As we’re spending more time at home, it’s important to find new ways to remain active and exercise is important. Mayo Clinic physical therapist Sunni Alessandria and her colleagues offer some insight and tips for exercises you can do at home.
As we’re spending more time at home, it’s important to find new ways to remain active and exercise is important. Mayo Clinic physical therapist Sunni Alessandria and her colleagues offer some insight and tips for exercises you can do at home.
 Microwaves are used in medicine for disinfection of soft contact lenses, dental instruments, dentures, milk, and urinary catheters for intermittent self-catheterization925-931. However, microwaves must only be used with products that are compatible (e.g., do not melt) 931. Microwaves are radio-frequency waves, which are usually used at a frequency of 2450 MHz. The microwaves produce friction of water molecules in an alternating electrical field. The intermolecular friction derived from the vibrations generates heat and some authors believe that the effect of microwaves depends on the heat produced while others postulate a nonthermal lethal effect932-934. The initial reports showed microwaves to be an effective microbicide. The microwaves produced by a “home-type” microwave oven (2.45 GHz) completely inactivate bacterial cultures, mycobacteria, viruses, and G. stearothermophilus spores within 60 seconds to 5 minutes depending on the challenge organism933, 935-937. Another study confirmed these resuIts but also found that higher power microwaves in the presence of water may be needed for sterilization932. Complete destruction of Mycobacterium bovis was obtained with 4 minutes of microwave exposure (600W, 2450 MHz)937. The effectiveness of microwave ovens for different sterilization and disinfection purposes should be tested and demonstrated as test conditions affect the results (e.g., presence of water, microwave power). Sterilization of metal instruments can be accomplished but requires certain precautions.926. Of concern is that home-type microwave ovens may not have even distribution of microwave energy over the entire dry device (there may be hot and cold spots on solid medical devices); hence there may be areas that are not sterilized or disinfected. The use of microwave ovens to disinfect intermittent-use catheters also has been suggested. Researchers found that test bacteria (e.g., E. coli, Klebsiella pneumoniae, Candida albicans) were eliminated from red rubber catheters within 5 minutes 931. Microwaves used for sterilization of medical devices have not been FDA cleared.
Microwaves are used in medicine for disinfection of soft contact lenses, dental instruments, dentures, milk, and urinary catheters for intermittent self-catheterization925-931. However, microwaves must only be used with products that are compatible (e.g., do not melt) 931. Microwaves are radio-frequency waves, which are usually used at a frequency of 2450 MHz. The microwaves produce friction of water molecules in an alternating electrical field. The intermolecular friction derived from the vibrations generates heat and some authors believe that the effect of microwaves depends on the heat produced while others postulate a nonthermal lethal effect932-934. The initial reports showed microwaves to be an effective microbicide. The microwaves produced by a “home-type” microwave oven (2.45 GHz) completely inactivate bacterial cultures, mycobacteria, viruses, and G. stearothermophilus spores within 60 seconds to 5 minutes depending on the challenge organism933, 935-937. Another study confirmed these resuIts but also found that higher power microwaves in the presence of water may be needed for sterilization932. Complete destruction of Mycobacterium bovis was obtained with 4 minutes of microwave exposure (600W, 2450 MHz)937. The effectiveness of microwave ovens for different sterilization and disinfection purposes should be tested and demonstrated as test conditions affect the results (e.g., presence of water, microwave power). Sterilization of metal instruments can be accomplished but requires certain precautions.926. Of concern is that home-type microwave ovens may not have even distribution of microwave energy over the entire dry device (there may be hot and cold spots on solid medical devices); hence there may be areas that are not sterilized or disinfected. The use of microwave ovens to disinfect intermittent-use catheters also has been suggested. Researchers found that test bacteria (e.g., E. coli, Klebsiella pneumoniae, Candida albicans) were eliminated from red rubber catheters within 5 minutes 931. Microwaves used for sterilization of medical devices have not been FDA cleared.
From the National Institutes of Health (NIH) (March 17, 2020):
 “Finding a safe and effective vaccine to prevent infection with SARS-CoV-2 is an urgent public health priority,” said NIAID Director Anthony S. Fauci, M.D. “This Phase 1 study, launched in record speed, is an important first step toward achieving that goal.”
