CBS Sunday Morning (April 21, 2024): We leave you this Sunday amid icebergs in the Southern Ocean off the Antarctic peninsula – icebergs rapidly melting as ocean temperatures rise. Videographer: Lee McEachern.
Tag Archives: Oceans
National Geographic Magazine – March 2024

National Geographic Magazine (February 14, 2024) – The new issue features ‘The Hidden World of Hyenas – Why these misunderstood – and maligned – animals are one of Africa’s most successful predators…
These creatures of the ‘twilight zone’ are vital to our oceans

The species help harness carbon dioxide, a greenhouse gas, deep in the ocean, but much is still unknown about this region and its fascinating inhabitants.
Love them or hate them, hyenas are getting the last laugh
The spotted hyena is Africa’s most successful predator—and one of its most misunderstood animals. But decades of cutting edge research is yielding greater understanding, respect, and protection.
REVIEWS: THE TOP TEN SCIENCE BOOKS OF 2023
:focal(800x602:801x603)/https://tf-cmsv2-smithsonianmag-media.s3.amazonaws.com/filer_public/54/95/5495bf57-cfac-40d7-a1ac-4fc8f56baa3e/booklist-2023-science.jpg)
Smithsonian Magazine (December 7, 2023) – From stories on the depths of the ocean to the stars in the sky, these are the works that moved us the most this year
Fire Weather: A True Story from a Hotter World by John Vaillant
In a year when record-setting forest fires raged across Canada and their smoke clouded the skies across North America, and a Maui forest fire incinerated the town of Lahaina in a deadly blaze, the most harrowing book we read about climate change featured a devastating forest fire. In Fire Weather, author John Vaillant crafts a thriller about a cataclysmic inferno that burned through the town of Fort McMurray, Alberta, in May 2016. (We ran an excerpt of the book here.) The blaze generated hurricane-force winds and lightning, and entire neighborhoods burned to the ground under a type of pyrocumulus cloud usually associated with volcanoes. Roughly 100,000 people evacuated what would become the costliest disaster in Canadian history.
Of Time and Turtles: Mending the World, Shell by Shattered Shell by Sy Montgomery
Scuttling Earth for at least 220 million years, turtles have survived more than one mass extinction, including the one that offed dinosaurs. But in a geologic instant, humans have pushed more than half their 360 known species to near-extinction. And in an actual instant, animals slated to live a century or more can be killed—after their shells are crushed by cars, their mouths are snagged by fishhooks or their ponds are drained by developers.
Yet there is hope for some turtles. The Turtle Rescue League in Southbridge, Massachusetts, rehabilitates hundreds of ailing turtles each year. In Of Time and Turtles, author Sy Montgomery joins the small squad in spring of 2020, just as routine life freezes for Covid-19. The book recounts her year with the league, as they incubated eggs, injected antibiotics, mended shattered shells and returned healed patients to nature.
Crossings: How Road Ecology Is Shaping the Future of Our Planet by Ben Goldfarb
From the start of Ben Goldfarb’s fascinating book on road ecology, Crossings, the reader is peppered with jaw-dropping facts. Some 40 million miles of roadways encircle the Earth. While a half-century ago 3 percent of land-dwelling mammals died on a road, in 2017 that percentage had quadrupled. In 1995, researchers estimated that, in the United States, deer factor into more than a million vehicle crashes annually, injure 29,000 drivers and passengers, and kill more than 200. (We ran an excerpt of the book, with many more surprising facts, here.) And the book is engrossing for other reasons. In it, Goldfarb chronicles roads from California to Canada to Tasmania to show how they have impacted the natural world—and that includes us. He explores how roads have affected everything from butterflies to mountain lions to frogs.
