Tag Archives: Health
Studies: High Usage Of Commonly Used Oral Antibiotics Increases Risk Of Parkinson’s Disease
From a Neuroscience News & Research online article:
 “The link between antibiotic exposure and Parkinson’s disease fits the current view that in a significant proportion of patients the pathology of Parkinson’s may originate in the gut, possibly related to microbial changes, years before the onset of typical Parkinson motor symptoms such as slowness, muscle stiffness and shaking of the extremities. It was known that the bacterial composition of the intestine in Parkinson’s patients is abnormal, but the cause is unclear. Our results suggest that some commonly used antibiotics, which are known to strongly influence the gut microbiota, could be a predisposing factor,” says research team leader, neurologist Filip Scheperjans MD, Ph.D. from the Department of Neurology of Helsinki University Hospital.
“The link between antibiotic exposure and Parkinson’s disease fits the current view that in a significant proportion of patients the pathology of Parkinson’s may originate in the gut, possibly related to microbial changes, years before the onset of typical Parkinson motor symptoms such as slowness, muscle stiffness and shaking of the extremities. It was known that the bacterial composition of the intestine in Parkinson’s patients is abnormal, but the cause is unclear. Our results suggest that some commonly used antibiotics, which are known to strongly influence the gut microbiota, could be a predisposing factor,” says research team leader, neurologist Filip Scheperjans MD, Ph.D. from the Department of Neurology of Helsinki University Hospital.
Higher exposure to commonly used oral antibiotics is linked to an increased risk of Parkinson’s disease according to a recently published study by researchers from the Helsinki University Hospital, Finland.
The strongest associations were found for broad-spectrum antibiotics and those that act against anaerobic bacteria and fungi. The timing of antibiotic exposure also seemed to matter.
The study suggests that excessive use of certain antibiotics can predispose to Parkinson’s disease with a delay of up to 10 to 15 years. This connection may be explained by their disruptive effects on the gut microbial ecosystem.
Healthcare: Geriatric Assessment Helps Select Proper Treatments For Cancer In Elderly Patients
From an NPR online article:
 More than 60% of cancers in the U.S. occur in people older than 65. As the population grows older, so will the rate of cancer among seniors. The cancer incidence in the elderly is expected to rise 67% from 2010 to 2030, according to a 2017 study in the Journal of Clinical Oncology. Yet many oncologists don’t have geriatric training.
More than 60% of cancers in the U.S. occur in people older than 65. As the population grows older, so will the rate of cancer among seniors. The cancer incidence in the elderly is expected to rise 67% from 2010 to 2030, according to a 2017 study in the Journal of Clinical Oncology. Yet many oncologists don’t have geriatric training.
“When the doctor saw how physically active and mentally sharp my father was at 89 years of age, but that he had several chronic, serious medical problems, including end stage kidney disease, she didn’t advise him to have aggressive treatment like the first time around,” says Griggs, who lives in Rochester, N.Y.
Geriatric assessment is an approach that clinicians use to evaluate their elderly patients’ overall health status and to help them choose treatment appropriate to their age and condition. The assessment includes questionnaires and tests to gauge the patients’ physical, mental and functional capacity, taking into account their social lives, daily activities and goals.
Health: “Feather Duvet Lung” Left Undiagnosed Risks Irreversible Lung Fibrosis (BMJ Case Reports)
From a British Medical Journal (BMJ) online release:
 Although he had no pet birds, on closer questioning he had recently acquired a duvet and pillows containing feathers. His symptoms, chest radiograph and lung function tests improved after removal of all feather bedding, and he was also started on oral corticosteroid therapy. Our case reinforces the importance of taking a meticulous exposure history and asking about domestic bedding in patients with unexplained breathlessness. Prompt recognition and cessation of antigen exposure may prevent the development of irreversible lung fibrosis.
Although he had no pet birds, on closer questioning he had recently acquired a duvet and pillows containing feathers. His symptoms, chest radiograph and lung function tests improved after removal of all feather bedding, and he was also started on oral corticosteroid therapy. Our case reinforces the importance of taking a meticulous exposure history and asking about domestic bedding in patients with unexplained breathlessness. Prompt recognition and cessation of antigen exposure may prevent the development of irreversible lung fibrosis.
