What’s new about the new Nutrition Facts label? Watch this Q&A with Susan T. Mayne, Ph.D., Director of FDA’s Center for Food Safety and Applied Nutrition.
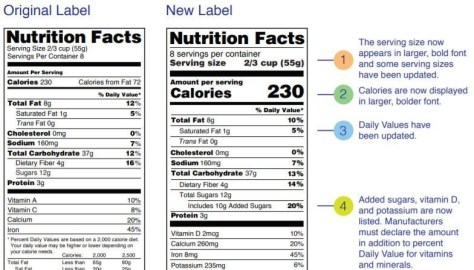
What’s new about the new Nutrition Facts label? Watch this Q&A with Susan T. Mayne, Ph.D., Director of FDA’s Center for Food Safety and Applied Nutrition.

From a BMJ Open Heart online study (March 8, 2020):
 Overall, the evidence in the literature suggests that spirulina improves several well-established CVD risk factors including hyperlipidaemia and seems to provide benefits around weight loss.
Overall, the evidence in the literature suggests that spirulina improves several well-established CVD risk factors including hyperlipidaemia and seems to provide benefits around weight loss.
Although caloric restriction and exercise are the mainstay treatments for obesity, spirulina has shown significant benefits in aiding weight loss. The phycocyanin in spirulina contains a light-harvesting chromophore called phycocyanobilin, which is capable of inhibiting nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate hydrogen (NADPH) oxidase, a significant source of oxidative stress in adipocytes playing a key role in inducing insulin resistance and shifting adipokine and cytokine production in hypertrophied adipocytes. Thus, by suppressing adipocyte oxidative stress, spirulina may lead to systemic anti-inflammatory and insulin-sensitising effects.