Starborn: How the Stars Made Us (and Who We Would Be Without Them) by Roberto Trotta
Without the stars, the history of our species would have been very different. That’s the central argument in Roberto Trotta’s engaging homage to the star-studded night sky, Starborn. The stars are more than just pretty: As Trotta shows, our efforts to understand the movements of the stars and planets (and the sun and the moon) played a crucial role in the development of navigation and precision timekeeping. In ancient Egypt, for example, the bright star Sirius was worshipped as a deity, and the start of the new year was signaled when Sirius first became visible in the pre-dawn sky. Seafaring Polynesians, meanwhile, traveled from island to island in the Pacific Ocean by memorizing the positions and movements of some 200 stars—aided by their knowledge of ocean currents, fish, birds and seaweed. Today’s most accurate timekeepers are atomic clocks, which count vibrations of a cesium atom—but even these need to be tweaked based on the sun and stars, because the Earth’s spin is gradually slowing.
Rough Sleepers: Dr. Jim O’Connell’s urgent mission to bring healing to homeless people by Tracy Kidder
In Rough Sleepers, author Tracy Kidder profiles a dedicated doctor who treats Boston’s homeless. Harvard-educated physician Jim O’Connell is the founder and president of the Boston Health Care for the Homeless Program. “The Program,” as O’Connell calls it, employs roughly 400 workers to treat more than 11,000 homeless people annually. O’Connell, who refers to the unhoused as “rough sleepers,” a 19th-century British term, is called Dr. Jim by his patients. He treats them in a clinic and drives a van to meet them on the streets. He addresses everything from lice and scabies to more advanced problems that patients have following years of neglect, including large tumors and, in one case, a hernia that dropped below a man’s knees. Aside from care, O’Connell sometimes hands out his own money and gift cards.Report this ad
How Far the Light Reaches: A Life in Ten Sea Creatures by Sabrina Imbler
Nature is unabashedly queer. We are surrounded by species that live outside our human experience, points of reflective contrast to our terrestrial lives. Sabrina Imbler’s scientifically steeped memoir How Far the Light Reaches revels in these differences, using an aquarium of undersea creatures as foils for significant moments in the author’s life. The preserved remains of a whale are a foil for dissecting a breakup, and our sometimes leering fascination with a marine worm called the sand striker gives form to a meditation on consent. Imbler’s essay “We Swarm,” especially, is a treasure. Squishy marine organisms called salps, which spend part of their lives in aggregations of hundreds of individuals, open a warm recollection of Pride celebrations along the New York shoreline.
The Devil’s Element: Phosphorus and a World Out of Balance by Dan Egan
As chemicals go, phosphorus—number 15 on the periodic table—is something of a paradox. In The Devil’s Element, journalist Dan Egan explains how phosphorus is essential for all life; it can be found in every cell in your body. But it is also combustible and explosive. So-called white phosphorus is a waxy substance that spontaneously combusts when exposed to oxygen—and can cause temperatures to hit 2,370 degrees Fahrenheit. White phosphorus was the key ingredient in the bombs dropped by the Allies on Hamburg, Germany, during World War II, unleashing a firestorm that leveled the city and killed some 37,000 people.Report this ad
My Father’s Brain: Life in the Shadow of Alzheimer’s by Sandeep Jauhar
Alzheimer’s disease robs a person’s memory, yes, but it also causes sweeping behavioral transformations that can include agitation and stubbornness. Those with the condition can become unrecognizable to their loved ones and difficult patients. The slow-acting and irreversible disease “is more feared than death itself,” writes Sandeep Jauhar in My Father’s Brain. After his father starts to show signs of dementia in 2014, Jauhar’s parents move states to be closer to their sons. But the close proximity does little to prevent his father’s Alzheimer’s from upending the lives of family members. Jauhar doesn’t shy away from narrating the ugly and difficult experiences of his father’s irrational behavior, which often leads to sibling fights and frustration for the author.
The Underworld: Journeys to the Depths of the Ocean by Susan Casey
In June, the world paid more attention than usual to deep-sea exploration when OceanGate’s Titan submersible went quiet while exploring the Titanic. Later, the public learned the craft imploded. That was the rare tragic episode of deep-ocean adventures, one years in the making due to the company’s failure to test and heed warnings. But a much more awe-inspiring exploration of the deep has been taking place for decades, and Susan Casey’s enthralling book, The Underworld, documents it in stunning detail. (We ran an excerpt of the book here.) As Casey points out, though you can view maps of Mars on your iPhone, 80 percent of Earth’s seafloor hasn’t been charted in sharp detail.
