Times Literary Supplement (September 29, 2023): The new issue features The First Folio at 400; how disease shaped global history; novels of queer experience; what Britain laughs at; literary thefts and coincidences – and much more…
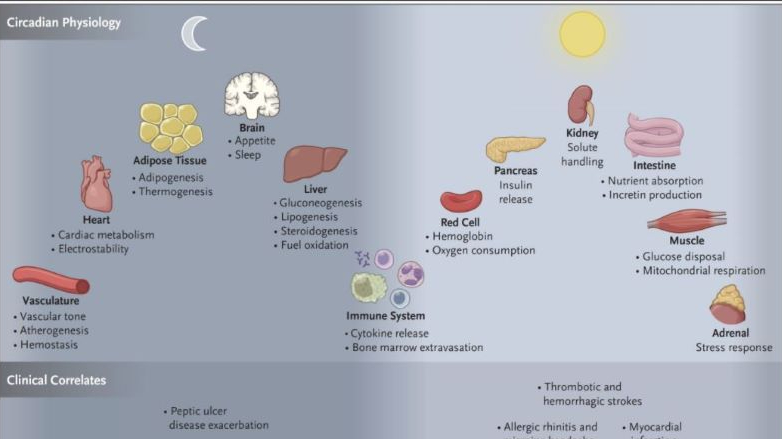
How disease has shaped global history
By Adam Rutherford
Scientists often make poor historians. Their shortcomings in describing and analysing the past include a failure to shed the whiggish stories that academic history moved away from decades ago. Straight lines are still drawn between Great Men and the impact of their brilliant insights on our view of reality. They also sometimes fail to treat the material of history with the seriousness they bring to their own discipline. Simple questions that are drummed into schoolchildren are frequently ignored in analysing documentary evidence: who wrote this, why, and for whom? The result is context-lite narrative that doesn’t stand up to scrutiny.
Works to commemorate the 400th anniversary of the First Folio
By Peter Holland
Next year, the Folger Shakespeare Library in Washington DC will reopen after a three-year closure for a large-scale renovation of its building, which dates from 1932. The centrepiece of the new Shakespeare Exhibition Hall, will be, as the press release puts it, something “that only the Folger could produce: all 82 copies of the 1623 First Folio of Shakespeare that were collected by Henry and Emily Folger”. The Folger holds slightly more than a third of all extant copies of the book and now eighty of them will be on permanent show in a “20-foot long visible vault”, while two more will be open in cases as part of an “interactive” visitor experience. Peering into the vault says much about the Folgers’ appetite for cornering the market in Folios but, since nearly all copies differ in some respects, it did make some kind of sense to buy many of them.
Nature Magazine – September 18, 2024: The latest issue features ‘Jumbo Jets’ – Record-breaking beams from a supermassive black hole…