At HMS, Maofu Liao is establishing a new research pipeline to improve the process of antibiotic development https://t.co/4G2nyGKzWQ
— Harvard Medical School (@harvardmed) November 4, 2021
Tag Archives: Antibiotics
Science: Accupuncture’s Inflammation Effect, Antibiotics & Gut Bacteria
The neurons behind acupuncture’s effect on inflammation, and how antibiotics affect gut bacteria.
In this episode:
00:54 The neuronal basis for acupuncture’s effect on inflammation
In mice, electroacupuncture has been shown to reduce inflammation, but only when certain points on the body are stimulated. Why this is has puzzled scientists, but now, researchers have identified the specific neurons that are involved. They hope that this knowledge could be used in future to help treat certain inflammatory-related diseases.
Research article: Liu et al.
News and Views: Electroacupuncture activates neurons to switch off inflammation
07:28 Research Highlights
The Aztec origins of an obsidian ‘spirit mirror’, and the damage done by a Soviet plutonium complex.
Research Highlight: A ‘spirit mirror’ used in Elizabeth I’s court had Aztec roots
Research Highlight: Cold-war spy pictures reveal a Soviet nuclear ‘cloud generator’
10:18 Assessing antibiotics’ collateral damage.
Antibiotics are known to cause damage to the communities of bacteria that live in our guts. To better understand why this happens, a team has mapped the effects that different antibiotics have on individual gut-bacteria species, which may offer new insights into preventing this collateral damage.
Research article: Maier et al.
17:32 Briefing Chat
We discuss some highlights from the Nature Briefing. This time, the latest species to be declared extinct in the US, and a potential planet that orbits three stars.
New York Times: Protected Too Late: U.S. Officials Report More Than 20 Extinctions
New York Times: This May Be the First Planet Found Orbiting 3 Stars at Once
Analysis: Multiresistant Bacteria That Outsmart Antibiotics (Video)
Antimicrobial resistance is one of the greatest medical challenges of our time. Among the causes are industrial livestock farming, poor hygiene in hospitals, and the misuse of antibiotics. This documentary looks at approaches to fighting multiresistant strains of bacteria.
Each year 33,000 people in Europe die after becoming infected with bacteria that are resistant to antibiotics. Hygiene specialist Dr. Ron Hendrix has been working for years to prevent outbreaks of infectious disease in hospitals. Dr. Hendrix says that he and other experts in the Netherlands recognized early on that they’d have to fight the spread of bacteria just as actively as they would the actual infection.
Hendrix has convinced a number of German hospitals to re-open their diagnostic laboratories, as well. In the early 2000s, many of these labs had been shut down as a cost-cutting measure. And farmers in Denmark voluntarily chose to sharply reduce their use of antibiotics, after evidence showed that intensive livestock farming caused multiresistant bacteria to multiply.
Infectious disease specialist Dr. Patrick Soentjens was able to convince Belgium’s health ministry to allow the use of “phages” to treat stubborn antimicrobial resistant pathogens. Phages are special viruses that kill bacteria. Dr. Soentjens is certain that this well-known, but largely forgotten option could save many lives. Belgium has become the first western European country where phages have been officially recognized as a legitimate medical treatment.
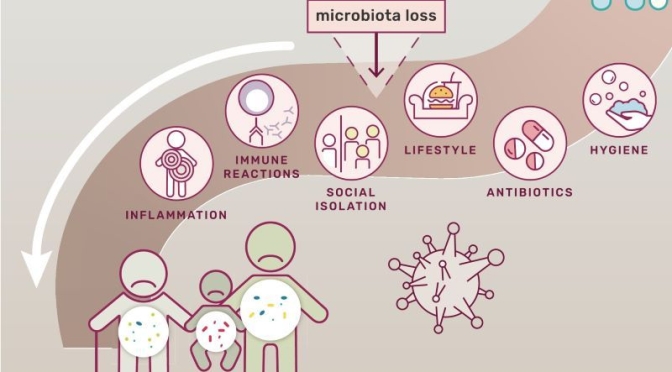
Covid-19 Analysis: The Negative Health Effects Of Microbiome Loss (PNAS)
Science Podcast: Fish Farming, Skin Microbes

These days, about half of the protein the world’s population eats is from seafood. Staff Writer Erik Stokstad joins host Sarah Crespi to talk about how brand-new biotech and old-fashioned breeding programs are helping keep up with demand, by expanding where we can farm fish and how fast we can grow them.
