From a MedPageToday online article:
 “Amyloid is important in initiating disease, but the actual damage in the brain is probably due to the accumulation of tau,” Holtzman told MedPage Today. “Normally, tau protein is inside cells, but there is more and more evidence suggesting that its spread to different parts of the brain is responsible for the progression of Alzheimer’s disease.”
“Amyloid is important in initiating disease, but the actual damage in the brain is probably due to the accumulation of tau,” Holtzman told MedPage Today. “Normally, tau protein is inside cells, but there is more and more evidence suggesting that its spread to different parts of the brain is responsible for the progression of Alzheimer’s disease.”
Two studies in January explored how sleep might be associated with Alzheimer’s tau pathology. The first, led by Brendan Lucey, MD, and David Holtzman, MD, both of Washington University in St. Louis, found that older adults who had less slow-wave sleep had higher levels of brain tau.
The findings, published in Science Translational Medicine, suggested that poor quality sleep in late life may signal deteriorating brain health.
Sleep patterns predicted amyloid and tau burden, reported Matthew Walker, PhD, of the University of California Berkeley, and co-authors, in June.





 Mr. Chambers, a 48-year-old physical therapist in Jersey City, N.J., modified his sleep, diet and exercise routines. Eighteen months later, his performance on a battery of cognitive tests improved, particularly in areas like processing speed and executive function, such as decision-making and planning.
Mr. Chambers, a 48-year-old physical therapist in Jersey City, N.J., modified his sleep, diet and exercise routines. Eighteen months later, his performance on a battery of cognitive tests improved, particularly in areas like processing speed and executive function, such as decision-making and planning.
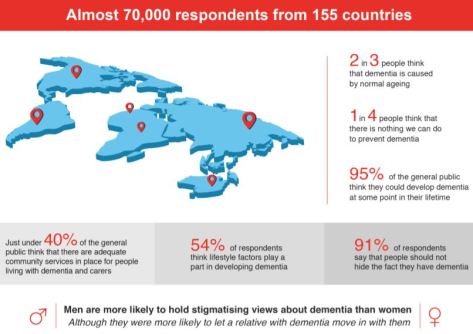
 LSE developed the survey to target four key groups:
LSE developed the survey to target four key groups: In the survey analysis we highlight the behavioural element first, giving prominence to the voices and experiences of people living with dementia as direct assessment of actual behaviour is central to discrimination and is the closest representation of the true impact of stigma on people living with dementia.
In the survey analysis we highlight the behavioural element first, giving prominence to the voices and experiences of people living with dementia as direct assessment of actual behaviour is central to discrimination and is the closest representation of the true impact of stigma on people living with dementia. “The risk for dementia is elevated about twofold in people who have diabetes or
“The risk for dementia is elevated about twofold in people who have diabetes or  A blood test to detect the brain changes of early Alzheimer’s disease has moved one step closer to reality. Researchers from Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis report that they can measure levels of the Alzheimer’s protein amyloid beta in the blood and use such levels to predict whether the protein has accumulated in the brain. The findings represent a key step toward a blood test to diagnose people on track to develop the devastating disease before symptoms arise.
A blood test to detect the brain changes of early Alzheimer’s disease has moved one step closer to reality. Researchers from Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis report that they can measure levels of the Alzheimer’s protein amyloid beta in the blood and use such levels to predict whether the protein has accumulated in the brain. The findings represent a key step toward a blood test to diagnose people on track to develop the devastating disease before symptoms arise. “We found staggering inconsistencies between how costs of dementia are calculated across studies and our analysis strongly supports that current estimates fail to recognise the true costs of the diseases, such as Alzheimer’s, that cause dementia. Some studies have estimated that out of pocket expenses for people with dementia are up to one third of their household wealth in the final five years of their life, and that caregivers have healthcare costs that are twice as high as non-caregivers. We also found evidence that costs begin rising up to 10 years prior to diagnosis — we need to better measure and factor all these into future societal cost estimates.”
“We found staggering inconsistencies between how costs of dementia are calculated across studies and our analysis strongly supports that current estimates fail to recognise the true costs of the diseases, such as Alzheimer’s, that cause dementia. Some studies have estimated that out of pocket expenses for people with dementia are up to one third of their household wealth in the final five years of their life, and that caregivers have healthcare costs that are twice as high as non-caregivers. We also found evidence that costs begin rising up to 10 years prior to diagnosis — we need to better measure and factor all these into future societal cost estimates.”
 Scientists are beginning to understand why Alzheimer’s disease affects more women than men and why the disease seems to progress more quickly in women’s brains.
Scientists are beginning to understand why Alzheimer’s disease affects more women than men and why the disease seems to progress more quickly in women’s brains.