
Bury your nose in tales of neurosyphilis, gender identity, the medical mysteries of sleep disorders, and more. JAMES DOLBOW
The Nocturnal Brain: Nightmares, Neuroscience and the Secret World of Sleep
Inspired by the legendary book The Man Who Mistook His Wife for a Hat by the late Oliver Sacks, neurologist and sleep scientist Guy Leschziner tells the curious true stories of his patients, their fascinating sleep disorders, and the neuroscience behind each. Also like the works of Sacks, The Nocturnal Brain is written with considerable introspection and wonder about each patient’s case, taking you on a journey from the first patient encounter, to diagnosis, and through treatment. The unusual and often bizarre cases will keep you intrigued and immersed, and make this unique book one you will find yourself looking forward to making time to read.
 How The Brain Lost Its Mind: Sex, Hysteria, and the Riddle of Mental Health
How The Brain Lost Its Mind: Sex, Hysteria, and the Riddle of Mental Health
In this mindful reflection on American and European pasts, authors Allan H. Ropper and Brian Burrell, also the writers of Reaching Down the Rabbit Hole, address our modern concept of mental illness by reviewing the interesting true story of the syphilis epidemic of the 19th century. This little known and fascinating history of neurosyphilis—how it was handled by society and medicine and how it shaped today’s understanding of mental illness—helps address not only why many stigmas exist, but why so many have persisted. This book will take you on an incredible journey through the puzzling diagnosis, eclectic treatments, and lasting social effects of the neurosyphilis epidemic of the 1800s, as well as offer important insight into the difference between diseases of the brain and the mind. This book is perfect for any scientist, psychologist, or historian with even the smallest interest in medical history or mental health theory.
 Compassionomics: The Revolutionary Scientific Evidence that Caring Makes a Difference
Compassionomics: The Revolutionary Scientific Evidence that Caring Makes a Difference
It is no secret that today’s medical atmosphere scarsely resembles anything similar to that of 50 years ago. Many have argued that this is in large part due to a lack of compassion in the modern medical system. If this is the case, where have we gone wrong, and is there scientific evidence to support that compassion is even beneficial to healthcare, personal relationships, and professional lives? These questions are raised and explored by authors Stephen Trzeciak and Anthony Mazzarelli through the telling of true stories of medical providers and patients that help demonstrate the incredible effect of the human connection. Coupled perfectly with these gripping stories are easily readable summaries of decades of research studying the effects of compassion as well as its implications in our lives. Addressing topics from healthcare cost to provider burnout, from caring for others to caring for ourselves, this evidence-based analysis of the importance of compassion is a must-read for anyone interested in the social science and psychology of the care we give in all settings of our lives.
To read more: https://www.the-scientist.com/news-opinion/opinion–the-best-neuroscience-books-of-2019-66863
 In 2016, Samantha Harvey began to lose sleep. She tried everything to appease her wakefulness: from medication to therapy, changes in her diet to changes in her living arrangements. Nothing seemed to help.
In 2016, Samantha Harvey began to lose sleep. She tried everything to appease her wakefulness: from medication to therapy, changes in her diet to changes in her living arrangements. Nothing seemed to help.







 How The Brain Lost Its Mind: Sex, Hysteria, and the Riddle of Mental Health
How The Brain Lost Its Mind: Sex, Hysteria, and the Riddle of Mental Health Compassionomics: The Revolutionary Scientific Evidence that Caring Makes a Difference
Compassionomics: The Revolutionary Scientific Evidence that Caring Makes a Difference
 When the five sleep factors were collapsed into binary categories of low risk vs. high risk (reference group), early chronotype, adequate sleep duration, free of insomnia, and no frequent daytime sleepiness were each independently associated with incident CVD, with a 7%, 12%, 8%, and 15% lower risk, respectively (Table
When the five sleep factors were collapsed into binary categories of low risk vs. high risk (reference group), early chronotype, adequate sleep duration, free of insomnia, and no frequent daytime sleepiness were each independently associated with incident CVD, with a 7%, 12%, 8%, and 15% lower risk, respectively (Table 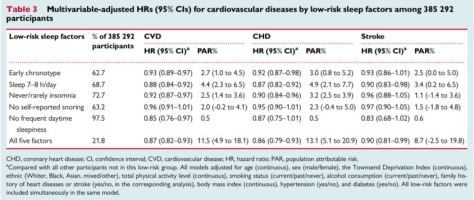 Cardiovascular disease (CVD), including coronary heart disease (CHD) and stroke, is among the leading causes of mortality globally.
Cardiovascular disease (CVD), including coronary heart disease (CHD) and stroke, is among the leading causes of mortality globally.

 Sleep problems may decrease the likelihood of recovery from chronic low
Sleep problems may decrease the likelihood of recovery from chronic low 
 Beyond the constant tossing and turning of a sleepless night, it might surprise you to know that insomnia is affecting a fair hunk of the Australian population. A recent study released by the Sleep Health Foundation found that 15 per cent of us suffer from chronic insomnia disorder, and very few people are choosing to access help.
Beyond the constant tossing and turning of a sleepless night, it might surprise you to know that insomnia is affecting a fair hunk of the Australian population. A recent study released by the Sleep Health Foundation found that 15 per cent of us suffer from chronic insomnia disorder, and very few people are choosing to access help.
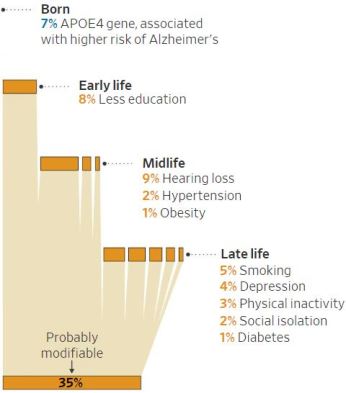
 When people are awake during the night, their behaviors are often mismatched with their internal body clocks. This can lead to nighttime eating, which can influence the way the body processes sugar and could lead to a higher risk in diabetes. “What happens when food is eaten when you normally should be fasting?” Scheer asked the audience. “What happens is that your glucose tolerance goes out the window….So your glucose levels after a meal are much higher.” This can increase people’s risk for diabetes.
When people are awake during the night, their behaviors are often mismatched with their internal body clocks. This can lead to nighttime eating, which can influence the way the body processes sugar and could lead to a higher risk in diabetes. “What happens when food is eaten when you normally should be fasting?” Scheer asked the audience. “What happens is that your glucose tolerance goes out the window….So your glucose levels after a meal are much higher.” This can increase people’s risk for diabetes. Mr. Chambers, a 48-year-old physical therapist in Jersey City, N.J., modified his sleep, diet and exercise routines. Eighteen months later, his performance on a battery of cognitive tests improved, particularly in areas like processing speed and executive function, such as decision-making and planning.
Mr. Chambers, a 48-year-old physical therapist in Jersey City, N.J., modified his sleep, diet and exercise routines. Eighteen months later, his performance on a battery of cognitive tests improved, particularly in areas like processing speed and executive function, such as decision-making and planning.