells, but there is more and more evidence suggesting that its spread to different parts of the brain is responsible for the progression of Alzheimer’s disease.”