Spirulina is both a salt and fresh water blue-green algae, which is being increasingly studied recently. Spirulina was initially classified under the plant kingdom due to its rich plant pigments and its ability to photosynthesize, but was later placed into bacterial kingdom (cyanobacteria) due to its genetic, physiological and biochemical makeup. Spirulina grows naturally in high salt alkaline water reservoirs in subtropical and tropical areas of America, Mexico, Asia and Central Africa.
From a BMJ Research online study (March 4, 2020):
 We found no association between egg consumption and risk of cardiovascular disease in three large US cohorts. Results from the updated meta-analysis lend further support to the overall lack of an association between moderate egg consumption (up to one egg per day) and cardiovascular disease risk.
We found no association between egg consumption and risk of cardiovascular disease in three large US cohorts. Results from the updated meta-analysis lend further support to the overall lack of an association between moderate egg consumption (up to one egg per day) and cardiovascular disease risk.
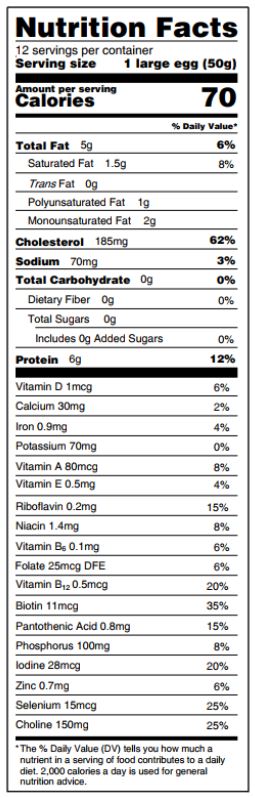 Eggs are a major source of dietary cholesterol, but they are also an affordable source of high quality protein, iron, unsaturated fatty acids, phospholipids, and carotenoids.
Eggs are a major source of dietary cholesterol, but they are also an affordable source of high quality protein, iron, unsaturated fatty acids, phospholipids, and carotenoids.
Introduction: In the United States, cardiovascular disease is the leading cause of death in men and women. Diet and lifestyle undisputedly play a major part in the development of cardiovascular disease. In the past, limiting dietary cholesterol intake to 300 mg per day was widely recommended to prevent cardiovascular disease. However, because of the weak association between dietary cholesterol and blood cholesterol, and considering that dietary cholesterol is no longer a nutrient of concern for overconsumption, the most recent 2015 dietary guidelines for Americans did not carry forward this recommendation.
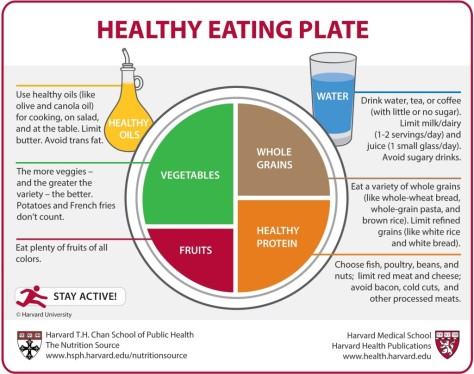
Aim for color and variety, and remember that potatoes don’t count as vegetables on the Healthy Eating Plate because of their negative impact on blood sugar.
Whole and intact grains—whole wheat, barley, wheat berries, quinoa, oats, brown rice, and foods made with them, such as whole wheat pasta—have a milder effect on blood sugar and insulin than white bread, white rice, and other refined grains.
Fish, poultry, beans, and nuts are all healthy, versatile protein sources—they can be mixed into salads, and pair well with vegetables on a plate. Limit red meat, and avoid processed meats such as bacon and sausage.
Choose healthy vegetable oils like olive, canola, soy, corn, sunflower, peanut, and others, and avoid partially hydrogenated oils, which contain unhealthy trans fats. Remember that low-fat does not mean “healthy.”
Skip sugary drinks, limit milk and dairy products to one to two servings per day, and limit juice to a small glass per day.
The red figure running across the Healthy Eating Plate’s placemat is a reminder that staying active is also important in weight control.
The main message of the Healthy Eating Plate is to focus on diet quality.
From BMJ Journal “Gut” study (February 17, 2020):
 We observed that increased adherence to the MedDiet modulates specific components of the gut microbiota that were associated with a reduction in risk of frailty, improved cognitive function and reduced inflammatory status.
We observed that increased adherence to the MedDiet modulates specific components of the gut microbiota that were associated with a reduction in risk of frailty, improved cognitive function and reduced inflammatory status.
Objective Ageing is accompanied by deterioration of multiple bodily functions and inflammation, which collectively contribute to frailty. We and others have shown that frailty co-varies with alterations in the gut microbiota in a manner accelerated by consumption of a restricted diversity diet. The Mediterranean diet (MedDiet) is associated with health. In the NU-AGE project, we investigated if a 1-year MedDiet intervention could alter the gut microbiota and reduce frailty.
Design We profiled the gut microbiota in 612 non-frail or pre-frail subjects across five European countries (UK, France, Netherlands, Italy and Poland) before and after the administration of a 12-month long MedDiet intervention tailored to elderly subjects (NU-AGE diet).
Results Adherence to the diet was associated with specific microbiome alterations. Taxa enriched by adherence to the diet were positively associated with several markers of lower frailty and improved cognitive function, and negatively associated with inflammatory markers including C-reactive protein and interleukin-17. Analysis of the inferred microbial metabolite profiles indicated that the diet-modulated microbiome change was associated with an increase in short/branch chained fatty acid production and lower production of secondary bile acids, p-cresols, ethanol and carbon dioxide. Microbiome ecosystem network analysis showed that the bacterial taxa that responded positively to the MedDiet intervention occupy keystone interaction positions, whereas frailty-associated taxa are peripheral in the networks.
Conclusion Collectively, our findings support the feasibility of improving the habitual diet to modulate the gut microbiota which in turn has the potential to promote healthier ageing.
“Our findings show dining out is a recipe for unhealthy eating most of the time,” said Dariush Mozaffarian, senior author and dean of the Friedman School.
At fast-food restaurants, 70 percent of the meals Americans consumed were of poor dietary quality in 2015-16, down from 75 percent in 2003-04. At full-service restaurants, about 50 percent were of poor nutritional quality, an amount that remained stable over the study period. The remainder were of intermediate nutritional quality.
BOSTON (Jan. 29, 2020, 9:00 a.m. EST)—The typical American adult gets one of every five  calories from a restaurant, but eating out is a recipe for meals of poor nutritional quality in most cases, according to a new study by researchers at the Friedman School of Nutrition Science and Policy at Tufts University.
calories from a restaurant, but eating out is a recipe for meals of poor nutritional quality in most cases, according to a new study by researchers at the Friedman School of Nutrition Science and Policy at Tufts University.

Published today in The Journal of Nutrition, the study analyzed the dietary selections of more than 35,000 U.S. adults from 2003-2016 in the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES) who dined at full-service (those with wait staff) or fast-food restaurants, which included pizza shops and what has become known as fast-casual. The researchers assessed nutritional quality by evaluating specific foods and nutrients in the meals, based on the American Heart Association 2020 diet score.
Did you know the food choices you make every day could help you feel younger? Try these 8 diet tips for feeling your best at any age.
Get more healthy living tips from the Mayo Clinic App: http://mayocl.in/2tbMb57