From a Harvard news online release:
 “The results we saw were stunning and suggest that holistically addressing aging via gene therapy could be more effective than the piecemeal approach that currently exists,” said first author Noah Davidsohn, a former research scientist at the Wyss Institute and HMS who is now chief technology officer of Rejuvenate Bio. “Everyone wants to stay as healthy as possible for as long as possible, and this study is a first step toward reducing the suffering caused by debilitating diseases.”
“The results we saw were stunning and suggest that holistically addressing aging via gene therapy could be more effective than the piecemeal approach that currently exists,” said first author Noah Davidsohn, a former research scientist at the Wyss Institute and HMS who is now chief technology officer of Rejuvenate Bio. “Everyone wants to stay as healthy as possible for as long as possible, and this study is a first step toward reducing the suffering caused by debilitating diseases.”
New research from the Wyss Institute for Biologically Inspired Engineering at Harvard University and Harvard Medical School (HMS) suggests that it may be possible someday to tend to multiple ailments with one treatment.
The study was conducted in the lab of Wyss core faculty member George Church as part of Davidsohn’s postdoctoral research into the genetics of aging. Davidsohn, Church, and their co-authors homed in on three genes that had been shown to confer increased health and lifespan benefits in mice that were genetically engineered to overexpress them: FGF21, sTGFβR2, and αKlotho. They hypothesized that providing extra copies of those genes to nonengineered mice via gene therapy would similarly combat age-related diseases and bring health benefits.



 “Another behavior change is physical exercise,” Pillemer said. “A paradox of pain is that exercise helps reduce it, but it’s difficult for people in pain to think about exercising. So they don’t exercise, they get more sedentary and the pain increases; it’s a vicious circle. So how do you get people to actually change their behavior?”
“Another behavior change is physical exercise,” Pillemer said. “A paradox of pain is that exercise helps reduce it, but it’s difficult for people in pain to think about exercising. So they don’t exercise, they get more sedentary and the pain increases; it’s a vicious circle. So how do you get people to actually change their behavior?”
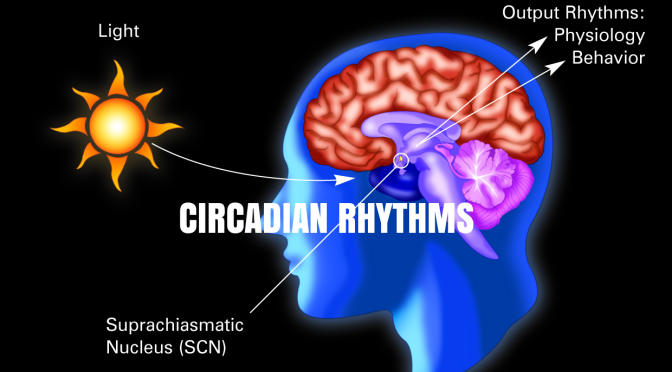
 When people are awake during the night, their behaviors are often mismatched with their internal body clocks. This can lead to nighttime eating, which can influence the way the body processes sugar and could lead to a higher risk in diabetes. “What happens when food is eaten when you normally should be fasting?” Scheer asked the audience. “What happens is that your glucose tolerance goes out the window….So your glucose levels after a meal are much higher.” This can increase people’s risk for diabetes.
When people are awake during the night, their behaviors are often mismatched with their internal body clocks. This can lead to nighttime eating, which can influence the way the body processes sugar and could lead to a higher risk in diabetes. “What happens when food is eaten when you normally should be fasting?” Scheer asked the audience. “What happens is that your glucose tolerance goes out the window….So your glucose levels after a meal are much higher.” This can increase people’s risk for diabetes.
 Measles is a dangerous infection that can kill. As many as 100,000 people die from the disease each year. For those who survive infection, the virus leaves a lasting mark—it appears to wipe out the immune system’s memory. News Intern Eva Fredrick joins host Sarah Crespi to talk about a pair of studies that looked at
Measles is a dangerous infection that can kill. As many as 100,000 people die from the disease each year. For those who survive infection, the virus leaves a lasting mark—it appears to wipe out the immune system’s memory. News Intern Eva Fredrick joins host Sarah Crespi to talk about a pair of studies that looked at 
 For new patients, whose visits entail more work than those of established patients,
For new patients, whose visits entail more work than those of established patients, 

 Researchers suggest that intensity is critical. Seniors who exercised using short, bursts of activity saw an improvement of up to 30 percent in
Researchers suggest that intensity is critical. Seniors who exercised using short, bursts of activity saw an improvement of up to 30 percent in 
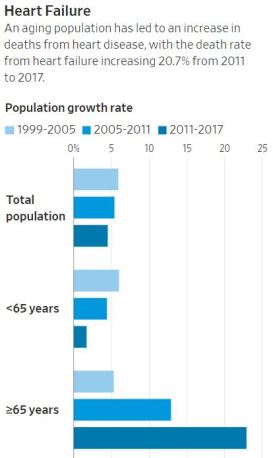 The findings help explain why a decadeslong decline in the death rate from cardiovascular disease has slowed substantially since 2011 and started rising in middle-aged people, helping
The findings help explain why a decadeslong decline in the death rate from cardiovascular disease has slowed substantially since 2011 and started rising in middle-aged people, helping  Mr. Chambers, a 48-year-old physical therapist in Jersey City, N.J., modified his sleep, diet and exercise routines. Eighteen months later, his performance on a battery of cognitive tests improved, particularly in areas like processing speed and executive function, such as decision-making and planning.
Mr. Chambers, a 48-year-old physical therapist in Jersey City, N.J., modified his sleep, diet and exercise routines. Eighteen months later, his performance on a battery of cognitive tests improved, particularly in areas like processing speed and executive function, such as decision-making and planning.