A 43-year-old non-smoker was referred with a 3-month history of malaise, fatigue and breathlessness. Blood avian precipitins were strongly positive. Lung function testing confirmed a restrictive pattern with impaired gas transfer. A ‘ground glass’ mosaic pattern was seen on CT imaging, suggestive of hypersensitivity pneumonitis.
Feather duvet lung (FDL), is an immunologically mediated form of hypersensitivity pneumonitis (HP), also sometimes called extrinsic allergic alveolitis. FDL is caused by inhalation of organic dust from duck or goose feathers found in duvets and pillows. Antigen inhalation triggers an immunological cascade, resulting in lung parenchymal inflammation. Repeated exposure may result in irreversible lung fibrosis.
To read more: https://casereports.bmj.com/content/12/11/e231237
Top New Travel Videos: “The Waters Of Slovenia” (National Geographic)
Slovenia is a country defined by water, with more than 60 rivers and streams, 300 artificial and natural lakes, and 7,500 freshwater springs – each of which is packed with minerals and nutrients.

Website: https://www.nationalgeographic.com/
Medical Diagnosis: 56-Year Old Woman Had Heart Attacks, But No Heart Disease? (New York Times)
From a New York Times Magazine article:
 It was all horribly familiar — a rerun of an episode 15 months earlier, when she was with her family in River Vale, N.J. Back then, the burning pressure sent her to the emergency department, and she was told the same thing: She was having a heart attack. Immediately the cardiologist looked for blockages in the coronary arteries, which feed blood and oxygen to the hardworking muscles of her heart. That was the cause of most heart attacks. But they found no blockage.
It was all horribly familiar — a rerun of an episode 15 months earlier, when she was with her family in River Vale, N.J. Back then, the burning pressure sent her to the emergency department, and she was told the same thing: She was having a heart attack. Immediately the cardiologist looked for blockages in the coronary arteries, which feed blood and oxygen to the hardworking muscles of her heart. That was the cause of most heart attacks. But they found no blockage.
Since childhood, she had frequent terrible canker sores that lasted for weeks. Sometimes it was hard to eat or even talk. Her mother, a nurse, told her everybody got them and thought she was being dramatic when she complained. So she had never brought them up with her doctors. Now the woman saw that her answer somehow made sense to the rheumatologist.
 Indeed, that was the clue that led the rheumatologist to a likely diagnosis: Behcet’s disease. It’s an unusual inflammatory disorder characterized by joint pains, muscle pains and recurrent ulcers in mucus membranes throughout the body. Almost any part of the body can be involved — the eyes, the nose and lungs, the brain, the blood vessels, even the heart. Behcet’s was named after a Turkish dermatologist who in 1937 described a triad of clinical findings including canker sores (medically known as aphthous ulcers), genital ulcers and an inflammatory condition of the eye.
Indeed, that was the clue that led the rheumatologist to a likely diagnosis: Behcet’s disease. It’s an unusual inflammatory disorder characterized by joint pains, muscle pains and recurrent ulcers in mucus membranes throughout the body. Almost any part of the body can be involved — the eyes, the nose and lungs, the brain, the blood vessels, even the heart. Behcet’s was named after a Turkish dermatologist who in 1937 described a triad of clinical findings including canker sores (medically known as aphthous ulcers), genital ulcers and an inflammatory condition of the eye.
Health Organizations: “Leukemia & Lymphoma Society” (Animated Video)
Director: Natalie Labarre
Agency: Oberland
Production Co: Hornet
Executive Producer: Hana Shimizu
Development Producer: Kristin Labriola
Producer: Matt Creeden
Editor: Anita Chao
Production Coordinator: Riley Spencer

The Leukemia and Lymphoma Society (LLS) and creative agency Oberland approached Hornet to create a 45-second spot detailing how LLS can help people come to terms with the earth-shattering news of a cancer diagnosis. Hornet’s own Natalie Labarre directed the spot. In her words, it was supposed to be “a visual representation of what it’s like to have your life fall apart.” So, she made it literally fall apart with an unraveling of structures around the characters, a blurry focus, and a swirl of levitating objects. The message is that once LLS comes into the picture, these characters feel grounded again. Ultimately, the film is a heartfelt, soothing, beautifully-illustrated 2D animation that has a heavy, yet hopeful, tone.