Sarah also spoke with Jan Claesen, an assistant professor at the Cleveland Clinic’s Lerner Research Institute, about skin microbes that use their own antibiotic to fight off harmful bacteria. Understanding the microbes native to our skin and the molecules they produce could lead to treatments for skin disorders such as atopic dermatitis and acne. Finally, in a segment sponsored by MilliporeSigma, Science’s Custom Publishing Director and Senior Editor Sean Sanders talks with Timothy Cernak, an assistant professor of medicinal chemistry and chemistry at the University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, about retrosynthesis—the process of starting with a known chemical final product and figuring out how to make that molecule efficiently from available pieces.
TOP JOURNALS: RESEARCH HIGHLIGHTS FROM SCIENCE MAGAZINE (NOV 6, 2020)
Medical Infographic: “Antimicrobial Resistance”
Top New Science Podcasts: ‘Sniff-Response’, Carbon Dioxide And Vaccinations Replacing Antibiotics
 This week, how the ‘sniff-response’ can help clinicians determine a patient’s state of consciousness, and how vaccines could help drive down antibiotic use.
This week, how the ‘sniff-response’ can help clinicians determine a patient’s state of consciousness, and how vaccines could help drive down antibiotic use.
In this episode:
00:45 Sniffing out consciousness
Researchers have found that the sniff reflex can indicate whether a patient is in a vegetative state, and even the likelihood that they will recover consciousness. Research Article: Arzi et al.
08:37 Research Highlights
The stupefying effect of carbon dioxide, and a chameleon gemstone that tricks your eyes. Research Highlight: Rising carbon dioxide levels will make us stupider; Research Highlight: How a chameleon gemstone changes from red to green
11:12 Vaccination and antibiotic usage
Looking at data from low- and middle-income countries, researchers have determined that vaccination could prevent millions of infections currently treated by antibiotics. Research Article: Lewnard et al.
16:49 Pick of the Briefing
We pick our highlights from the Nature Briefing, including the forgotten mother of climate change science, and a new global study on insect declines. Chemistry World: Eunice Foote: the mother of climate change; Science: Meta-analysis reveals declines in terrestrial but increases in freshwater insect abundances
Study: “Probiotic Drink” Developed That Thwarts Antibiotic Resistance
From a Genetic Engineering & Biotechnology News online article:
 “We were able to show that if you can stop the plasmid from replicating, then most of the bacteria lose the plasmid as the bacteria grow and divide. This means that infections that might otherwise be hard to control, even with the most powerful antibiotics available, are more likely to be treatable with standard antibiotics.”
“We were able to show that if you can stop the plasmid from replicating, then most of the bacteria lose the plasmid as the bacteria grow and divide. This means that infections that might otherwise be hard to control, even with the most powerful antibiotics available, are more likely to be treatable with standard antibiotics.”