“Finding a safe and effective vaccine to prevent infection with SARS-CoV-2 is an urgent public health priority,” said NIAID Director Anthony S. Fauci, M.D. “This Phase 1 study, launched in record speed, is an important first step toward achieving that goal.”
The vaccine is called mRNA-1273 and was developed by NIAID scientists and their collaborators at the biotechnology company Moderna, Inc., based in Cambridge, Massachusetts. The Coalition for Epidemic Preparedness Innovations (CEPI) supported the manufacturing of the vaccine candidate for the Phase 1 clinical trial.
 A Phase 1 clinical trial evaluating an investigational vaccine designed to protect against coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) has begun at Kaiser Permanente Washington Health Research Institute (KPWHRI) in Seattle. The National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases (NIAID), part of the National Institutes of Health, is funding the trial. KPWHRI is part of NIAID’s Infectious Diseases Clinical Research Consortium. The open-label trial will enroll 45 healthy adult volunteers ages 18 to 55 years over approximately 6 weeks. The first participant received the investigational vaccine today.
A Phase 1 clinical trial evaluating an investigational vaccine designed to protect against coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) has begun at Kaiser Permanente Washington Health Research Institute (KPWHRI) in Seattle. The National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases (NIAID), part of the National Institutes of Health, is funding the trial. KPWHRI is part of NIAID’s Infectious Diseases Clinical Research Consortium. The open-label trial will enroll 45 healthy adult volunteers ages 18 to 55 years over approximately 6 weeks. The first participant received the investigational vaccine today.
The study is evaluating different doses of the experimental vaccine for safety and its ability to induce an immune response in participants. This is the first of multiple steps in the clinical trial process for evaluating the potential benefit of the vaccine.
From a New York Times online article (March 16, 2020):
 “Maintaining weight loss can get easier over time. Over time, less intentional effort, though not no effort, is needed to be successful. After about two years, healthy eating habits become part of the routine. Healthy choices become more automatic the longer people continue to make them. They feel weird when they don’t.”
“Maintaining weight loss can get easier over time. Over time, less intentional effort, though not no effort, is needed to be successful. After about two years, healthy eating habits become part of the routine. Healthy choices become more automatic the longer people continue to make them. They feel weird when they don’t.”
Among the useful strategies identified in the new study is to keep lower calorie foods like fruits and vegetables more accessible. “We eat what we see,” Dr. Phelan noted. The corollary is equally important: keep high-calorie, less nourishing foods relatively inaccessible and out of sight if not out of the house entirely.
The new study led by Dr. Phelan, professor of kinesiology and public health at California Polytechnic State University, identified habits and strategies that can be keys to success for millions. Yes, like most sensible weight-loss plans, they involve healthful eating and regular physical activity. But they also include important self-monitoring practices and nonpunitive coping measures that can be the crucial to long-term weight management.
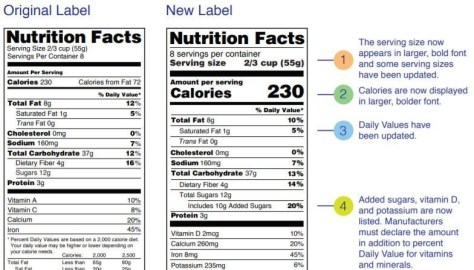
What’s new about the new Nutrition Facts label? Watch this Q&A with Susan T. Mayne, Ph.D., Director of FDA’s Center for Food Safety and Applied Nutrition.
From a BMJ Research online study (March 4, 2020):
 We found no association between egg consumption and risk of cardiovascular disease in three large US cohorts. Results from the updated meta-analysis lend further support to the overall lack of an association between moderate egg consumption (up to one egg per day) and cardiovascular disease risk.
We found no association between egg consumption and risk of cardiovascular disease in three large US cohorts. Results from the updated meta-analysis lend further support to the overall lack of an association between moderate egg consumption (up to one egg per day) and cardiovascular disease risk.
