From a Technology Networks online article:
 By comparing the pancreatic cells of type 2 diabetic human donors with those of healthy people, researchers at the University of Geneva (UNIGE) and at the University Hospitals of Geneva (HUG), Switzerland, were able to demonstrate, for the first time, that the pancreatic islet cells derived from the Type 2 Diabetic human donors bear compromised circadian oscillators.
By comparing the pancreatic cells of type 2 diabetic human donors with those of healthy people, researchers at the University of Geneva (UNIGE) and at the University Hospitals of Geneva (HUG), Switzerland, were able to demonstrate, for the first time, that the pancreatic islet cells derived from the Type 2 Diabetic human donors bear compromised circadian oscillators.
The disruption of the circadian clocks was concomitant with the perturbation of hormone secretion. Moreover, using clock modulator molecule dubbed Nobiletin, extracted from lemon peel, the researchers succeeded in “repairing” the disrupted cellular clocks and in partial restoring of the islet cell function. These results, published in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States, provide a first insight into innovative approach for diabetes care.

Read full study
The circadian clock system (from Latin “circa diem”, about a day) allows the organisms to anticipate periodical changes of geophysical time, and to adjust to these changes. Nearly all the cells in our body comprise molecular clocks that regulate and synchronize metabolic functions to a 24-hour cycle of day-night changes.
Today, increasing evidence show that disturbances in our internal clocks stemming from frequent time zone changes, irregular working schedules or ageing, have a significant impact on the development of metabolic diseases in human beings, including type-2 diabetes. Such disturbances seem to prevent the proper functioning of the cells in the pancreatic islet that secrete insulin and glucagon, the hormones that regulate blood sugar levels.
To read more
 “Dysfunctional sleep likely is by far the most prevalent comorbidity in CVD. This makes it essential to explore the nature of sleep, but this is reliant on the enthusiasm of clinician scientists,” according to the editorialists.
“Dysfunctional sleep likely is by far the most prevalent comorbidity in CVD. This makes it essential to explore the nature of sleep, but this is reliant on the enthusiasm of clinician scientists,” according to the editorialists.

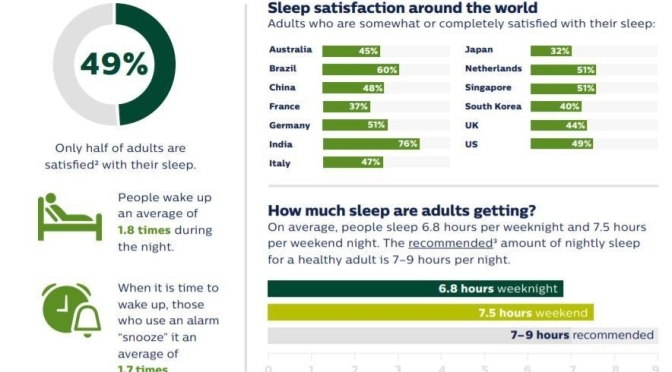
 “The decrease in people taking action to improve sleep is alarming, especially when it is clear people around the world deeply value sleep. Sleep deficit impacts people both mentally and physically, so we need to educate people on available sleep resources and empower them with the confidence that their efforts will pay off,” said Mark Aloia, PhD, Global Lead for Behavior Change, Sleep & Respiratory Care at Philips.
“The decrease in people taking action to improve sleep is alarming, especially when it is clear people around the world deeply value sleep. Sleep deficit impacts people both mentally and physically, so we need to educate people on available sleep resources and empower them with the confidence that their efforts will pay off,” said Mark Aloia, PhD, Global Lead for Behavior Change, Sleep & Respiratory Care at Philips.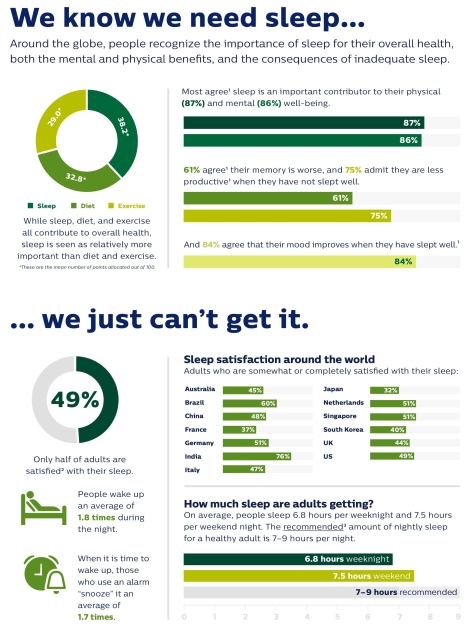

