
Conclusion: The study was inconclusive with respect to potential differences in progression of individual radiographic features after surgical and non-surgical treatment for degenerative meniscal tear. Further, we found no strong evidence in support of differences in development of incident radiographic knee osteoarthritis or patient-reported outcomes between exercise therapy and arthroscopic partial meniscectomy.
Objective: To evaluate progression of individual radiographic features 5 years following exercise therapy or arthroscopic partial meniscectomy as treatment for degenerative meniscal tear.
Design: Randomized controlled trial including 140 adults, aged 35-60 years, with a magnetic resonance image verified degenerative meniscal tear, and 96% without definite radiographic knee osteoarthritis. Participants were randomized to either 12-weeks of supervised exercise therapy or arthroscopic partial meniscectomy. The primary outcome was between-group difference in progression of tibiofemoral joint space narrowing and marginal osteophytes at 5 years, assessed semi-quantitatively by the OARSI atlas. Secondary outcomes included incidence of radiographic knee osteoarthritis and symptomatic knee osteoarthritis, medial tibiofemoral fixed joint space width (quantitatively assessed), and patient-reported outcome measures. Statistical analyses were performed using a full analysis set. Per protocol and as treated analysis were also performed.
Results: The risk ratios (95% CI) for progression of semi-quantitatively assessed joint space narrowing and medial and lateral osteophytes for the surgery group were 0.89 (0.55-1.44), 1.15 (0.79-1.68) and 0.77 (0.42-1.42), respectively, compared to the exercise therapy group. In secondary outcomes (full-set analysis) no statistically significant between-group differences were found.


 This relationship between higher glucose levels and poorer cognitive functioning extended beyond just CASI z-score, as well, Cukierman-Yaffe noted. Higher HbA1c levels were also tied to significantly poorer performance in other psychological tests, including the clock making test of executive functioning, test of discriminative ability, and for the test of verbal fluency.
This relationship between higher glucose levels and poorer cognitive functioning extended beyond just CASI z-score, as well, Cukierman-Yaffe noted. Higher HbA1c levels were also tied to significantly poorer performance in other psychological tests, including the clock making test of executive functioning, test of discriminative ability, and for the test of verbal fluency.
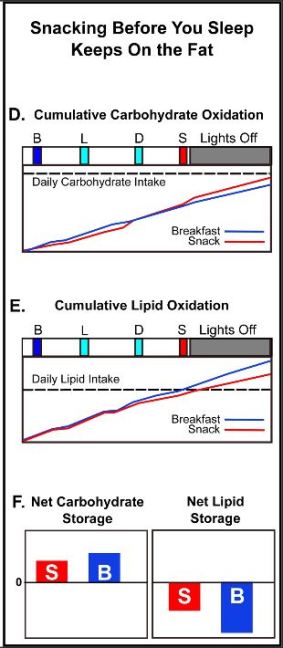
 These daily oscillations are controlled by the circadian clock, which is composed of an autoregulatory biochemical mechanism that is expressed in tissues throughout the body and is coordinated by a master pacemaker located in the suprachiasmatic nuclei of the brain (aka the SCN [
These daily oscillations are controlled by the circadian clock, which is composed of an autoregulatory biochemical mechanism that is expressed in tissues throughout the body and is coordinated by a master pacemaker located in the suprachiasmatic nuclei of the brain (aka the SCN [
 When your heart beats faster than usual, it can mean that you’re coming down with a cold, flu, coronavirus, or other viral infection. That’s the conclusion of recent medical
When your heart beats faster than usual, it can mean that you’re coming down with a cold, flu, coronavirus, or other viral infection. That’s the conclusion of recent medical 
 “Maintaining weight loss can get easier over time. Over time, less intentional effort, though not no effort, is needed to be successful. After about two years, healthy eating habits become part of the routine. Healthy choices become more automatic the longer people continue to make them. They feel weird when they don’t.”
“Maintaining weight loss can get easier over time. Over time, less intentional effort, though not no effort, is needed to be successful. After about two years, healthy eating habits become part of the routine. Healthy choices become more automatic the longer people continue to make them. They feel weird when they don’t.”
 Overall, the evidence in the literature suggests that spirulina improves several well-established CVD risk factors including hyperlipidaemia and seems to provide benefits around weight loss.
Overall, the evidence in the literature suggests that spirulina improves several well-established CVD risk factors including hyperlipidaemia and seems to provide benefits around weight loss. 