Better Living Through Birding: Notes from a Black Man in the Natural World by Christian Cooper
In little more than two minutes captured on video in May 2020, the life of New York City birder Christian Cooper drastically changed. He saw a dog run through a forested section of Central Park and asked its owner, a white woman, to leash her pet in accordance with the law. When she refused, he began to film her with his smartphone, and as he did, she said she would call the police on him and tell them “an African American man is threatening my life.” As the racist incident came to national attention, Cooper quickly became the best-known birder in America. And, amid a hobby that is largely older and white, “the fact that that birder is Black turned heads,” Cooper writes.
Ecosystems: The ‘Sea Of Hope’ In Chilean Patagonia
SeaLegacy Films (October 16, 2023) – At the foot of the iconic mountain peaks of Chilean Patagonia, just below the blue surface of the sea, lies a biodiverse and pristine kelp forest. In this episode of “Sea of Hope,” Mission Blue ocean policy expert Max Bello and Chilean Environment Minister Maisa Rojas join the SeaLegacy team to explore how wonderful and spectacular this unique ecosystem is. in the world.
Abundant and diverse life forms find their home in the world’s longest continuous kelp forest, just off the coast, in a region home to hundreds of fjords and more than 40,000 islands and islets. Join our co-founder Andy Mann as he embarks with the exploration team on an adventure to discover the treasures of Chilean Patagonia and evaluate the health of this productive and wild ecosystem. Discover the natural neon colors, the huge stems of kelp, some of the marine characters that inhabit the area, and the impressive carbon capture abilities of the underwater forests!
BBC Earth Wildlife Views: Sir David Attenborough Tours Seven Continents
BBC Earth (July 7, 2023) – Sir David Attenborough presents remarkable, new animal behaviors from all the continents, including a kidnapping macaque to thirsty bats navigating crocodile-infested waters.
From ‘Seven Worlds One Planet’.
Oceans: Marine Life In The Midnight Zone (BBC Earth)
BBC Earth (June 28, 2023) – A kilometre beneath the surface and beyond the reach of the sun, life can still flourish in this dark expanse.
The midnight zone is the single largest habitat on the planet, accounting for 70% of all seawater, but because of its remote location, it is poorly understood. Little is known about the animals that inhabit these waters, and even less is known about microbial life in this zone.
Oceans: “Into The Abyss – Worlds Of The Deep” (2023)
Natural World Facts Films (June 17, 2023) – Explore the wonders of the deep ocean as you’ve never seen them before. This is a collaborative film series with Schmidt Ocean Institute, using their extensive library of 4K footage from an array of deep sea ecosystems.
Below are the episodes in order (subject to change):
- 1 – The Twilight Zone
- 2 – The Midnight Zone
- 3 – The Abyssal Plain
- 4 – Seamounts and Canyons
- 5 – Hydrothermal Vents
Schmidt Ocean Institute is a non-profit oceanographic research foundation that has been pioneering deep-sea research and discovery since 2009, on board their old vessel RV Falkor and their brand new RV Falkor (too), the most advanced marine research vessels in the world.
Their remotely operated vehicle (ROV) SuBastian is equipped with a suite of sensors and a 4K camera that has illuminated the depths and live-streamed dives around the world. All footage shown is filmed and provided by Schmidt Ocean Institute.
Marine Wildlife: The Giant Mantas Of Coastal Mexico
SeaLegacy (May 26, 2023) – Five years after its protection, Mexico’s Revillagigedo National Park bounds with a resurgence of life– welcoming back the region’s incredible native species, like the endangered giant manta ray. Co-founder Cristina Mittermeier and marine scientist Frida Lara explore what’s possible when we give aquatic life space to recover and thrive.
The pair greet a giant manta as an old friend, as it flips, flies, and glides through the water. The curious creature holds great symbolic significance and plays a vital ecological role within the ocean and all the marine life impacted by its sheer presence. The bounty and diversity of life Cristina captures within Revillagigedo National Park prove that protecting our marine ecosystems is the solution to saving our ocean.
Only brightened by the endangered giant manta’s presence, this region’s achievements act as a guiding light of hope for conservation worldwide.