Website: https://www.lls.org/
Health Care: VillageMD Opens First Primary Clinic Called Village Medical At Walgreens In Houston
From a Becker’s Hospital Review online release:
 The VillageMD primary care clinic, called Village Medical at Walgreens, is the first of five sites to open in Houston. Four more clinics are slated to open by the end of the year. The Village Medical clinics are located next to Walgreens stores and offer services including annual preventive care, women’s health services, vaccinations, diagnostic testing, smoking cessation, chronic care management and some specialty care. The clinics offer same-day, walk-in appointments, as well as house calls and virtual visits. The clinics are staffed by primary care physicians, nurses, pharmacists and social workers.
The VillageMD primary care clinic, called Village Medical at Walgreens, is the first of five sites to open in Houston. Four more clinics are slated to open by the end of the year. The Village Medical clinics are located next to Walgreens stores and offer services including annual preventive care, women’s health services, vaccinations, diagnostic testing, smoking cessation, chronic care management and some specialty care. The clinics offer same-day, walk-in appointments, as well as house calls and virtual visits. The clinics are staffed by primary care physicians, nurses, pharmacists and social workers.
Chicago-based primary care company VillageMD is celebrating the opening Nov. 20 of its first primary care clinic at a Walgreens store in Houston, the company announced on Twitter. The Village Medical at Walgreens opening comes just weeks after Walgreens announced plans in October to shutter nearly 160 in-store health clinics.
Health Studies: Reduced Mental Alertness (“Brain Fog”) Is Caused By Inflammation In The Body
From a Genetic Engineering & Biotechnology News release:
 “These results show quite clearly that there’s a very specific part of the brain network that’s affected by inflammation,” noted Mazaheri. “This could explain ‘brain fog’.”
“These results show quite clearly that there’s a very specific part of the brain network that’s affected by inflammation,” noted Mazaheri. “This could explain ‘brain fog’.”
Raymond added that “this research finding is a major step forward in understanding the links between physical, cognitive, and mental health and tells us that even the mildest of illnesses may reduce alertness.”
Researchers at the University of Birmingham’s Centre for Human Brain Health in collaboration with the University of Amsterdam say they have uncovered a possible explanation for the mental sluggishness that often accompanies illness. The team investigated the link between “mental fog” and inflammation, the body’s response to illness. In a study (“Selective effects of acute low-grade inflammation on human visual attention”) published in Neuroimage, they showed that inflammation appears to have a particularly negative impact on the brain’s readiness to reach and maintain an alert state.
Brain Health: “Package Of Lifestyle Changes” (Brisk Exercise, Healthy Diet & Sleep, Cognitive Training) Helps Prevent Dementia
From a Wall Street Journal online article:
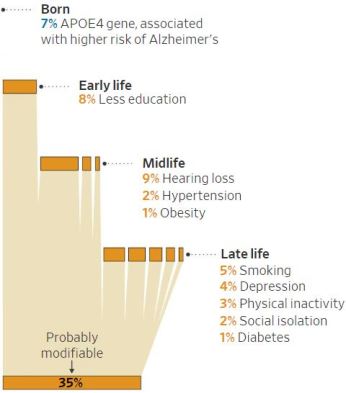
Dementia is a complicated disease that has multiple causes and risk factors, some of which remain unknown. Nevertheless, there is increasing evidence that people—even those who inherit genes that put them at greater risk of developing Alzheimer’s in later life—can improve their chances by adopting lifestyle changes.
“It’s not just about running three times a week,” says Sarah Lenz Lock, executive director of AARP’s Global Council on Brain Health. “Instead, it’s about a package of behaviors, including aerobic exercise, strength training, a healthy diet, sleep and cognitive training.”
When it comes to battling dementia, the unfortunate news is this: Medications have proven ineffective at curing or stopping the disease and its most common form, Alzheimer’s disease. But that isn’t the end of the story. According to a recent wave of scientific studies, we have more control over our cognitive health than is commonly known. We just have to take certain steps—ideally, early and often—to live a healthier lifestyle.
In fact, according to a recent report commissioned by the Lancet, a medical journal, around 35% of dementia cases might be prevented if people do things including exercising and engaging in cognitively stimulating activities. “When people ask me how to prevent dementia, they often want a simple answer, such as vitamins, dietary supplements or the latest hyped idea,” says Eric Larson, a physician at Kaiser Permanente in Seattle and one of a group of scientists who helped prepare the report. “I tell them they can take many common-sense actions that promote health throughout life.”
To read more: https://www.wsj.com/articles/what-science-tells-us-about-preventing-dementia-11574004600