 cookies and pies, salty snacks, frozen and shelf-stable dishes, pizza, and breakfast cereals.
cookies and pies, salty snacks, frozen and shelf-stable dishes, pizza, and breakfast cereals.
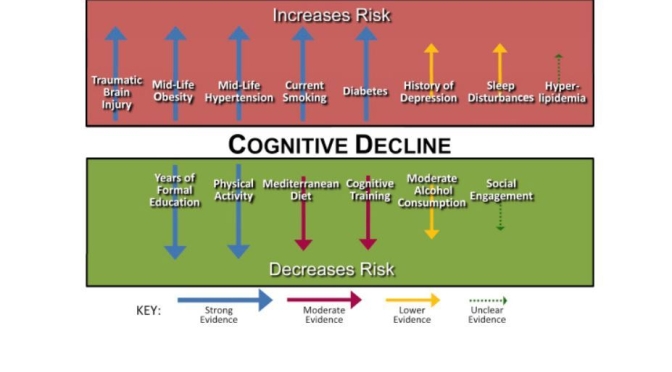
 “These results are exciting, as they suggest that people may potentially prevent brain shrinking and the effects of aging on the brain simply by becoming more active,” said study author Yian Gu, Ph.D., of Columbia University in New York and a member of the American Academy of Neurology.
“These results are exciting, as they suggest that people may potentially prevent brain shrinking and the effects of aging on the brain simply by becoming more active,” said study author Yian Gu, Ph.D., of Columbia University in New York and a member of the American Academy of Neurology.
 Habitual fish oil supplementation is associated with a 13% lower risk of all cause mortality, a 16% lower risk of CVD mortality, and a 7% lower risk of CVD events among the general population
Habitual fish oil supplementation is associated with a 13% lower risk of all cause mortality, a 16% lower risk of CVD mortality, and a 7% lower risk of CVD events among the general population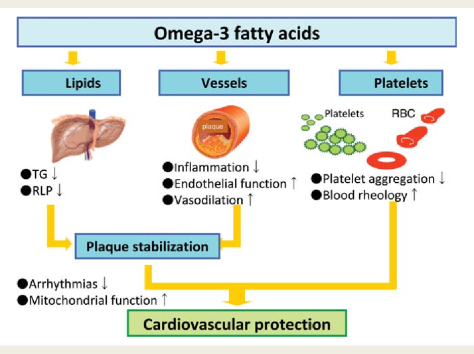

 Seasonal variation in blood pressure has been known for 40 years, but, to our knowledge, for the first time we show here that this occurs independently of temperature. The reduction in blood pressure is more marked with a rise in UVB than UVA, and in whites than black people. Dermatological concerns about the skin cancer inducing effects of UV radiation need to be balanced against the observed blood pressure lowering effects of sunlight, particularly given the greatly higher burden of disease caused by hypertension.
Seasonal variation in blood pressure has been known for 40 years, but, to our knowledge, for the first time we show here that this occurs independently of temperature. The reduction in blood pressure is more marked with a rise in UVB than UVA, and in whites than black people. Dermatological concerns about the skin cancer inducing effects of UV radiation need to be balanced against the observed blood pressure lowering effects of sunlight, particularly given the greatly higher burden of disease caused by hypertension. Sunlight exposure appears to lower blood pressure; insufficient exposure to natural ultraviolet radiation and/or active avoidance of sunlight may be new risk factors for hypertension.
Sunlight exposure appears to lower blood pressure; insufficient exposure to natural ultraviolet radiation and/or active avoidance of sunlight may be new risk factors for hypertension.