 Our findings suggest that LAN (low-level light at night) exposure increases the incidence of diabetes in a general elderly population. Further research involving a large cohort with new-onset diabetes is warranted to elucidate these findings.
Our findings suggest that LAN (low-level light at night) exposure increases the incidence of diabetes in a general elderly population. Further research involving a large cohort with new-onset diabetes is warranted to elucidate these findings.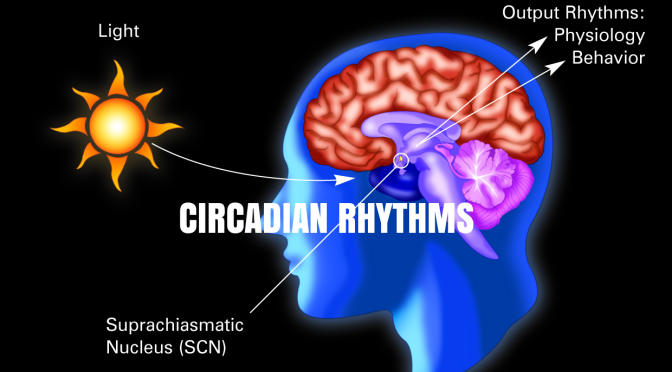
 By comparing the pancreatic cells of type 2 diabetic human donors with those of healthy people, researchers at the University of Geneva (UNIGE) and at the University Hospitals of Geneva (HUG), Switzerland, were able to demonstrate, for the first time, that the pancreatic islet cells derived from the Type 2 Diabetic human donors bear compromised circadian oscillators.
By comparing the pancreatic cells of type 2 diabetic human donors with those of healthy people, researchers at the University of Geneva (UNIGE) and at the University Hospitals of Geneva (HUG), Switzerland, were able to demonstrate, for the first time, that the pancreatic islet cells derived from the Type 2 Diabetic human donors bear compromised circadian oscillators. 

 can develop a conditioned fear of not being able to sleep, which puts them in a state of hyperarousal when they attempt to fall asleep. This makes their inability to sleep a self-fulfilling prophecy.
can develop a conditioned fear of not being able to sleep, which puts them in a state of hyperarousal when they attempt to fall asleep. This makes their inability to sleep a self-fulfilling prophecy.
 “Amyloid is important in initiating disease, but the actual damage in the brain is probably due to the accumulation of tau,” Holtzman told MedPage Today. “Normally, tau protein is inside cells, but there is more and more evidence suggesting that its spread to different parts of the brain is responsible for the progression of Alzheimer’s disease.”
“Amyloid is important in initiating disease, but the actual damage in the brain is probably due to the accumulation of tau,” Holtzman told MedPage Today. “Normally, tau protein is inside cells, but there is more and more evidence suggesting that its spread to different parts of the brain is responsible for the progression of Alzheimer’s disease.”
 In 2016, Samantha Harvey began to lose sleep. She tried everything to appease her wakefulness: from medication to therapy, changes in her diet to changes in her living arrangements. Nothing seemed to help.
In 2016, Samantha Harvey began to lose sleep. She tried everything to appease her wakefulness: from medication to therapy, changes in her diet to changes in her living arrangements. Nothing seemed to help.



 When the five sleep factors were collapsed into binary categories of low risk vs. high risk (reference group), early chronotype, adequate sleep duration, free of insomnia, and no frequent daytime sleepiness were each independently associated with incident CVD, with a 7%, 12%, 8%, and 15% lower risk, respectively (Table
When the five sleep factors were collapsed into binary categories of low risk vs. high risk (reference group), early chronotype, adequate sleep duration, free of insomnia, and no frequent daytime sleepiness were each independently associated with incident CVD, with a 7%, 12%, 8%, and 15% lower risk, respectively (Table 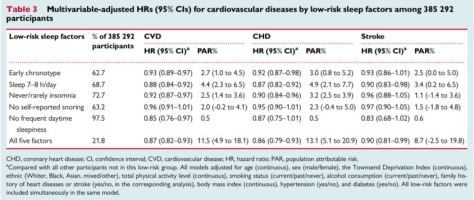 Cardiovascular disease (CVD), including coronary heart disease (CHD) and stroke, is among the leading causes of mortality globally.
Cardiovascular disease (CVD), including coronary heart disease (CHD) and stroke, is among the leading causes of mortality globally.