Quanta Magazine (December 21, 2023): 2023’s Biggest Breakthroughs in Biology and Neuroscience.
Video timeline: 00:05 The Investigation of Consciousness – Our minds are constantly taking in new external information while also creating their own internal imagery and narratives. How do we distinguish reality from fantasy? This year, researchers discovered that the brain has a “reality threshold” against which it constantly evaluates processed signals. Original paper: “Subjective signal strength distinguishes reality from imagination”
04:30 Microbiomes Evolve With Us – This year, scientists provided clear evidence that the organisms in our microbiome —the collection of bacteria and other cells that live in our guts and elsewhere on our body — spread between people, especially those with whom we spend the most time. This raises the intriguing possibility that some illnesses that aren’t usually considered communicable might be.
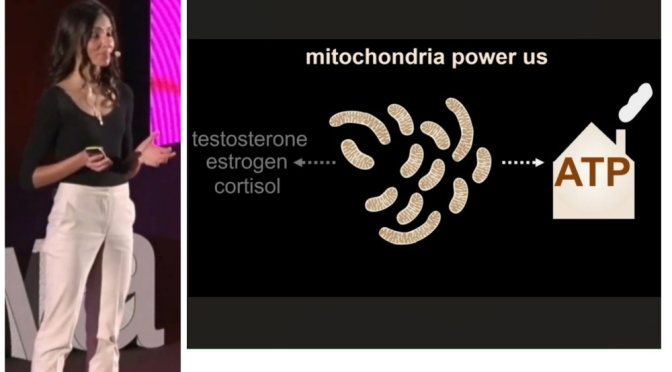
08:43 How Life Keeps Time – The rate at which an embryo develops and the timing of when its tissues mature vary dramatically between species. What controls the ticking of this developmental clock that determines an animal’s final form? This year, a series of careful experiments suggest that mitochondria may very well serve dual roles as both the timekeeper and power source for complex cells.