 We take a look back over the past six months of the pandemic, and discuss how far the world has come. It’s been a period of turmoil and science has faced an unprecedented challenge. What lessons can be learned from the epidemic so far to continue the fight in the months to come?
We take a look back over the past six months of the pandemic, and discuss how far the world has come. It’s been a period of turmoil and science has faced an unprecedented challenge. What lessons can be learned from the epidemic so far to continue the fight in the months to come?
Also in this episode:
12:55 Unanswered questions
After months of intensive research, much is known about the new coronavirus – but many important questions remain unanswered. We look at the knowledge gaps researchers are trying to fill.
Nature Medicine: Real-time tracking of self-reported symptoms to predict potential COVID-19
20:36 How has lockdown affected fieldwork?
The inability to travel during lockdown has seriously hampered many researchers’ ability to gather fieldwork data. We hear from three whose work has been affected, and what this means for their projects.



 The consensus among economists is that the U.S. recovery will most likely be something in between a V and a W — a sharp drop, a relatively small bounce back, and then a long period of slow growth.
The consensus among economists is that the U.S. recovery will most likely be something in between a V and a W — a sharp drop, a relatively small bounce back, and then a long period of slow growth.


 In fact,
In fact, 
 Staff Writer Kelly Servick joins host Sarah Crespi to talk about the ins and outs of coronavirus contact tracing apps—what they do, how they work, and how to calculate whether they are crushing the curve.
Staff Writer Kelly Servick joins host Sarah Crespi to talk about the ins and outs of coronavirus contact tracing apps—what they do, how they work, and how to calculate whether they are crushing the curve. 
 For instance, more hospitals are remotely triaging and registering patients before they even arrive. Clinicians can consult with patients from their home via telemedicine to help determine how sick they are and if they need to come to the ER at all. From there, admissions are made with as little contact with staff or other patients as possible.
For instance, more hospitals are remotely triaging and registering patients before they even arrive. Clinicians can consult with patients from their home via telemedicine to help determine how sick they are and if they need to come to the ER at all. From there, admissions are made with as little contact with staff or other patients as possible.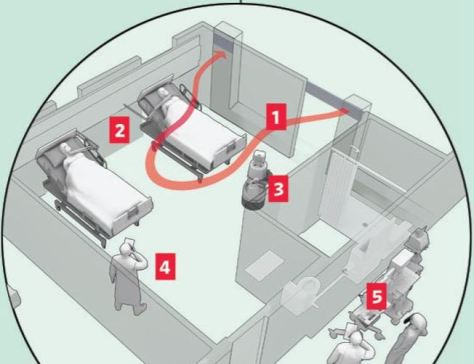
 With the potential for resurgences of the coronavirus, and some scientists warning about outbreaks of other infectious diseases, hospitals don’t want to be caught flat-footed again. So, more of them are turning to new protocols and new technology to overhaul standard operating procedure, from the time patients show up at an emergency room through admission, treatment and discharge.
With the potential for resurgences of the coronavirus, and some scientists warning about outbreaks of other infectious diseases, hospitals don’t want to be caught flat-footed again. So, more of them are turning to new protocols and new technology to overhaul standard operating procedure, from the time patients show up at an emergency room through admission, treatment and discharge.