Research Preview: Nature Magazine – May 18, 2023

nature Magazine – May 18, 2023 issue: The cover shows an artist’s impression of two male mammoths fighting. During episodes of musth, adult male elephants undergo periods of elevated testosterone levels associated with aggression and competition for mating. In this week’s issue, Michael Cherney and his colleagues show that male woolly mammoths (Mammuthus primigenius) experienced similar episodes of musth.
The ocean is hotter than ever: what happens next?
Record temperature combined with an anticipated El Niño could devastate marine life and increase the chances of extreme weather.
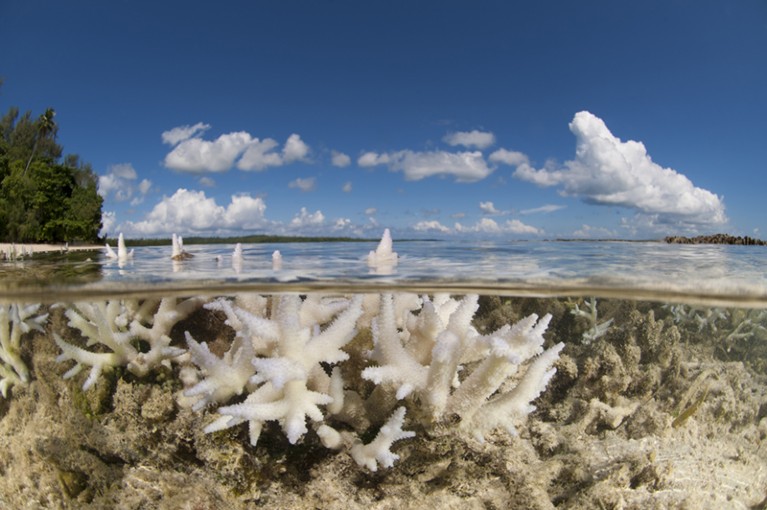

The global ocean hit a new record temperature of 21.1 ºC in early April, 0.1 ºC higher than the last record in March 2016. Although striking, the figure (see ‘How the ocean is warming’) is in line with the ocean warming anticipated from climate change. What is remarkable is its occurrence ahead of — rather than during — the El Niño climate event that is expected to bring warmer, wetter weather to the eastern Pacific region later this year.
For chemists, the AI revolution has yet to happen
Machine-learning systems in chemistry need accurate and accessible training data. Until they get it, they won’t achieve their potential.
Many people are expressing fears that artificial intelligence (AI) has gone too far — or risks doing so. Take Geoffrey Hinton, a prominent figure in AI, who recently resigned from his position at Google, citing the desire to speak out about the technology’s potential risks to society and human well-being.
Documentaries: What Causes ‘Monster Waves’?
DW Documentary (April 30, 2023) – Statistically, a large ship is lost in the world’s oceans almost once every seven days. One reason for this: monster waves that appear to come from nowhere. Unlike tsunamis, they are completely unpredictable. That means there’s no way to issue any kind of warning.
Scientists still know astonishingly little about these freak waves. For centuries, many people dismissed them as the stuff of legend. The first scientific proof of their existence didn’t come until 1995. A laser on the Draupner oil rig in the North Sea measured a wave almost 26 meters high. Wave models in use at the time deemed this to be an impossibility.
But the data, captured by chance, changed the course of research forever. Scientists have focused on three theories in their bid to explain the emergence of freak waves. The first is the current model: currents flowing in opposite directions reduce the length of the waves, pushing them together to create a monster surge. But freak waves are also a phenomenon in regions where currents aren’t particularly strong.
That’s why researchers came up with a second theory: superposition. In this linear process, faster, longer waves catch up with short, slower waves. They overlap and form monster waves. But in some places, freak waves occur with a frequency that can’t be explained by this linear theory, either.
For several years now, scientists have been considering a third possibility: when non-linear wave trains are unstable, they can develop into monster waves through a highly complex energy “theft”. Research is divided over whether it’s the linear or non-linear effects that form freak waves out at sea – a question that’s crucial for shipping!




















