The Mighty Elvis is a commemoration of his life and times in the form of an art book, told through the unique vision of legendary designer and illustrator Seymour Chwast. Beautifully illustrated throughout, it presents an enhanced portrait of one of America’s greatest celebrities.
With text by author Steven Brower (Satchmo: The Life and Art of Louis Armstrong), The Mighty Elvis reminds us of the continuing stardom of one of the most popular American singers of all time. Through Chwast’s illustrations, cartoons and comics we get to relive his early life, his meteoric rise to fame and how he was affected by, and in turn, affected the world of music in the many genres he mastered. The book covers his first appearances on television, Graceland, his meeting with President Nixon, his wedding to Priscilla, and much more. Millions of fans loved him, purchased his records, attended his sold-out shows, and went to his 33 films. Death, 40 years ago, has not diminished his fame. “Elvis Lives!”




 His work was displayed in many exhibitions in the UK and twenty four of his paintings were exhibited in New York in 1960. the exhibition was entitled ‘British Motoring Achievements’ and was a collection of paintings depicting outstanding performances of British cars during the previous ten years. These included the Vanwall and Cooper in Grand Prix, Monte Carlo and Alpine Rallies, speed records by MG and Austin, and Le Mans wins by Jaguar and Aston Martin.
His work was displayed in many exhibitions in the UK and twenty four of his paintings were exhibited in New York in 1960. the exhibition was entitled ‘British Motoring Achievements’ and was a collection of paintings depicting outstanding performances of British cars during the previous ten years. These included the Vanwall and Cooper in Grand Prix, Monte Carlo and Alpine Rallies, speed records by MG and Austin, and Le Mans wins by Jaguar and Aston Martin.

 Shortly after George Orwell’s death in 1950, his widow Sonia was visited in London by two representatives of the American film producer, Louis de Rochemont. They sought the rights to Orwell’s novel from five years earlier, Animal Farm. It’s said Sonia took some convincing but eventually agreed, on the promise that de Rochemont would introduce her to her hero, Clark Gable.
Shortly after George Orwell’s death in 1950, his widow Sonia was visited in London by two representatives of the American film producer, Louis de Rochemont. They sought the rights to Orwell’s novel from five years earlier, Animal Farm. It’s said Sonia took some convincing but eventually agreed, on the promise that de Rochemont would introduce her to her hero, Clark Gable. A conventional, live-action adaptation was out of the question given that the book’s main characters were farmyard animals, so an animated movie was decided upon instead. De Rochemont chose to have it made in the UK rather than the US — partly because of lower production costs, partly because he admired the work of British husband-and-wife duo
A conventional, live-action adaptation was out of the question given that the book’s main characters were farmyard animals, so an animated movie was decided upon instead. De Rochemont chose to have it made in the UK rather than the US — partly because of lower production costs, partly because he admired the work of British husband-and-wife duo 



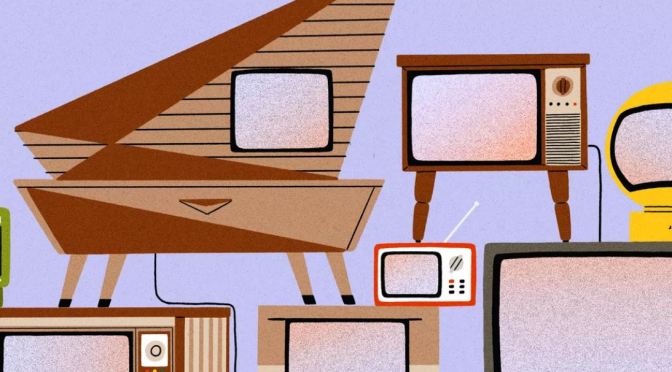
 The postwar boom made TV ubiquitous: In 1950, 3,880,000 households in America had a TV—about 9 percent of the total population. By 1960, 90 percent of all households had at least one. This was the golden age of appliance marketing for all kinds of durable goods, from cars to dishwashers, and television marketers initially took a curious tack with their wares. While the auto industry and manufacturers of coffee makers and cooktops positioned their products as accessible components of a high-tech future, the makers of television sets often sold their devices as elegant pieces of contemporary or even classic furniture.
The postwar boom made TV ubiquitous: In 1950, 3,880,000 households in America had a TV—about 9 percent of the total population. By 1960, 90 percent of all households had at least one. This was the golden age of appliance marketing for all kinds of durable goods, from cars to dishwashers, and television marketers initially took a curious tack with their wares. While the auto industry and manufacturers of coffee makers and cooktops positioned their products as accessible components of a high-tech future, the makers of television sets often sold their devices as elegant pieces of contemporary or even classic furniture.