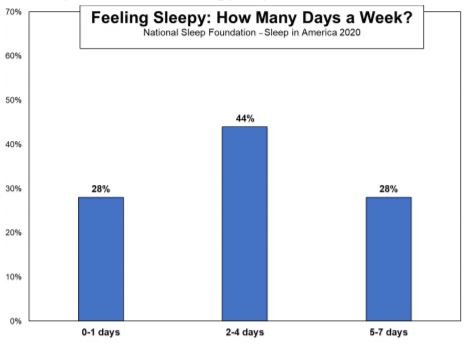
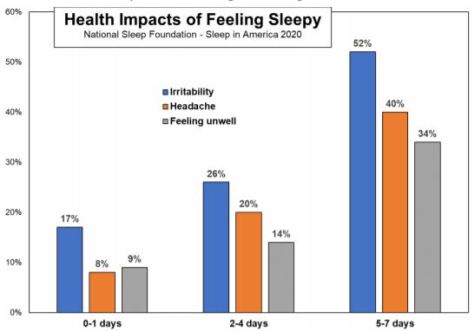
From U.S. News (July 7, 2020):
“Numerous studies have linked insufficient sleep with significant health consequences. Yet, many people ignore the signs of sleep problems or don’t allow enough time to get adequate sleep,” said lead researcher Eileen Leary. She is a senior manager of clinical research at Stanford University in Palo Alto, Calif.

“REM sleep appears to be a reliable predictor of mortality and may have other predictive health values,” Leary said. “Strategies to preserve REM may influence clinical therapies and reduce mortality risk, particularly for adults with less than 15% of REM sleep.”
REM (rapid eye movement) sleep is when dreams occur and the body repairs itself from the ravages of the day. For every 5% reduction in REM sleep, mortality rates increase 13% to 17% among older and middle-aged adults, researchers report.
For the study, Leary and her colleagues included more than 2,600 men, average age 76, who were followed for a median of 12 years. They also collected data on nearly 1,400 men and women, average age 52, who were part of another study and were followed for a median of 21 years.
Poor REM sleep was tied to early death from any cause as well as death from cardiovascular and other diseases, the researchers found.



 “The sleep environment is something that can easily be fixed,” Salas says. By giving a little thought to positioning your body and bed, you might find your slumber is even sweeter.
“The sleep environment is something that can easily be fixed,” Salas says. By giving a little thought to positioning your body and bed, you might find your slumber is even sweeter.

 His mission was to educate the world about the importance of sleep, which he believed was dangerously undervalued. His motto, “drowsiness is red alert,” is a message he tirelessly broadcast to his students, trainees, members of Congress and the world at large.
His mission was to educate the world about the importance of sleep, which he believed was dangerously undervalued. His motto, “drowsiness is red alert,” is a message he tirelessly broadcast to his students, trainees, members of Congress and the world at large.  With a handful of other scientists, Dement, a longtime faculty member of the
With a handful of other scientists, Dement, a longtime faculty member of the 
 “We’ve discovered that fragmented sleep is associated with a unique pathway — chronic circulating inflammation throughout the blood stream — which, in turn, is linked to higher amounts of plaques in coronary arteries,” said study senior author Matthew Walker, a UC Berkeley professor of psychology and neuroscience.
“We’ve discovered that fragmented sleep is associated with a unique pathway — chronic circulating inflammation throughout the blood stream — which, in turn, is linked to higher amounts of plaques in coronary arteries,” said study senior author Matthew Walker, a UC Berkeley professor of psychology and neuroscience.
 The first signs of insufficient sleep are universally familiar. There’s tiredness and fatigue, difficulty concentrating, perhaps irritability or even tired giggles. Far fewer people have experienced the effects of prolonged sleep deprivation, including disorientation, paranoia, and hallucinations.
The first signs of insufficient sleep are universally familiar. There’s tiredness and fatigue, difficulty concentrating, perhaps irritability or even tired giggles. Far fewer people have experienced the effects of prolonged sleep deprivation, including disorientation, paranoia, and hallucinations.



 The sleep industry caters to a working consumer’s wish to sleep less, yet sleep more productively, and accommodates transnational industry which has joined the state as a custodian of biopolitics. Jonathan Crary’s 24/7 spells out in detail how the state and a capitalist economy are encroaching stupendously on the private sphere, in which sleep was one of the last vestiges of unfettered time.
The sleep industry caters to a working consumer’s wish to sleep less, yet sleep more productively, and accommodates transnational industry which has joined the state as a custodian of biopolitics. Jonathan Crary’s 24/7 spells out in detail how the state and a capitalist economy are encroaching stupendously on the private sphere, in which sleep was one of the last vestiges of unfettered time.