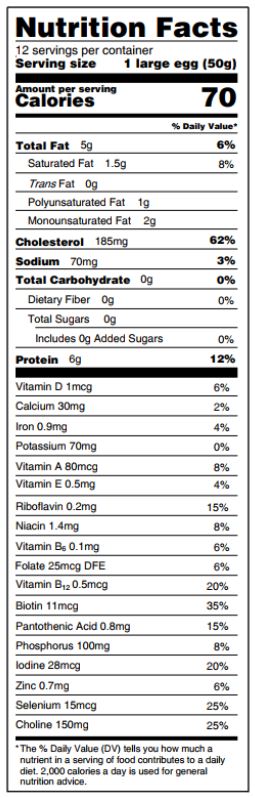 Eggs are a major source of dietary cholesterol, but they are also an affordable source of high quality protein, iron, unsaturated fatty acids, phospholipids, and carotenoids.
Eggs are a major source of dietary cholesterol, but they are also an affordable source of high quality protein, iron, unsaturated fatty acids, phospholipids, and carotenoids.
Introduction: In the United States, cardiovascular disease is the leading cause of death in men and women. Diet and lifestyle undisputedly play a major part in the development of cardiovascular disease. In the past, limiting dietary cholesterol intake to 300 mg per day was widely recommended to prevent cardiovascular disease. However, because of the weak association between dietary cholesterol and blood cholesterol, and considering that dietary cholesterol is no longer a nutrient of concern for overconsumption, the most recent 2015 dietary guidelines for Americans did not carry forward this recommendation.
From a Stanford University online article (March 2, 2020):
 “The opioid epidemic has added fuel to the HCV fire, substantially increasing transmission,” said Owens. “HCV is now an enormous public health problem, affecting a much broader age range of people than before. Fortunately, we have the tools to identify people and treatment is now successful in the vast majority of patients, so screening can prevent the mortality and morbidity from HCV.”
“The opioid epidemic has added fuel to the HCV fire, substantially increasing transmission,” said Owens. “HCV is now an enormous public health problem, affecting a much broader age range of people than before. Fortunately, we have the tools to identify people and treatment is now successful in the vast majority of patients, so screening can prevent the mortality and morbidity from HCV.”
A task force of national health experts recommends clinicians screen all adults 18 to 79 for the hepatitis C virus (HCV), noting that the viral infection is now associated with more deaths in the United States than the top 60 reportable infectious diseases combined. Many people are unaware they are carrying the viral infection.

“People with hepatitis C do not always feel sick and may not know they have it,” says chair of the U.S. Preventive Services Task Force Douglas K. Owens, M.D, M.S. “Screening is key to finding this infection early, when it’s easier to treat and cure, helping reduce illnesses and deaths.”
Owens, who is the director of Stanford Health Policy and the Henry J. Kaiser, Jr., Professor of Medicine, said the opioid epidemic now plays an important role in the prevalence of HCV. There are more than three times the number of acute HCV cases than a decade ago, particularly among young, white, injection drug users who live in rural areas. Women aged 15 to 44 have also been hit hard by the virus that is spread through contaminated blood.
Mar.03 — World Health Organization spokesman Tarik Jasarevic speaks from Geneva about the latest advice for avoiding the coronavirus. He also comments on efforts to develop a vaccine and advice for public health workers. He speaks on “Bloomberg Markets: European Open.”
From a BMJ Opinion article (Feb 28, 2020):
 A lack of adequate knowledge is probably the driving force for the public panic, particularly at the early stages of an outbreak—highlighting the fact that information is crucial. Misunderstandings about the information that is available, even worse exaggerating such information, may further aggravate the panic. Unfortunately, these phenomena are not uncommon. To relieve the public panic, an effective approach would be timely publication of trustworthy research evidence in a manner appropriate for the public.
A lack of adequate knowledge is probably the driving force for the public panic, particularly at the early stages of an outbreak—highlighting the fact that information is crucial. Misunderstandings about the information that is available, even worse exaggerating such information, may further aggravate the panic. Unfortunately, these phenomena are not uncommon. To relieve the public panic, an effective approach would be timely publication of trustworthy research evidence in a manner appropriate for the public.
Click here for real-time update
To date, there have been a number of reports and research papers published in peer reviewed journals. However, this information is largely aimed at researchers and healthcare professionals. The study findings are often obscure for the general public. Some of the published evidence is reporting on early findings and there are some methodological limitations. If inappropriately interpreted, they could misinform the public and could potentially cause further panic or psychological stress. We believe that providing the public with timely and credible evidence and appropriate interpretation is very important. Disseminating the evidence effectively is critical to improving the public’s understanding of the outbreak.
