From a MiddleTownPress.com online article:
 The quality scorecard rates health care organizations through a five-star system on more than 30 health measures outlined by an advisory council composed of consumer advocates, providers, community organizations, state agencies, and payers. The range of measures focus on the quality of care provided by primary care providers and span more than 10 areas, including behavioral health, children’s health, women’s health, chronic conditions, and preventative health.
The quality scorecard rates health care organizations through a five-star system on more than 30 health measures outlined by an advisory council composed of consumer advocates, providers, community organizations, state agencies, and payers. The range of measures focus on the quality of care provided by primary care providers and span more than 10 areas, including behavioral health, children’s health, women’s health, chronic conditions, and preventative health.
Health care organizations are also evaluated on patient experience in four categories: office staff, provider communication, timely care, and an overall patient experience rating.
Users can access interactive tables and graphs to compare provider networks, like Hartford HealthCare and Western Connecticut Health Network, to each other and the state average for any given health measure, such as asthma or diabetes. In addition, users can compare the overall performance rating of provider networks against all networks across all quality measures.
To read more click on following link: https://www.middletownpress.com/middletown/article/New-CT-health-care-rating-system-helps-patients-14290596.php


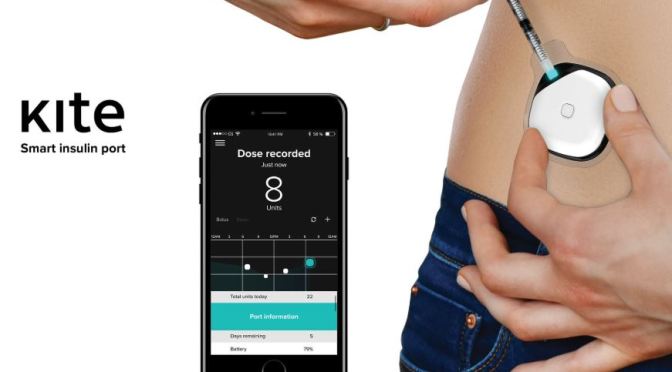
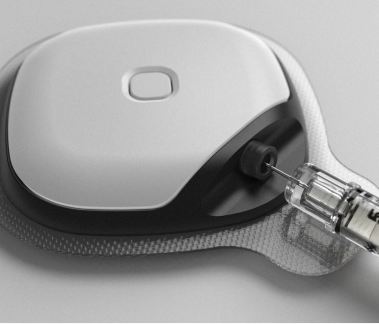 Imagine a smart insulin port attached to your skin, delivering the right dose, and at the right time. At the same moment, getting all information regarding your sugar levels, meds timings and health data, managed and analyzed with the accompanying app.
Imagine a smart insulin port attached to your skin, delivering the right dose, and at the right time. At the same moment, getting all information regarding your sugar levels, meds timings and health data, managed and analyzed with the accompanying app.
 At the Charité University Hospital in Berlin, I’ve employed what’s called intermittent fasting, or time-restricted eating, to help patients with an array of chronic conditions. These include diabetes, high blood pressure, rheumatism and bowel diseases, as well as pain syndromes such as migraines and osteoarthritis.
At the Charité University Hospital in Berlin, I’ve employed what’s called intermittent fasting, or time-restricted eating, to help patients with an array of chronic conditions. These include diabetes, high blood pressure, rheumatism and bowel diseases, as well as pain syndromes such as migraines and osteoarthritis.
 Low and high levels of hemoglobin are associated with an increased risk of dementia, including AD, which may relate to differences in white matter integrity and cerebral perfusion.
Low and high levels of hemoglobin are associated with an increased risk of dementia, including AD, which may relate to differences in white matter integrity and cerebral perfusion.





 This study, combined with the results of previous studies, supports the hypothesis that engaging in morning exercise may result in more weight loss compared to engaging in a similar amount of exercise later in the day. Furthermore, we observed individuals who performed most of their exercise sessions in the afternoon or evening tended to have slightly higher levels of EI and reduced NEPA and NEEx, suggesting that there are potentially important differences in the components of energy balance based on time of day exercise is performed.
This study, combined with the results of previous studies, supports the hypothesis that engaging in morning exercise may result in more weight loss compared to engaging in a similar amount of exercise later in the day. Furthermore, we observed individuals who performed most of their exercise sessions in the afternoon or evening tended to have slightly higher levels of EI and reduced NEPA and NEEx, suggesting that there are potentially important differences in the components of energy balance based on time of day exercise is performed.
 “We found staggering inconsistencies between how costs of dementia are calculated across studies and our analysis strongly supports that current estimates fail to recognise the true costs of the diseases, such as Alzheimer’s, that cause dementia. Some studies have estimated that out of pocket expenses for people with dementia are up to one third of their household wealth in the final five years of their life, and that caregivers have healthcare costs that are twice as high as non-caregivers. We also found evidence that costs begin rising up to 10 years prior to diagnosis — we need to better measure and factor all these into future societal cost estimates.”
“We found staggering inconsistencies between how costs of dementia are calculated across studies and our analysis strongly supports that current estimates fail to recognise the true costs of the diseases, such as Alzheimer’s, that cause dementia. Some studies have estimated that out of pocket expenses for people with dementia are up to one third of their household wealth in the final five years of their life, and that caregivers have healthcare costs that are twice as high as non-caregivers. We also found evidence that costs begin rising up to 10 years prior to diagnosis — we need to better measure and factor all these into future societal cost estimates.” “A healthy diet and lifestyle are generally recognized as good for health, but this study is the first large randomized controlled trial to look at whether lifestyle changes actually influence Alzheimer’s disease-related brain changes,” said Susan Landau, a research neuroscientist at Berkeley’s Helen Wills Neuroscience Institute, and principal investigator of the add-on study.
“A healthy diet and lifestyle are generally recognized as good for health, but this study is the first large randomized controlled trial to look at whether lifestyle changes actually influence Alzheimer’s disease-related brain changes,” said Susan Landau, a research neuroscientist at Berkeley’s Helen Wills Neuroscience Institute, and principal investigator of the add-on study.
 PBHWB of 40–42.5 °C was associated with both improved self-rated sleep quality and SE, and when scheduled 1–2 h before bedtime for little as 10 min significant shortening of SOL. These findings are consistent with the mechanism of PBHWB effects being the extent of core body temperature decline achieved by increased blood perfusion to the palms and soles that augments the distal-to-proximal skin temperature gradient to enhance body heat
PBHWB of 40–42.5 °C was associated with both improved self-rated sleep quality and SE, and when scheduled 1–2 h before bedtime for little as 10 min significant shortening of SOL. These findings are consistent with the mechanism of PBHWB effects being the extent of core body temperature decline achieved by increased blood perfusion to the palms and soles that augments the distal-to-proximal skin temperature gradient to enhance body heat