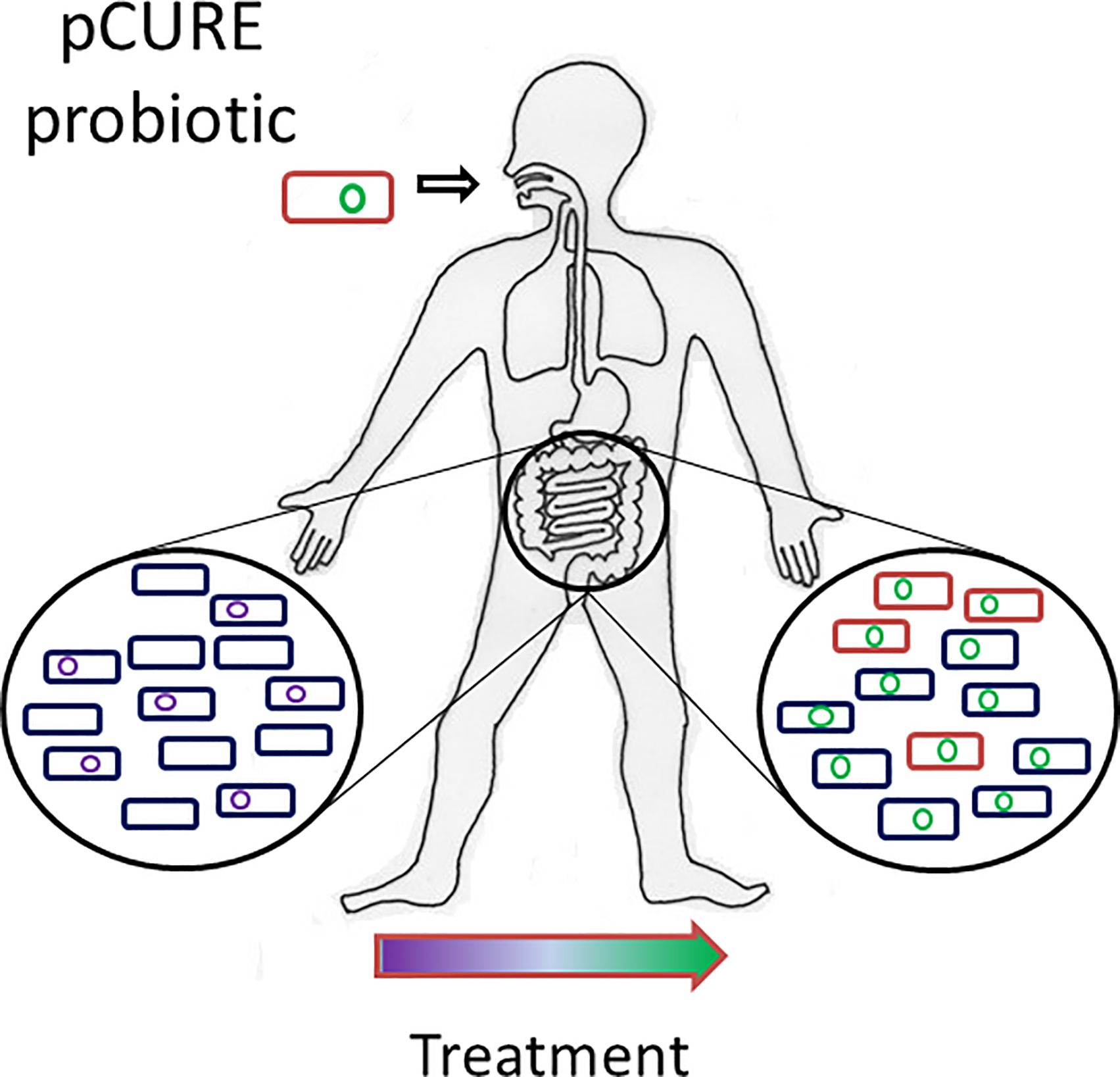
Researchers headed by a team at the University of Birmingham in the U.K. have developed a probiotic drink containing genetic elements that are designed to thwart antimicrobial resistance (AMR) in gut bacteria at the genetic level. The drink targets small DNA elements called plasmids that carry antibiotic resistance genes, and which are able to replicate independently and spread between bacteria. By preventing these plasmids from replicating, the antibiotic resistance genes are displaced, effectively resensitizing the bacteria to antibiotics.
New Health Studies: 43% Of Americans Prescribed Antibiotics Improperly
From a British Medical Journal (BMJ) online article:
 …primary care providers (general practice, paediatrics, and internal medicine) performed the best, giving a considerably lower percentage of antibiotic prescriptions without a documented indication (12%) than other specialists such as gynaecologists and urologists, who commonly prescribed antibiotics (24%), as well as those in all other specialties (29%).
…primary care providers (general practice, paediatrics, and internal medicine) performed the best, giving a considerably lower percentage of antibiotic prescriptions without a documented indication (12%) than other specialists such as gynaecologists and urologists, who commonly prescribed antibiotics (24%), as well as those in all other specialties (29%).
As many as two in five antibiotic prescriptions (43%) provided in outpatient settings in the US could be inappropriate, a study published by The BMJ has found.1
Researchers from Oregon, USA, looked at prescriptions in ambulatory settings such as primary care and found that a quarter (25%) were deemed to be inappropriate, while a further 18% did not have an indication.
To read more: https://www.bmj.com/content/367/bmj.l6961