From a New England Journal of Medicine article (March 11, 2020):
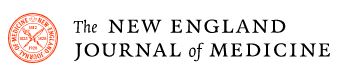 A central strategy for health care surge control is “forward triage” — the sorting of patients before they arrive in the emergency department (ED). Direct-to-consumer (or on-demand) telemedicine, a 21st-century approach to forward triage that allows patients to be efficiently screened, is both patient-centered and conducive to self-quarantine, and it protects patients, clinicians, and the community from exposure.
A central strategy for health care surge control is “forward triage” — the sorting of patients before they arrive in the emergency department (ED). Direct-to-consumer (or on-demand) telemedicine, a 21st-century approach to forward triage that allows patients to be efficiently screened, is both patient-centered and conducive to self-quarantine, and it protects patients, clinicians, and the community from exposure.
It can allow physicians and patients to communicate 24/7, using smartphones or webcam-enabled computers. Respiratory symptoms — which may be early signs of Covid-19 — are among the conditions most commonly evaluated with this approach. Health care providers can easily obtain detailed travel and exposure histories. Automated screening algorithms can be built into the intake process, and local epidemiologic information can be used to standardize screening and practice patterns across providers.
More than 50 U.S. health systems already have such programs. Jefferson Health, Mount Sinai, Kaiser Permanente, Cleveland Clinic, and Providence, for example, all leverage telehealth technology to allow clinicians to see patients who are at home. Systems lacking such programs can outsource similar services to physicians and support staff provided by Teladoc Health or American Well. At present, the major barrier to large-scale telemedical screening for SARS-CoV-2, the novel coronavirus causing Covid-19, is coordination of testing. As the availability of testing sites expands, local systems that can test appropriate patients while minimizing exposure — using dedicated office space, tents, or in-car testing — will need to be developed and integrated into telemedicine workflows.
Read full article





 Coffee and tea have been consumed for hundreds of years and have become an important part of cultural traditions and social life.
Coffee and tea have been consumed for hundreds of years and have become an important part of cultural traditions and social life.

 Interview with Dr. Nicole Lurie on rapid vaccine development, including new tools to facilitate vaccine testing and manufacturing and persistent challenges.
Interview with Dr. Nicole Lurie on rapid vaccine development, including new tools to facilitate vaccine testing and manufacturing and persistent challenges.
 Featuring articles on deaths due to e-cigarette– or vaping-associated lung injury, apixaban for venous thromboembolism in cancer, the management of coronary disease in patients with advanced kidney disease, health-status outcomes in the ISCHEMIA-CKD trial, and ten weeks to crush the curve.
Featuring articles on deaths due to e-cigarette– or vaping-associated lung injury, apixaban for venous thromboembolism in cancer, the management of coronary disease in patients with advanced kidney disease, health-status outcomes in the ISCHEMIA-CKD trial, and ten weeks to crush the curve. 
 Cardiovascular consults are way down. Is the threat of COVID-19 infection scaring people away from ED’s?
Cardiovascular consults are way down. Is the threat of COVID-19 infection scaring people away from ED’s?

 Though U.S. legislation targeting the problem of surprise medical bills advanced out of key congressional committees in 2019 with support from leaders in both parties, Congress ultimately failed to pass a law to end such bills.
Though U.S. legislation targeting the problem of surprise medical bills advanced out of key congressional committees in 2019 with support from leaders in both parties, Congress ultimately failed to pass a law to end such bills.
 A central strategy for health care surge control is “forward triage” — the sorting of patients before they arrive in the emergency department (ED). Direct-to-consumer (or on-demand) telemedicine, a 21st-century approach to forward triage that allows patients to be efficiently screened, is both patient-centered and conducive to self-quarantine, and it protects patients, clinicians, and the community from exposure.
A central strategy for health care surge control is “forward triage” — the sorting of patients before they arrive in the emergency department (ED). Direct-to-consumer (or on-demand) telemedicine, a 21st-century approach to forward triage that allows patients to be efficiently screened, is both patient-centered and conducive to self-quarantine, and it protects patients, clinicians, and the community from exposure. 