From a New York Times online article (March 16, 2020):
 “Maintaining weight loss can get easier over time. Over time, less intentional effort, though not no effort, is needed to be successful. After about two years, healthy eating habits become part of the routine. Healthy choices become more automatic the longer people continue to make them. They feel weird when they don’t.”
“Maintaining weight loss can get easier over time. Over time, less intentional effort, though not no effort, is needed to be successful. After about two years, healthy eating habits become part of the routine. Healthy choices become more automatic the longer people continue to make them. They feel weird when they don’t.”
Among the useful strategies identified in the new study is to keep lower calorie foods like fruits and vegetables more accessible. “We eat what we see,” Dr. Phelan noted. The corollary is equally important: keep high-calorie, less nourishing foods relatively inaccessible and out of sight if not out of the house entirely.
The new study led by Dr. Phelan, professor of kinesiology and public health at California Polytechnic State University, identified habits and strategies that can be keys to success for millions. Yes, like most sensible weight-loss plans, they involve healthful eating and regular physical activity. But they also include important self-monitoring practices and nonpunitive coping measures that can be the crucial to long-term weight management.



 Overall, the evidence in the literature suggests that spirulina improves several well-established CVD risk factors including hyperlipidaemia and seems to provide benefits around weight loss.
Overall, the evidence in the literature suggests that spirulina improves several well-established CVD risk factors including hyperlipidaemia and seems to provide benefits around weight loss. 

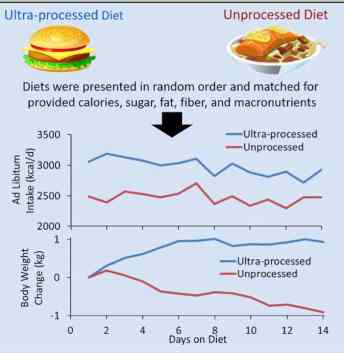 cookies and pies, salty snacks, frozen and shelf-stable dishes, pizza, and breakfast cereals.
cookies and pies, salty snacks, frozen and shelf-stable dishes, pizza, and breakfast cereals.
 Habitual fish oil supplementation is associated with a 13% lower risk of all cause mortality, a 16% lower risk of CVD mortality, and a 7% lower risk of CVD events among the general population
Habitual fish oil supplementation is associated with a 13% lower risk of all cause mortality, a 16% lower risk of CVD mortality, and a 7% lower risk of CVD events among the general population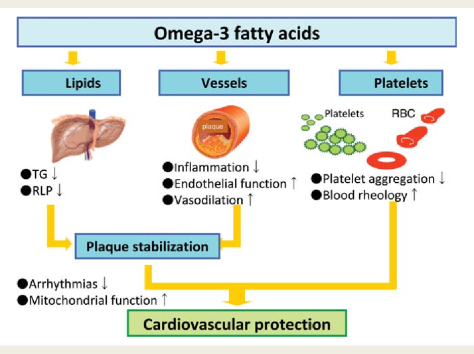

 We found no association between egg consumption and risk of cardiovascular disease in three large US cohorts. Results from the updated meta-analysis lend further support to the overall lack of an association between moderate egg consumption (up to one egg per day) and cardiovascular disease risk.
We found no association between egg consumption and risk of cardiovascular disease in three large US cohorts. Results from the updated meta-analysis lend further support to the overall lack of an association between moderate egg consumption (up to one egg per day) and cardiovascular disease risk. 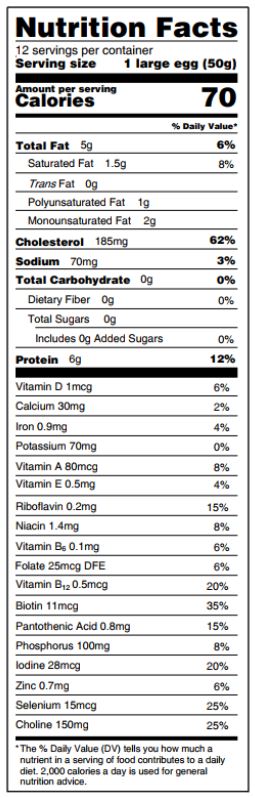 Eggs are a major source of dietary cholesterol, but they are also an affordable source of high quality protein, iron, unsaturated fatty acids, phospholipids, and carotenoids.
Eggs are a major source of dietary cholesterol, but they are also an affordable source of high quality protein, iron, unsaturated fatty acids, phospholipids, and carotenoids.
 The National Diabetes Statistics Report is a periodic publication of the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) that provides updated statistics about diabetes in the United States for a scientific audience. It includes information on prevalence and incidence of diabetes, prediabetes, risk factors for complications, acute and long-term complications, deaths, and costs. These data can help focus efforts to prevent and control diabetes across the United States.
The National Diabetes Statistics Report is a periodic publication of the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) that provides updated statistics about diabetes in the United States for a scientific audience. It includes information on prevalence and incidence of diabetes, prediabetes, risk factors for complications, acute and long-term complications, deaths, and costs. These data can help focus efforts to prevent and control diabetes across the United States.

 Across the 6 studies of 8699 participants, mean age ranged between 70 and 74 years and mean gait speed ranged between 1.05 and 1.26 m/s. Incident dementia ranged from 5 to 21 per 1000 person-years. Compared with usual agers, participants with only memory decline had 2.2 to 4.6 times higher risk for developing dementia…
Across the 6 studies of 8699 participants, mean age ranged between 70 and 74 years and mean gait speed ranged between 1.05 and 1.26 m/s. Incident dementia ranged from 5 to 21 per 1000 person-years. Compared with usual agers, participants with only memory decline had 2.2 to 4.6 times higher risk for developing dementia… 
 In our opinion, the current recommendation to greatly increase consumption of dairy foods to 3 or more servings per day does not appear to be justified…When consumption of milk is low, the two nutrients of primary concern, calcium and vitamin D (which is of particular concern at higher latitudes), be obtained from other foods or supplements without the potential negative consequences of dairy foods.
In our opinion, the current recommendation to greatly increase consumption of dairy foods to 3 or more servings per day does not appear to be justified…When consumption of milk is low, the two nutrients of primary concern, calcium and vitamin D (which is of particular concern at higher latitudes), be obtained from other foods or supplements without the potential negative consequences of dairy foods. 
 In this analysis of commercially insured patients who had undergone elective surgery with an in-network surgeon at an in-network facility, approximately 1 in 5 received an out-of-network bill, with a mean potential balance bill of $2011.
In this analysis of commercially insured patients who had undergone elective surgery with an in-network surgeon at an in-network facility, approximately 1 in 5 received an out-of-network bill, with a mean potential balance bill of $2011.
 Our findings suggest that LAN (low-level light at night) exposure increases the incidence of diabetes in a general elderly population. Further research involving a large cohort with new-onset diabetes is warranted to elucidate these findings.
Our findings suggest that LAN (low-level light at night) exposure increases the incidence of diabetes in a general elderly population. Further research involving a large cohort with new-onset diabetes is warranted to elucidate these findings.